Carbaryl
    ОчО¬ТтЈ¬°·јЧЭБЈ¬јЧЭБНю ОчО¬ТтЈ¬°·јЧЭБЈ¬јЧЭБНю
Introduction: Carbaryl is a wide-spectrum carbamate insecticide which controls over 100 species of insects on citrus, fruit, cotton, forests, lawns, nuts, ornamentals, shade trees, and other crops, as well as on poultry, livestock and pets. It is also used as a molluscicide and an acaricide. Carbaryl works whether it is ingested into the stomach of the pest or absorbed through direct contact.
Common name: Carbaryl
Another name: Sevin, 1-Naphthyl-N-methylcarbamate, Antigale, Carbaril, Carbyl, Carylderm, Concentrat VO 18, Dog Net Insecticide Poudre, Dog-Net Insecticide Poudre, DogNet Insecticide Poudre, Fido's Free Itch, Fido's Free-Itch, Fido's FreeItch, G Wizz, G-Wizz, GWizz, Joseph Lyddy, Lyddy, Joseph, Poudre insecticide Moureau
Poudre insecticide Vetoquinol, Poutic, SЁҰpou, Tigal, Vetoquinol, Poudre insecticide
Chemical name: 1-naphthyl methylcarbamate
Empirical formula: C12H11NO2
Structural formula:
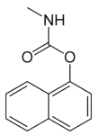
Mol. Weight: 201.23 g/mol
CAS No.: 63-25-2
Specifications
Leading Carbaryl supplier
Carbaryl 85% WP
Carbaryl 98% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum ect.
SMALL PACKING
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500mL/Bottle, 250mL/Bottle, 100mL/Bottle, 50mL/Bottle etc.
Customerized Packing label
Fenobucarb FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H302: Harmful if swallowed.
H332: Harmful if inhaled.
H351: Suspected of causing cancer.
H400: Very toxic to aquatic life.
Precautionary statement(s)
P201: Obtain special instructions before use.
P202: Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood.
P261: Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapors/spray.
P264: Wash ... thoroughly after handling.
P270: Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product.
P271: Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area.
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P281: Use personal protective equipment as required.
P301+P312: IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER/doctor/... IF you feel unwell.
P304+P312: IF INHALED: Call a POISON CENTER/doctor/... if you feel unwell.
P304+P340: IF INHALED: Remove person to fresh air and keep comfortable for breathing.
P308+P313: IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention.
P312: Call a POISON CENTER or doctor/... if you feel unwell.
P330: Rinse mouth.
P391: Collect spillage.
P405: Store locked up.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to ...
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rat: 614 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rat: >5000 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rat: 2.4 a.i. mg/L. 4) slight-irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) slight-irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). No reproductive or fetal effects were observed during a long-term study of rats which were fed high doses of carbaryl. Numerous studies indicate that carbaryl poses only a slight mutagenic risk. Carbaryl has not caused tumors in ten long term and lifetime studies of mice and rats.
ADI: 0.008 mg/kg b.w./day [2001]
Classification:
Toxicity class WHO (a.i.): II (Moderately hazardous)
EC Risk Classification: Carcinogen category 3: R40; Xn - Harmful: R20/22; N - Dangerous for the environment: R50
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: low toxicity to birds, acute LD50 for Mallard ducks is ˃2000 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: moderate toxicity to fish, acute 96 hour LC50 for Fathead minnow is 2.6 a.i.mg/L. Effect on aquatic invertebrates: high toxicity to aquatic invertebrates, acute 48 hour EC50 for Daphnia magna is 0.0064 a.i.mg/L. Effect on algae: moderate toxicity to algae, acute 72 hour EC50 for Chlorella spp. is 0.6 a.i.mg/L. Effect on honeybees: high toxicity to honeybees, contact acute 48 hour LD50 is 0.14 a.i.ҰМg/bee; Oral acute 48 hour LD50 is 0.21 a.i.ҰМg/bee. Effect on earthworms: high toxicity to earthworms, acute 14 day LC50 is <4 a.i.mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Carbaryl's production may result in its release to the environment through various waste streams; its use as an insecticide will result in its direct release to the environment. If released to air, a vapor pressure of 1.36ЎБ10-6 mm Hg at 25 deg C indicates carbaryl will exist in both the vapor and particulate phases in the atmosphere. Vapor-phase carbaryl will be degraded in the atmosphere by reaction with photochemically-produced hydroxyl radicals; the half-life for this reaction in air is estimated to be 15 hours. Particulate-phase carbaryl will be removed from the atmosphere by wet or dry deposition. The photolytic half-life of a thin film of carbaryl irradiated at >290 nm is 51.66 hr at 33-36 deg C. If released to soil, carbaryl is expected to have moderate mobility based upon measured Koc values of 230, 370, and 390. Volatilization from moist soil surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon a Henry's Law constant of 2.8ЎБ10-9 atm-cu m/mole. Carbaryl is not expected to volatilize from dry soil surfaces based upon its vapor pressure. Carbaryl is expected to photolyze slowly on surface soil at a rate dependent on the water content. Average biodegradation half-life of 10 days in four different soils suggests that biodegradation is an important environmental fate process in soil. If released into water, carbaryl is expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon the Koc values. Carbaryl's half-lives in aquatic environments have been reported as 1.7 days in river water and 5.8 days in mountain streams. In raw seawater, carbaryl was biodegraded to undetectable levels within 96 hrs. Volatilization from water surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon this compound's Henry's Law constant. BCF values of 34, 30, and 9 suggest bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is low. At 20 deg C, hydrolysis half-lives of carbaryl in water are 10.5 days, 1.8 days, 2.5 hours, and 15 min at pH values of 7, 8, 9, and 10, respectively. In neutral and alkaline soils, carbaryl is expected to hydrolyze rapidly. In acidic soils, hydrolysis is expected to occur more slowly.
Usage: History Insecticide reported by H. L. Haynes et al. (Contrib. Boyce Thompson Inst., 1957, 18, 507). Introduced by Union Carbide Corp. (now Bayer CropScience). Patents US 2903478 Manufacturers Agrochem; Bayer CropScience; Crystal; Drexel; Hunan Linxiang; Jin Hung; Kuo Ching; Sannong; Sundat.
Application: Biochemistry Weak cholinesterase inhibitor. Mode of action Insecticide with contact and stomach action, and slight systemic properties. Uses Control of Lepidoptera, Coleoptera, and other chewing and sucking insects, at 0.25-2.0 kg/ha, on more than 120 different crops, including vegetables, tree fruit (including citrus), mangoes, bananas, strawberries, nuts, vines, olives, okra, cucurbits, peanuts, soya beans, cotton, rice, tobacco, cereals, beet, maize, sorghum, alfalfa, potatoes, ornamentals, forestry, etc. Control of earthworms in turf. Used as a growth regulator for fruit thinning of apples. Also used as an animal ectoparasiticide. Phytotoxicity Non-phytotoxic if used as directed. Under certain conditions, some varieties of apple and pear may be injured.
| 






