CYROMAZINE
    ГрУ¬°· ГрУ¬°·
Introduction: Cyromazine is a triazine insect growth regulator used as an insecticide and an acaricide. It is a cyclopropyl derivative of melamine. Cyromazine works by affecting the nervous system of the immature larval stages of certain insects. Cyromazine is used to control many insects and mites including those resistant to carbamate, organophosphate and pyrethroid compounds. In veterinary medicine, cyromazine is used as an ectoparasiticide.
Common name: Cyromazine
Another name: Larvadex, Vetrazin, Trigard, Cyclopropylmelamine, Cyromazin, Vetrazine, Neporex, Citation, Cypromazine, Azimethiphos, Armor, N-cyclopropylmelamine, Vetrazin (pesticide), Cyromazinum, Ciromazina, Larvadex Premix, Neporex (TN), Cyromazinum [INN-Latin], Ciromazina [INN-Spanish], Patron, Neoprex
Chemical name: N-cyclopropyl-1,3,5-triazine-2,4,6-triamine
Empirical formula: C6H10N6
Structural formula:
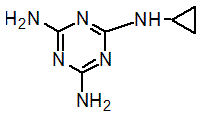
Mol. Weight: 166.18 g/mol
CAS No.: 66215-27-8
Specifications
Leading Cyromazine supplier
Cyromazine 75% WP
Cyromazine 99% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Solid: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
SMALL PACKING
Solid: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Customerized Packing label
Cyromazine FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H315 (37.66%): Causes skin irritation.
H319 (36.36%): Causes serious eye irritation.
H335 (35.06%): May cause respiratory irritation.
H411 (62.34%): Toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P261: Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapors/spray.
P264: Wash ... thoroughly after hanling.
P271: Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area.
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P280: Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection.
P302+P352: IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of water.
P304+P340: IF INHALED: Remove person to fresh air and keep comfortable for breathing.
P305+P351+P338: IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses if present and easy to do - continue rinsing.
P312: Call a POISON CENTER or doctor/... if you feel unwell.
P321: Specific treatment (see ... on this label).
P332+P313: IF SKIN irritation occurs: Get medical advice/attention.
P337+P313: IF eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/attention.
P362: Take off contaminated clothing.
P391: Collect spillage.
P403+P233: Store in a well-ventilated place. Keep container tightly closed.
P405: Store locked up.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to ...
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rat: 3387 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rat: >3100 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rat: >3.6 a.i. mg/L. 4) mild- irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) non-irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). NOEL (2 y) for rats is 300, mice is 1000 mg/kg diet.
ADI (JMPR): 0.02 mg/kg b.w.[1990]
Classification:
Toxicity class WHO (a.i.): III (Slightly hazardous)
US EPA Classification (formulation): III (Caution - Slightly toxic)
EC Risk Classification: Xn - Harmful: R20/22; Xi - Irritant: R36/37/38
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: moderate toxicity to birds, acute oral LD50 for Bobwhites quail is >1785 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: low toxicity to fish, acute 96 hour LC50 for Rainbow trout is >100 a.i.mg/L. Effect on aquatic invertebrates: low toxicity to aquatic invertebrates, acute 48 hour EC50 for Daphnia magna is >100 a.i.mg/L. Effect on algae: low toxicity to algae, acute 72 hour EC50 for Scenedemus subspicatus is 124 a.i.mg/L. Effect on honeybees: low toxicity to honeybees, contact acute 48 hour LD50 is >200 a.i.ҰМg/bee; Oral acute 48 hour LD50 is 186 a.i.ҰМg/bee. Effect on earthworms: low toxicity to earthworms, acute 14 day LC50 for Eisenia foetida is >1000 a.i.mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Cyromazine's production may result in its release to the environment through various waste streams; its use as an insect growth regulator will result in its direct release to the environment. If released to air, a measured solid-phase vapor pressure of 3.36ЎБ10-9 mm Hg at 25 deg C, that corresponds to a super-cooled vapor pressure of 3.2X10-7 mm Hg, indicates cyromazine will exist in both the vapor and particulate phases in the atmosphere. Vapor-phase cyromazine will be degraded in the atmosphere by reaction with photochemically-produced hydroxyl radicals; the half-life for this reaction in air is estimated to be 12.7 days. Particulate-phase cyromazine will be removed from the atmosphere by wet or dry deposition. If released to soil, cyromazine is expected to have low mobility based upon a recommended Koc of 765, determined from a measured Koc range of 81 to 1,800. Cyromazine has also been reported to have moderate mobility in soil, which would correspond to the lower Koc values measured in some soils. An agricultural runoff study found that cyromazine (applied to soil via chicken manure) was present in runoff waters with concentrations increasing as rainfall rates increased. Volatilization from moist soil surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon an estimated Henry's Law constant of 5.65ЎБ10-14 atm-cu m/mole. Studies conducted in the laboratory and field have demonstrated thecyromazine is degraded by biological mechanisms. Field dissipation half-lives have been reported to range from 75-284 days with a median of 189 days. The aerobic half-life in sand and a sandy loam soil were observed to be 107 and 142 days, respectively. Cyromazine is reported to be stable in anaerobic soil. If released into water, cyromazine may adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon the Koc. Volatilization fromwater surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon this compound's Henry's Law constant. An estimated BCF of 3 suggests bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is low. Cyromazine is reported to be stable to aqueous hydrolysis and stable in aqueous solution exposed to sunlight. Occupational exposure to cyromazine may occur through inhalation and dermal contact with this compound at workplaces wherecyromazine is produced or used. (SRC)
Usage: Insect growth regulator reported by R. D. Hall et al. (J. Econ. Entomol., 1980, 73, 564) and by R. E. Williams et al. (Poultry Sci., 1980, 59, 2207). Introduced as an insecticide by Ciba-Geigy AG (now Syngenta AG). Patents GB 1587573; BE 857896 Manufacturers: Gilmore; Sannong; Syngenta
Application: Biochemistry Chitin synthesis inhibitor. Insect growth regulator with contact action, which interferes with moulting and pupation. When used on plants, action is systemic: applied to the leaves, it exhibits a strong translaminar effect; applied to the soil, it is taken up by the roots and translocated acropetally. Uses Control of Diptera larvae in chicken manure by feeding to the poultry or treating the breeding sites. Also used to control flies on animals. Used as a foliar spray to control leaf miners (Liriomyza spp.) in vegetables (e.g. celery, melons, tomatoes, lettuce), mushrooms, potatoes and ornamentals, at 75-225 g/ha; also used at 190-450 g/ha in drench or drip irrigation.
| 






