FLUFENOXURON
    ·ъіжле ·ъіжле
Introduction: Flufenoxuron is an insecticide used to control immature stages of phytophagous mites including aculus, brevipalpus, panonychus, phyllocoptruta, tetranychus spp. and other insect pests on Fruit including apples, cherry, grape, citrus, strawberry; Vegetables including brassicas, onions, leeks, eggplant; Cotton; Ornamentals.
Common name: Flufenoxuron
Another name: Cascade, Flufenoxuron [ISO], WL 115110, UNII-OD068OSS0N, RYLHNOVXKPXDIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N.
Chemical name: 1-[4-(2-chloro-ҰБ,ҰБ,ҰБ-trifluoro-p-tolyloxy)-2-fluorophenyl]-3-(2,6-difluorobenzoyl)urea
Empirical formula: C21H11ClF6N2O3
Structural formula:
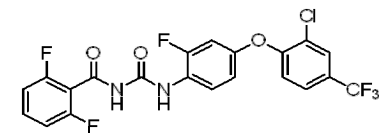
Mol. Weight: 488.77 g/mol
CAS No.: 101463-69-8
Specifications
Leading Flufenoxuron supplier
Flufenoxuron 50 g/L EC
Flufenoxuron 95% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Powder: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum ect.
SMALL PACKING
Powder: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized packing label
Flufenoxuron FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H362: May cause harm to breast-fed children.
H400: Very toxic to aquatic life.
H410: Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P201: Obtain special instructions before use.
P260: Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapors/spray.
P263: Avoid contact during pregnancy/while nursing.
P264: Wash ... thoroughly after handling.
P270: Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product.
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P308+P313:
P391: Collect spillage.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to ...
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rat: >3000 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rat: >2000 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rat: >3.3 a.i. mg/L. 4) Non-irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Non- irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). No component of this product present at levels greater than or equal to 0.1% is identified as probable, possible or confirmed human carcinogen by IARC.
ADI(JMPR): 0.04 mg/kg b.w. [2014]
Classification:
Toxicity class WHO (a.i.): III (Slightly hazardous)
US EPA Classification (formulation): III (Caution - Slightly toxic)
EC Risk Classification: Xn - Harmful: R20; N - Dangerous for the environment: R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: low toxicity to birds, acute LD50 for Colinus virginianus is >2000 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: high toxicity to fish, acute 96 hour LC50 for Rainbow trout is >0.0049 a.i.mg/L. Effect on aquatic invertebrates: high toxicity to aquatic invertebrates, acute 48 hour EC50 for Daphnia magna is 0.000043 a.i.mg/L. Effect on algae: moderate toxicity to algae, acute 72 hour EC50 for Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata, Biomass is 5.11 a.i.mg/L. Effect on honeybees: low toxicity to honeybees, contact acute 48 hour LD50 is >100 a.i.ҰМg/bee; Oral acute 48 hour LD50 is >109.1 a.i.ҰМg/bee. Effect on earthworms: moderate toxicity to earthworms, acute 14 day LC50 for Eisenia foetida is >500 a.i.mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Flufenoxuron's production may result in its release to the environment through various waste streams; its use as an insecticide/acaracide will result in its direct release to the environment. If released to air, a vapor pressure of 4.89ЎБ10-14 mm Hg at 20 deg C indicates flufenoxuron will exist solely in the particulate phase in the atmosphere. Particulate-phase flufenoxuron will be removed from the atmosphere by wet or dry deposition. Flufenoxuron is stable to natural sunlight, and therefore is not expected to be susceptible to direct photolysis by sunlight. If released to soil, flufenoxuron is expected to have no mobility based upon an estimated Koc of 1.3ЎБ104. Volatilization from moist soil surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon an estimated Henry's Law constant of 2.6ЎБ10-12 atm-cu m/mole. Flufenoxuron may not volatilize from dry soil surfaces based upon its vapor pressure. Biodegradation data were not available. If released into water, flufenoxuron is expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon the estimated Koc. Volatilization from water surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon this compound's estimated Henry's Law constant. An estimated BCF of 5400 suggests the potential for bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is very high, provided the compound is not metabolized by the organism. Hydrolysis half-lives of 112 days (pH 5), 104 days (pH 7), 36.7 days (pH 9), and 2.7 days (pH 12) indicate that the compound does undergo hydrolysis in the environment but the rate is affected by pH. An aqueous photodegradation half-life of 11 days in ambient water was reported. Occupational exposure to flufenoxuron may occur through inhalation and dermal contact with this compound at workplaces where flufenoxuron is produced or used. Limited monitoring data indicate that the general US population may be exposed to flufenoxuron via ingestion of imported food.
Usage: Flufenoxuron was discovered by M. Anderson, developed by Shell International Chemical Co., then American Cyanamid Cc. is the main manufacturer of the Chemical.
Application: Control of immature stages of many phytophagous mites (Aculus, Brevipalpus, Panonychus, Phyllocoptruta, Tetranychus spp) and insect pests on pome fruit, vines, citrus fruit, tea, cotton, maize, soya beans, vegetables and ornamentals. Applied at 25200 g/ha, depending on the crop and pests.
| 






