Fenbutatin Oxide
  ұҪ¶ЎОэ ұҪ¶ЎОэ
Introduction: Fenbutatin Oxide is an insecticide that specifically target mites (acaricide). It is used primary on fruit trees and nut trees, but is also approved for use on ornamentals. Fenbutatin Oxide is used to control the following: mites, aphids, thrips, mealybugs, whiteflies and scales, although it was originally created as a miticide (acaricide). It is applied only to agricultural sites, as residential use is not permitted. Fenbutatin Oxide may be applied 2-4 times per year at a rate of 1.25-2lbs active ingredient per Acre.
Common name: Fenbutatin Oxide
Another name: Vendex; Torque; 1,1,1,3,3,3-Hexakis(2-methyl-2-phenylpropyl) distannoxane; Hexakis; Osdaran; Bendex; Fenbutatin-oxide; Fenbutatin-oxyde; etc.
Chemical name: bis[tris(2-methyl-2-phenylpropyl)tin] oxide
Empirical formula: C60H78OSn2
Structural formula:
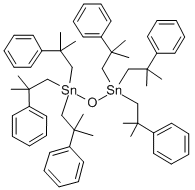
Mol. Weight: 1052.68 g/mol
CAS No.: 13356-08-6
Specifications
Leading Fenbutatin Oxide supplier
Fenbutatin Oxide 95% TC
Fenbutatin Oxide 90% TC
Fenbutatin Oxide 50% WP
Fenbutatin Oxide 25% WP
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Powder: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum etc.
SMALL PACKING
Powder: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized packing label
Fenbutatin Oxide FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H315: Causes skin irritation.
H319: Causes serious eye irritation.
H330: Fatal if inhaled.
H400: Very toxic to aquatic life.
H410: Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P260: Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapors/spray.
P264: Wash ... thoroughly after handling.
P271: Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area.
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P280: Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection.
P284: [In case of inadequate ventilation] Wear respiratory protection.
P302+P352: IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of water.
P304+P340: IF INHALED: Remove victim to fresh air and keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing.
P305+P351+P338: IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses if present and easy to do - continue rinsing.
P310: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician.
P320: Specific treatment is urgent (see ... on this label).
P321: Specific treatment (see ... on this label).
P332 +P313: IF SKIN irritation occurs: Get medical advice/attention.
P337 +P313: IF eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/attention.
P362: Take off contaminated clothing.
P391: Collect spillage.
P403 + P233: Store in a well-ventilated place. Keep container tightly closed.
P405: Store locked up.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to.
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rats is >3000 mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rats is >2000 mg/kg. 3) Acute inhalation toxicity LC50 (4 h) for rats is 0.046 mg/l. 4) Skin irritation: Slightly irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Eye irritation: Highly irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Skin sensitization for guinea pig: Not a skin sensitiser.
NOEL: (2 y) for rats is 2.5 mg/kg/day, (2 y) for dogs is 15 mg/kg/day. Other Not genotoxic, not teratogenic.
ADI (JMPR) 0-0.03 mg/kg b.w. [1992, 1977]
Classification:
WHO Classification: III (Slightly hazardous)
EC Risk Classification: T+ - Very toxic: R26; Xi - Irritant: R36/38; N - Dangerous for the environment: R50, R53.
US EPA Classification (formulation): III (Caution - Slightly toxic)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: Acute oral LD50 for Mallard is >969 mg/kg. Effect on fish: Acute LC50 (96 h) for Rainbow trout is 0.00114 mg/l. Effects on aquatic invertebrates: Acute EC50 (48 h) for Daphnia magna is 0.048 mg/l. Effects on algae: Acute 72 hour EC50 for Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata is >0.0036 mg/l. Effects on bees: Contact acute (48 h) LD50 is >200 ҰМg/bee, Oral acute (48 h) LD50 is >200 ҰМg/bee. Effects on earthworms: Acute 14 day LC50 is >500 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Soil/Environment In soil, it is metabolised to dihydroxy-bis(2-methyl-2-phenyl propyl)stannane and 2-methyl-2-phenylpropyl stannonic acid, presumably ultimately forming tin oxide/hydroxide. In tests in commercial use, there was minimal movement of fenbutatin oxide or its metabolites out of the top 30 cm of soil.
Usage: Fenbutatin Oxide was introduced in USA by Shell Chemical Co. (now DuPont Agricultural Products) and elsewhere by Shell International Chemical Co., Ltd (now BASF AG). It is an acaricide used to control a wide range of phytophagous mites and other insects, such as spidermites, aphids, mealybugs, thrips, whitefiles, scale, in fruit trees including citrus, apples, apricots; currants; vines; nuts; ornamentals, etc.
Application: Biochemistry Inhibitor of oxidative phosphorylation; disruptor of ATP formation. Mode of action Non-systemic acaricide with contact and stomach action. Uses Control of all motile stages of a wide range of phytophagous mites on pome fruit, stone fruit, citrus fruit, soft fruit, vines, bananas, cucurbits, ornamentals, and glasshouse crops. Gives long residual control. Phytotoxicity Phytotoxic to tangerines, tangelos, and some varieties of grapefruit. Otherwise, non-phytotoxic when used as directed.
| 






