Dichlorvos
    өРөРО· өРөРО·
Introduction: Dichlorvos is the International Organization for Standardization (ISO)-approved common name for 2,2-dichlorovinyl dimethyl phosphate (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) or 2,2-dichloroethenyl dimethyl phosphate (Chemical Abstracts Service No. 62-73-7). It is a broad-spectrum organophosphorus insecticide, and, like other organophosphorus compounds, its mode of action is via the inhibition of cholinesterase (ChE) activity. Its main food use is for stored grain and potatoes, while it is also applied to animal, green, glass and mushroom houses. Outdoor use includes the treatment of garbage bins, picnic areas and rockeries. Home garden products formulated as peststrips (and ministrips) or solid tablets are available for use in rooms or non-food storage areas such as wardrobes and drawers, or in outside garbage bins.
Common name: Dichlorvos
Another name: DDVP; Dichlofos; Dichlorophos; Dichlorvos; Dimethyl Dichlorovinyl Phosphate; Divipan; Novotox; Phosphoric acid 2,2 dichloroethenyl dimethyl ester; Phosphoric acid 2,2-dichloroethenyl dimethyl ester; etc.
Chemical Name (IUPAC): 2,2-dichlorovinyl dimethyl phosphate
Structural formula:
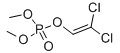
Empirical formula: C4H7C12O4P
Mol. Weight: 220.98
CAS No.: 62-73-7
Specifications
Leading Dichlorvos supplier
Dichlorvos 95% TC
Dichlorvos 97% TC
Dichlorvos 98% TC
Dichlorvos 1000 g/L EC
Dichlorvos 80% EC
Dichlorvos 50% EC
Packing
BULK PACKING
Powder: 25KG/Bag, 25KG/Drum, 50KG/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum ect.
SMALL PACKING
Powder: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized Packing label
Dichlorvos FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H317: May cause an allergic skin reaction.
H330: Fatal if inhaled. H400: Very toxic to aquatic life.
H410: Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects. Precautionary statement(s)
P264: Wash hands thoroughly after handling.
P270: Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product.
P304 + P340: IF INHALED: Remove victim to fresh air and keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing.
P330: Rinse mouth.
P501: Dispose of contents/container in accordance with local regulation.
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rats is 80 mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rats is 120 mg/kg. 3) Acute inhalation toxicity LC50 (4 h) for rats is 0.083 mg/l. 4) Skin irritation: Slightly irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Eye irritation: Slightly irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Skin sensitization for guinea pig: Skin sensitiser.
NOEL: NOEL (2 y) for mice is 10 mg/kg diet. Other Not mutagenic or teratogenic. ADI (JMPR) 0-0.004 mg/kg b.w. [1966, 1967, 1970, 1977, 1993, 2001].
Classification:
WHO Classification: Ib (Highly hazardous)
EC Risk Classification: T+ - Very toxic: R26; T - Toxic: R24/25; Xn - Harmful: R43; N - Dangerous for the environment: R50.
US EPA Classification (formulation): I (Danger - Highly toxic)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: Acute oral LD50 for Bobwhite quail is 24 mg/kg. Effect on fish: Acute LC50 (96 h) for Rainbow trout is 0.55 mg/l. Effects on aquatic invertebrates: Acute EC50 (48 h) for Daphnia magna is 0.00019 mg/l. Effects on algae: Acute EC50 (72 h) for Scenedemus subspicatus is 52.8 mg/l. Effects on bees: Oral acute (48 h) LD50 is 0.29 ҰМg/bee. Effects on earthworms: Acute 14 day LC50 is 14 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Breakdown of Chemical in Soil and Groundwater: Dichlorvos does not adsorb to soil particles and it is likely to contaminate groundwater. When spilled on soil, dichlorvos leached into the ground with 18 to 20% penetrating to a depth of 30 cm within 5 days. In soil, dichlorvos is subject to hydrolysis and biodegradation. Volatilization from moist soils is expected to be slow. Half-lives of 7 days were measured on clay, sandy-clay, and loose sandy soil . Dichlorvos is rapidly broken down in the air and in damp media such as soil. The pH of the media determines the rate of breakdown. Alkaline soils, water, etc., show rapid breakdown, whereas acidic media shows slow degradation. For instance, at a pH of 9.1 the half-life of dichlorvos is about 4.5 hours. At a pH of 1 (very acidic), the half- life is 50 hours. Dichlorvos is non-persistent. Breakdown of Chemical in Water: In water dichlorvos remains in solution and does not adsorb to sediments. It degrades primarily by hydrolysis, with a half-life of approximately 4 days in lakes and rivers. This half-life will vary from 20 to 80 hours between pH 4 and pH 9. Hydrolysis is slow at pH 4 and rapid at pH 9. Biodegradation may occur, especially under acidic conditions which slow hydrolysis, or where populations of acclimated micro-organisms exist, as in polluted waters. Volatilization from water is expected to be slow. The volatilization half-life from river and pond waters have been estimated at 57 and over 400 days respectively. Breakdown of Chemical in Vegetation: Except for cucumbers, roses, and some chrysanthemums, plants tolerate dichlorvos very well.
Usage: Dichlorvos was developed by Bayer Crop Science. It is effective against mushroom flies, aphids, spider mites, caterpillars, thrips, and whiteflies in greenhouse, outdoor fruit, and vegetable crops. It is also used in the milling and grain handling industries and to treat a variety of parasitic worm infections in dogs, livestock, and humans. It is fed to livestock to control bot fly larvae in the manure.
Application: Biochemistry Cholinesterase inhibitor. Mode of action Insecticide and acaricide with respiratory, contact, and stomach action. Gives rapid knockdown. Uses Control of household and public health insect pests, e.g. flies, mosquitoes, cockroaches, bedbugs, ants, etc.; stored-product pests in warehouses, storerooms, etc.; flies and midges in animal houses; sciarid and phorid flies in mushrooms; sucking and chewing insects, and spider mites in a wide range of crops, including fruit, vines, vegetables, ornamentals, tea, rice, cotton, hops, glasshouse crops, etc. Also used as a veterinary anthelmintic.
| 






