Carbofuran
  ҝЛ°ЩНю ҝЛ°ЩНю
Introduction: Carbofuran is a broad spectrum carbamate pesticide that kills insects, mites and nematodes on contact or after ingestion. It is used against soil and foliar pests of field, fruit, vegetable and forest crops.
Common name: Carbofuran
Another name: Furadan, Curaterr, Yaltox, Chinufur, Crisfuran, Furacarb, Carbofurane, Pillarfuran, Kenofuran, Karbofuranu, Brifur, Carbodan, Furodan, Karbofuranu [Polish], Furadane, Diafuran, Sunfuran, Terafuran, Brifer, Curater, Tripart nex, Carbofuran mixture
Chemical name: 2,3-dihydro-2,2-dimethylbenzofuran-7-yl methylcarbamate
Empirical formula: C12H15NO3
Structural formula:
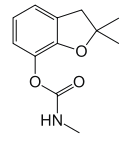
Mol. Weight: 221.26 g/mol
CAS No.: 1563-66-2
Specifications
Leading Carbofuran supplier
Carbofuran 10% GR
Carbofuran 480 g/L SC
Carbofuran 75% PREMIX
Carbofuran 97% TC
Carbofuran 98% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Powder: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum ect.
SMALL PACKING
Powder: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500mL/Bottle, 250mL/Bottle, 100mL/Bottle, 50mL/Bottle etc.
Customerized Packing label
Fenobucarb FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H300: Fatal if swallowed.
H330: Fatal if inhaled.
H400: Very toxic to aquatic life.
H410: Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P260: Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray.
P264: Wash ... thoroughly after handling.
P270: Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product.
P271: Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area.
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P284: [In case of inadequate ventilation] Wear respiratory protection.
P301+P310: IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/ physician.
P304+P340: IF INHALED: Remove person to fresh air and keep comfortable for breathing.
P310: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician.
P320: Specific treatment is urgent (see ... on this label).
P321: Specific treatment (see ... on this label).
P330: Rinse mouth.
P391: Collect spillage.
P403+P233: Store in a well-ventilated place. Keep container tightly closed.
P405: Store locked up.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to ...
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rat: 7 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rat: >1000 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rat: 0.05 a.i. mg/L. 4) mildly-irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) mildly-irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). NOEL (2 y) for rats and mice 20 mg/kg diet; (1 y) for dogs 10 mg/kg diet. Daily feeding of 100 ppm of carbofuran to pregnant rats greatly reduced the ability of the pups to survive. The lowest amount of carbofuran that proved teratogenic to mice in the mother's diet (TDlo) was 210 ug/kg (fed throughout pregnancy). No mutagenic effects have been reported in animals or bacteria. Sufficient data are available from animal studies to indicate that carbofuran does not pose a risk of cancer to humans.
ADI (JMPR) 0.002 mg/kg b.w. [1996].
Classification:
Toxicity class WHO (a.i.): Ib (Highly hazardous)
US EPA Classification (formulation): I, II (Danger - Highly toxic, Warning - Moderately toxic)
EC Risk Classification: T+ - Very toxic: R26/28; N - Dangerous for the environment: R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: high toxicity to birds, acute LD50 for Mallard ducks is 0.71 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: moderate toxicity to fish, acute 96 hour LC50 for Bluegill sunfish is 0.18 a.i.mg/L. Effect on aquatic invertebrates: high toxicity to aquatic invertebrates, acute 48 hour EC50 for Daphnia magna is 0.0094 a.i.mg/L. Effect on algae: moderate toxicity to algae, acute 72 hour EC50 for Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata is 6.5 a.i.mg/L. Effect on honeybees: high toxicity to honeybees, contact acute 48 hour LD50 is 0.036 a.i.ҰМg/bee; Oral acute 48 hour LD50 is 0.05 a.i.ҰМg/bee. Effect on earthworms: moderate toxicity to earthworms, acute 14 day LC50 for Eisenia foetida is 224 a.i.mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Carbofuran's production may result in its release to the environment through various waste streams; its use as an insecticide will result in its direct release to the environment. If released to air, a vapor pressure of 5.4ЎБ10-7 mm Hg at 25 deg C indicates carbofuran will exist in both the vapor and particulate phases in the atmosphere. Vapor-phase carbofuran will be degraded in the atmosphere by reaction with photochemically-produced hydroxyl radicals; the half-life for this reaction in air is estimated to be 14 hours. Particulate-phase carbofuran will be removed from the atmosphere by wet or dry deposition. Carbofuran strongly absorbs light at wavelengths between 295 and 305 nm and, therefore, may be susceptible to direct photolysis by sunlight. If released to soil, carbofuran is expected to have very high to high mobility based upon Koc values of 7.3 to 123. Volatilization from moist soil surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon an estimated Henry's Law constant of 4.5ЎБ10-10 atm-cu m/mole. Carbofuran is not expected to volatilize from dry soil surfaces based upon its vapor pressure. The half-life of carbofuran in soil has been reported as 11-75 days. Experimental data indicate that carbofuran degrades faster in soil that has previously been treated with carbofuran or other pesticides. If released into water, carbofuran is not expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon the Koc values. Carbofuran dissipation from paddy water was rapid with an estimated half-life of 3 days and a 95% removal time of 13 days; dissipation was due to both hydrolysis and biodegradation. The aqueous hydrolysis half-life at 27 deg C was found to be 5.1 weeks at pH 7.0 and 1.2 hours at pH 10. Volatilization from water surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon this compound's estimated Henry's Law constant. A BCF of 117 using Tilapia nilotica suggests bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is high. The half-lives for degradation of carbofuran in river, lake, and seawater following irradiation with sunlight were approximately 2, 6, and 12 hours, respectively; it was not reported whether the degradation was due to direct photolysis, indirect photooxidation or other processes.
Usage: History Insecticide reported by F. L. McEwen & A. C. Davis (J. Econ. Entomol., 1965, 58, 369) and E. J. Armburst & G. C. Gyrisco (ibid., p. 940). Introduced by FMC Corp. and by Bayer AG. Patents US 3474170; US 3474171 both to FMC; DE 1493646 to Bayer Manufacturers Agrochem; Bayer CropScience; Dow AgroSciences; FMC; Hesenta; Hunan Linxiang; Jin Hung; Kuo Ching; Makhteshim-Agan; Pilarquim; Sinon; Sundat; Taiwan Tainan Giant.
Application: Biochemistry Cholinesterase inhibitor. Mode of action Systemic, with predominantly contact and stomach action. Uses Control of soil-dwelling and foliar-feeding insects (including wireworms, white grubs, millipedes, symphylids, frit flies, bean seed flies, root flies, flea beetles, weevils, sciarid flies, aphids, thrips, etc.) and nematodes in vegetables, ornamentals, beet, maize, sorghum, sunflowers, oilseed rape, potatoes, alfalfa, peanuts, soya beans, sugar cane, rice, cotton, coffee, cucurbits, tobacco, lavender, citrus, vines, strawberries, bananas, mushrooms, and other crops.
| 






