Diflubenzuron
    іэіжле іэіжле
Introduction: Diflubenzuron is a benzamide insecticide used on forest and field crops to selectively control insects and parasites. Principle target insect species are the gypsy moth, forest tent caterpiller, several evergreen eating moths and the boll weevil. Diflubenzuron is a stomach and contact poison which acts by inhibiting the production of chitin (a compound that makes the outer covering of the insect hard) and so interferes with the formation of the insect's cuticle or shell. It is also used as a larvae control chemical in mushroom operations and animal houses.
Common name: Diflubenzuron
Another name: Difluron; Dimilin; Duphacid; Larvakil; Micromite; Astonex; Dimilin G1; Dimilin G4; Dimilin ODC-45; Dimilin WP-25; Thompson Hayward 6040; Thompson-hayward TH6040; Philips-duphar PH 60-40; etc.
Chemical name: 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-(2,6-difluorobenzoyl)urea
Empirical formula: C14H9ClF2N2O2
Structural formula:
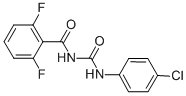
Mol. Weight: 310.68 g/mol
CAS No.: 35367-38-5
Specifications
Leading Diflubenzuron supplier
Diflubenzuron 95% TC
Diflubenzuron 25% WP
Diflubenzuron 200 g/L SL
Diflubenzuron 480 g/L SC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Powder: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum etc.
SMALL PACKING
Powder: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized packing label
Diflubenzuron FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H312: Harmful in contact with skin.
H400: Very toxic to aquatic life.
H410: Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P280: Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection.
P302+P352: IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of water.
P312: Call a POISON CENTER or doctor/... if you feel unwell.
P322: Specific measures (see ...on this label).
P363: Wash contaminated clothing before reuse.
P391: Collect spillage.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to.
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rats is >4640 mg/kg 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rats is >2000 mg/kg. 3) Acute inhalation toxicity LC50 (4 h) for rats is >2.5 mg/L. 4) Skin irritation: Non-irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Eye irritation: Slightly irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Skin sensitization for guinea pig: Non-sensitizing.
NOEL: (104 w) for rats is 2 mg/kg/day, (91 w) for mice is 1.2 mg/kg/day, (52 w) for dogs is 2 mg/kg/day. Other Not carcinogenic. Not genotoxic.
ADI (JMPR) 0-0.02 mg/kg b.w. [1985, 1994, 2001]
Classification:
WHO Classification: III (Slightly hazardous)
EC Risk Classification: Xi - Irritant: R36; N - Dangerous for the environment: R50/53
US EPA Classification (formulation): III (Caution - Slightly toxic)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: Acute oral LD50 for Bobwhite quail is >5000 mg/kg. Effect on fish: Acute LC50 (96 h) for Rainbow trout is >0.13 mg/l. Effects on aquatic invertebrates: Acute EC50 (48 h) for Daphnia magna is 0.0026 mg/l. Effects on algae: Acute 72 hour EC50 for Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata is 20 mg/l. Effects on bees: Contact acute 48 hour LD50 is >30 ҰМg/bee, oral acute 48 hour LD50 is >25 ҰМg/bee. Effects on earthworms: Acute 14 day LC50 is >500 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 184 (WHO, 1996). Animals In rats, following oral administration, elimination is partly as the unchanged parent compound in the faeces, partly as hydroxylated metabolites (for c. 80%) and as 4-chlorophenylurea plus 2,6-difluorobenzoic acid (for c. 20%). The intestinal absorption is strongly related to the dosage administered - the higher the dosage, the more (relatively) is excreted unchanged in the faeces. Plants Non-systemic. Not metabolised on plants (idem, ibid.). Soil/Environment Diflubenzuron is strongly absorbed by soil/humic acid complex and is virtually immobile in soil. Rapidly degraded in soil, with a half-life of <7 days. The principal degradation products are 4-chlorophenylurea and 2,6-difluorobenzoic acid.
Usage: Diflubenzuron was introduced in 1975 by Philips-Duphar B.V. (now Crompton Corp.). It is an insecticide of the benzoylurea class. It is used in forest management and on field crops to selectively control insect pests, particularly forest tent caterpillar moths, boll weevils, gypsy moths, and other types of moths.
Application: Biochemistry Chitin synthesis inhibitor; and so interferes with the formation of the insect cuticle. This action is quite specific; related biochemical processes, such as chitin synthesis in fungi, and biosynthesis of hyaluronic acid and other mucopolysaccharides in chickens, mice and rats are not affected. Mode of action Non-systemic insect growth regulator with contact and stomach action. Acts at time of insect moulting, or at hatching of eggs. Uses For control of a wide range of leaf-eating insects in forestry, woody ornamentals and fruit. Controls certain major pests in cotton, soya beans, citrus, tea, vegetables and mushrooms. Also controls larvae of flies, mosquitoes, grasshoppers and migratory locusts. Used as an ectoparasiticide on sheep for control of lice, fleas and blowfly larvae. Due to its selectivity and rapid degradation in soil and water, diflubenzuron has no or only a slight effect on the natural enemies of various harmful insect species. These properties make it suitable for inclusion in integrated control programmes. Diflubenzuron is effective at 25-75 g/ha against most leaf-feeding insects in forestry; in concentrations of 0.01-0.015% a.i. against codling moth, leaf miners and other leaf-eating insects in top fruit; in concentrations of 0.0075-0.0125% a.i. against citrus rust mite in citrus; and at a dosage of 50-150 g/ha against a number of pests in cotton (cotton boll weevil, armyworms, leafworms), soya beans (soya bean looper complex) and maize (armyworms). Also for control of larvae of mushroom flies in mushroom casing (1 g/m2); mosquito larvae (25-100 g/ha); fly larvae in animal housings (0.5-1 g/m2 surface); and locusts and grasshoppers (60-67.5 g/ha).
| 






