Gibberellic acid
  іаГ№Лб іаГ№Лб
Introduction:Gibberellic acid (also called Gibberellin A3, GA, and GA3) is a hormone found in plants and fungi. Plants in their normal state produce large amounts of GA3. It is possible to produce the hormone industrially using microorganisms. Nowadays, it is produced by submerse fermentation, but this process presented low yield with high production costs and hence higher sale value. One alternative process to reduce costs of the GA3 production is Solid-State Fermentation (SSF) that allows the use of agro-industrial residues. Gibberellic acid is a simple gibberellin, a pentacyclic diterpene acid promoting growth and elongation of cells. It affects decomposition of plants and helps plants grow if used in small amounts, but eventually plants develop tolerance to it[citation needed]. GA stimulates the cells of germinating seeds to produce mRNA molecules that code for hydrolytic enzymes. Gibberellic acid is a very potent hormone whose natural occurrence in plants controls their development. Since GA regulates growth, applications of very low concentrations can have a profound effect while too much will have the opposite effect.
Common name: Gibberellic acid
Another name: Gibberellin A3; Gibberellin; Gibreskol; Brellin; etc.
Chemical name: (3S,3aS,4S,4aS,7S,9aR,9bR,12S)-7,12-dihydroxy-3-methyl-6-methylene-2-oxoperhydro-4a,7-methano-9b,3-propenoazuleno[1,2-b]furan-4-carboxylic acid
Empirical formula: C19H22O6
Structural formula:
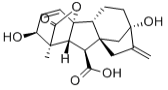
Mol. Weight: 346.37 g/mol
CAS No.: 77-06-5
Specifications
Leading Gibberellic acid supplier
Gibberellic acid 99% TC
Gibberellic acid 90% TC
Gibberellic acid 20% TA
Gibberellic acid 10% SP
Gibberellic acid 10% TA
Gibberellic acid 20 g/L EC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Powder: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum etc.
SMALL PACKING
Powder: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized packing label
Gibberellic acid FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H319 (100%): Causes serious eye irritation.
Precautionary statement(s)
P264: Wash ... thoroughly after handling.
P280: Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection.
P305+P351+P338: IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses if present and easy to do - continue rinsing.
P313: Get medical advice/attention.
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rats is >5000 mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rats is >2000 mg/kg. 3) Acute inhalation toxicity LC50 (4 h) for rats is >4.49 mg/L. 4) Skin irritation: Non-irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Eye irritation: Non-irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Skin sensitization for guinea pig: Non-sensitizing.
NOEL: NOEL (90 d) for rats is 680 mg/kg diet. Other Not genotoxic.
ADI 0-0.55 mg/kg b.w.
Classification:
WHO Classification: U (Unlikely to present an acute hazard)
EC Risk Classification: None allocated at this time
US EPA Classification (formulation): III (Caution - Slightly toxic)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: Acute oral LD50 for Bobwhite quail is >2250 mg/kg. Effect on fish: Acute LC50 (96 h) for Rainbow trout is >120 mg/l. Effects on aquatic invertebrates: Acute EC50 (48 h) for Daphnia magna is 76 mg/l. Effects on algae: Acute 72 hour EC50 for Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata is 17.0 mg/l. Effects on bees: contact acute 48 hour LD50 is >25 ҰМg/bee. Effects on earthworms: Acute 14 day LC50 is >1250 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
The rate constant for the vapor-phase reaction of gibberellic acid with photochemically-produced hydroxyl radicals has been estimated as 1.3ЎБ10-10 cu cm/molecule-sec at 25Ўж(SRC) using a structure estimation method.. This corresponds to an atmospheric half-life of about 3 hours at an atmospheric concentration of 5ЎБ10+5 hydroxyl radicals per cu cm.. Gibberellic acid is slowly hydrolyzed by water and rapidly decomposed by heat or chlorine.
Usage: Gibberellic acid was introduced by ICI (now Syngenta AG). It is a plant growth regulator with a variety of uses including improving fruit set, increasing berry size and controlling fruit maturity.
Application: Mode of action Acts as a plant growth regulator on account of its physiological and morphological effects in extremely low concentrations. Translocated. Generally affects only the plant parts above the soil surface. Uses Has a variety of applications, e.g. to improve fruit setting of clementines and pears (especially William pears); to loosen and elongate clusters and increase berry size in grapes; to control fruit maturity by delaying development of the yellow colour in lemons; to reduce rind stain and retard rind ageing in navel oranges; to counteract the effects of cherry yellows virus diseases in sour cherries; to produce uniform seedling growth in rice; to promote elongation of winter celery crop; to induce uniform bolting and increase seed production in lettuce for seed; to break dormancy and stimulate sprouting in seed potatoes; to extend the picking season by hastening maturity in artichokes; to increase the yield in forced rhubarb; to increase the malting quality of barley; to produce brighter-coloured, firmer fruit, and to increase the size of sweet cherries; to increase yields and aid harvesting of hops; to reduce internal browning and increase yields of Italian prunes; to increase fruit set and yields of tangelos and tangerines; to improve fruit setting in blueberries; to advance flowering and increase the yield of strawberries; and also a variety of applications on ornamentals. Application rates up to 80 g/a per application, depending on desired effect.
| 






