STREPTOMYCIN
    ��ù�� ��ù��
Introduction: It is an aminoglycoside with systemic action that is used on fruits, vegetables, tobacco, ornamentals, and in ponds and aquaria. It controls a number of commercially important bacterial plant pathogens including fireblight of pear and apple, walnut blight, tomato canker, bacterial canker, angular leaf blight, and others. Gram positive species of bacteria are much more susceptible to its action than gram negative species.
Common name: Streptomycin
Another name: streptomycine, streptomycin sulfate or streptomycin nitrate
Chemical name: O-2-deoxy-2-methylamino-��-L-glucopyranosyl-(1-2)-O-5-deoxy-3-C-formyl-��-L-lyxofuranosyl-(1-4)-N1,N3-diamidino-D-streptamine
Empirical formula: C21H39N7O12
Structural formula:
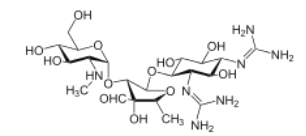
Mol. Weight: 581.57 g/mol
CAS No.: 57-92-1
Specifications
Leading Streptomycin supplier
Streptomycin 10% WP
Streptomycin 72% SP
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Solid: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
SMALL PACKING
Solid: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Customerized packing label
Streptomycin FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H351 (38.98%): Suspected of causing cancer.
H361 (100%): Suspected of damaging fertility or the unborn child.
Precautionary statement(s)
P201: Obtain special instructions before use.
P202: Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood.
P281: Use personal protective equipment as required.
P308+P313: IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention.
P405: Store locked up.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to ...
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rat: >9000 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rat: 325 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Streptomycin may cause mild skin irritation or allergic skin reactions. 4) Sensitive patients have shown reactions including rash, hives, headache, drop in blood pressure, nausea, and vomiting. Rabbits dosed with 5 or 10 mg/kg/day of streptomycin showed no teratogenic effects.
Classification:
US EPA Classification (formulation): IV (Caution - Not acutely toxic)
EC Risk Classification: Xn - Harmful: R22; Xi - Irritant: R36/37/38
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: low toxicity to birds, acute oral LD50 for Mallard ducks is >4640 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: low toxicity to fish, acute 96 hour LC50 for Rainbow trout is >180 a.i.mg/L. Effect on aquatic invertebrates: low toxicity to aquatic invertebrates, acute 48 hour EC50 for Daphnia magna is 487 a.i.mg/L. Effect on algae: moderate toxicity to algae, acute 72 hour EC50 is 0.133 a.i.mg/L.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Streptomycin's production and administration as a veterinary and human medication may result in its release to the environment through various waste streams. Its former use in the US as an agricultural bactericide/fungicide resulted in its direct release to the environment. It is derived from the gram-positive soil bacteria actinomycete Streptomyces griseus. If released to air, an estimated vapor pressure of 5.8��10-28 mm Hg at 25 deg C indicates streptomycin will exist solely in the particulate phase in the atmosphere. Particulate-phase streptomycin will be removed from the atmosphere by wet and dry deposition. Streptomycin does not contain chromophores that absorb at wavelengths >290 nm and, therefore, is not expected to be susceptible to direct photolysis by sunlight. If released to soil, streptomycin is expected to be immobile as it adsorbs strongly onto negatively charged clay soils. Volatilization of streptomycin from moist soil surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process as streptomycin is a highly polar organic base and ions do not volatilize. Streptomycin is not expected to volatilize from dry soil surfaces based upon its vapor pressure. Biodegradation data in soil or water were not available. If released into water, streptomycin is expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon it's strong adsorption to clay. Stroptomycin is a strong polar base and will exist almost entirely in the cation form at pH values of 5 to 9. Therefore, volatilization from water surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process. An estimated BCF of 3 suggests the potential for bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is low. Hydrolysis is not expected to be an important environmental fate process since this compound lacks functional groups that hydrolyze under environmental conditions (pH 5 to 9). Occupational exposure to streptomycin may occur through inhalation and dermal contact with this compound at workplaces where streptomycin is produced or used. The general public is not likely to be exposed to streptomycin unless by direct medical treatment. (SRC)
Usage: Streptomycin was discovered in 1943 from Streptomyces griseus. Used as a bactericidal antibiotic.
Application: Streptomycin as an aminoglycoside antibiotic drugs.Streptomycin sulphate of n/med tuberculosis bacili have strong antibacterial effect, for most gram-positive cocci (such as all kinds of streptococcus pneumoniae) and bacillus (e.g., pseudomonas aeruginosa, anaerobic bacteria) antibacterial effect is not strong, for many gram-negative bacilli has strong antimicrobial effect, tuberculosis is effective to all kinds of skin, inhibiting the bacteria and toxins produced by function, high concentration (>0.4 mu g/mL) have antiseptic effect. N/med tuberculosis bacili of streptomycin resistance quickly, should be associated with other anti-tuberculosis medicine application.
| 






