 |
| Ш§Щ„ШұШҰЩҠЩҖШіЩҠШ© - مبيد الحشرات |
| Name Of Product |
CAS NO. |
Specification |
MSDS |
| Chlorfluazuron |
71422-67-8 |
94%TC,5%EC |

|
|
|
Chlorfluazuron Basic information
|
|
|
|
|
|
Chlorfluazuron Chemical Properties
|
|
Melting point
|
approximate 220Ўж
|
|
density
|
1.5919 (estimate)
|
|
vapor pressure
|
<1 xl0-5 mPa (20 ЎгC)
|
|
storage temp.
|
Sealed in dry,2-8ЎгC
|
|
form
|
neat
|
|
pka
|
8.10 (acid)
|
|
Water Solubility
|
Јј0.01mg l-1(20 ЎгC)
|
|
BRN
|
8369967
|
|
CAS DataBase Reference
|
71422-67-8(CAS DataBase Reference)
|
|
EPA Substance Registry System
|
Chlorfluazuron (71422-67-8)
|
|
RIDADR
|
3077
|
|
WGK Germany
|
3
|
|
RTECS
|
CV3459580
|
|
HazardClass
|
9
|
|
PackingGroup
|
III
|
|
|
|
Chlorfluazuron Usage And Synthesis
|
|
Overview
|
Chlorfluazuron is a benzoylurea fluorinated nitrogen heterocyclic pesticide with unique mechanism of action, high efficiency, low toxicity and being environmentally friendly. It can be used in vegetables, cotton, fruit trees and pine trees. It is mainly used for controlling Pieris rapae, Plutella xylostella, Helicoverpa armigera, apple peach moth, and pine caterpillars. Its prevention and cure effect is remarkable, especially for the control of vegetable pests; it is expected that it is one of the main varieties that replace the current highly toxic pesticide, providing a new pesticide variety for the production of green food.
|
|
Chemical properties
|
Pure product appears as white or yellowish white tasteless crystalline powder with a melting point of 226.5 Ўж (decomposition). It is hard to be dissolved in water, being easily soluble in ketones, aromatic hydrocarbons and alcohols. Stable under light and heat, stable under neutral and weak acid conditions; it is easily subject to decomposition to alkali treatment.
Pure product appears as white odor-free crystal. m. p. 232-233.5 Ўг C, relative density 1.4977 (20 Ўг C), vapor pressure <1 x 10-10 Pa (20 Ўг C). Solubility: cyclohexanone 110g / L, acetone 52.1g / L, ethyl acetate 45.7g / L, ethylene dichloride 22g / L, toluene 6.5g / L, xylene 3g / L, methanol 2.5 (2.2) g / L, ethanol 2.0 g / L, n-octanol 1 g / L, hexane 10 mg / L and water 0.016 mg / L. Stable at room temperature; stable to light. The proto-drug is yellow-brown crystal with a melting point of220 ~ 223.9 Ўж.
|
|
Characteristics
|
It is of gastric poisoning, contact kill (inhibition of chitin synthesis) effect with high efficacy against pests, but the efficacy is slow. The mechanism of action is through inhibition of chitin synthesis, hindering insect normal molting, egg hatching, larvae molting and pupal developmental deformity and block of adult feather.
An overview of chlorfluazuron, physical and chemical properties, characteristics, synthesis, precautions, etc. are edited by Shi Yan, Chemicalbook. (2015-11-17)
|
|
Application
|
Benzoyl urea insect growth regulator. Major effect is through stomach poisoning, coupled with strong contact action. Its permeability is poor with no endosuction effect.
Insecticidal mechanism is through inhibiting the formation of chitin, hindering the normal molting, causing egg hatching, larvae molting, kidney malformations, adult emergence and obstruction of eggs, so as to achieve the effect of insecticide. It has high activity and slow acting speed, and has a longer half-life in larvae. The agent is a broad-spectrum insecticide and is effective against various Lepidoptera pests and Diptera, Orthoptera and Hymenoptera. It is quite effective on insects on the vegetables, can also be used to control a variety of pests on cabbage, cotton, tea trees and fruit trees.
|
|
Synthesis
|
Have 2, 6-dichloro-4-aminophenol and 2, 3-dichloro-5-trifluoromethylpyridine subject to etherification to give 3, 5-dichloro-4- (3- -trifluoromethyl-2-pyridyloxy) aniline, followed by reaction with 2, 6-difluorobenzoyl isocyanate (the reaction product of 2, 6-difluorobenzamide and solid phosgene) to obtain the target product Chlorfluazuron through condensation reaction; confirm its structure at the total yield of 95%.
Synthesis of 1, 3, 5-dichloro-4- (3-chloro-5-trifluoromethyl-2-pyridyloxy) aniline (4)
18.2g (0.10 mol) of 2,6-dichloro-4-aminophenol, 21.6 g (0.10 mol) of 2,3- dichloro-5-trifluoromethylpyridine Potassium and 0.5 g of catalyst were dissolved in 120 mL of DMF and reacted at 110-115 Ўг C; apply chromatography monitoring, when the raw material 2,3-dichloro-5-trifluoromethylpyridine has a content ЎЬ 0.5%, stop the reaction for about 6h. After the completion of the reaction, the residue was removed by filtration and the solvent was removed under reduced pressure. The residue was further extracted with 3 ЎБ 100 mL of dichloroethane, washed with 3 ЎБ 150 mL of water until neutral and dried by anhydrous magnesium sulfate overnight to give the dichloroethane solution of 3,5-dichloro-4- (3-chloro-5-trifluoromethyl-2-pyridyloxy) aniline (4) (to be used).
Synthesis of 2, 2, 6-difluorobenzoyl isocyanate (3)
15.7 g (0.10 mol) of 2, 6-difluorobenzamide (2) was dissolved in 150 mL of dichloroethane and 15.0 g (0.05 mol) of solid phosgene was added at -5 Ўг C. After holding for 1 hour, the mixture was heated to reflux 5h; the exhaust gas was absorbed by 5% sodium hydroxide solution. Apply chromatographic monitoring, when 2,6 - difluorobenzamide content ЎЬ 0.5%, cooled to room temperature for stand-by.
Synthesis of chlorfluazuron (1).
The dichloroethane solution of 3,5-dichloro-4- (3-chloro-5-trifluoromethyl-2-pyridyloxy) aniline (4) was slowly added dropwise at 80 to 85 ?C to the dichloroethane solution of 2,6-difluorobenzoyl isocyanate (3); the dropwise addition time is controlled at about 30min; incubate for 2h, then apply sampling control; when the etherate content ЎЬ 0.5%, apply atmospheric recovery of the solvent dichloroethane, filtered, and dried to give 47.0 g of off-white to white chlorfluazuron product.
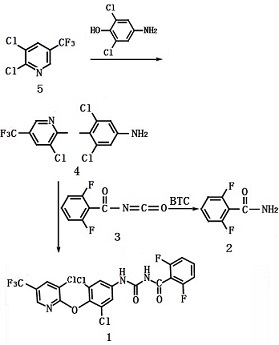
Figure 1 shows the synthesis of chlorfluazuron
|
|
Controlling objects and synthesis methods
|
It is of high activity against Lepidoptera, Coleoptera, Orthoptera, Hymenoptera and Diptera with no effects on aphids, leafhoppers and planthoppers.
ЎӨ Control Pieris rapae and diamondback moth; during 1 to 3 instar larvae stage, apply 1 000 ~ 4 000 times 5% EC times for spray. Make appropriate adjustment in the above concentration range according to the severity of the pest and the size of insect instar.
ЎӨ Control Eucalyptus ladybugs, potato ladybugs, Spodoptera litura and cutworm; during the larval hatch stage, use 2000~3000 times 5% EC for spray.
ЎӨ Prevention and control of pod borer, use 1 000 ~ 2 000 times liquid to administrate once in both the crop flowering stage and pest egg stage.
|
|
Production
|
Preparation of 2, 6 - difluorobenzonitrile
2, 6-dichlorobenzonitrile can be made through single-step method using ammonia oxidation of 2, 6-dichlorotoluene. Take 2,6-dichlorobenzonitrile as raw material, potassium fluoride as fluorinating agent and DMF, DMSO or sulfolane as solvent, the reaction temperature is 200-250 Ўж.
Synthesis method of 2,6-difluorobenzonitrile has the following improvements, such as: ўЩ use phase transfer catalysts such as quaternary ammonium salt, crown ether and polyether for synthesis, if polyether is used as the catalyst, the reaction temperature is 210 ~ 230 Ўж, the time is 8 ~ 10h, the yield is 86%; ўЪ Owing to the strong electron-withdrawing group -CN, under normal fluorination condition, the halogen of the ortho-aryl group will be lost. After adding dinitrobenzene, the above phenomenon was obviously inhibited, thereby increasing the yield; ўЫ Japanese patent reports, the above reaction uses segmented insulation method (170 Ўж, 0.5h, 175 Ўж, 2h, 220 Ўж, 4h) with the yield being 95.6%; Increase the surface area of KF, use spray drying method to produce ultra-fine anhydrous KF, yield up to 80%.
Preparation of 2, 6-difluorobenzamide
Use sulfuric acid as a catalyst, apply 2, 6-difluorobenzonitrile and water to have nucleophilic addition reaction to obtain the corresponding sulfate. Use alkali to neutralize to pH 6 to give 2, 6-difluorobenzamide.
Synthesis of chlorfluazuron
2,6-Difluorobenzamide was reacted with phosgene in dichloroethane solvent at 50 Ўг C for 1 h to yield 2,6-difluorobenzoyl isocyanate, which was then reacted with 4- (3-chloro-5-trifluoromethylpyridin-2-yloxy) -3,5-dichloroaniline to give chlorfluazuron.
|
|
Attention
|
1. Its application period is generally 3 days earlier than normal organophosphate, pyrethrins insecticide; in the best case, spray during the young larvae stage; for boring pests, it should be applied during the peak stage of egging.
2. No suction conduction effect; the application must be uniform and thoughtful.
3. Avoid using it in the mulberry fields, fish ponds and other places.
4. For cotton and cabbage area, do not use more than 3 times for crops per season; for citrus, do not use more than 2 times. The safe interval is 21 days for cotton and citrus and 7 days for cabbage.
|
|
Toxicity
|
Rats acute oral LD50 8500mg / kg, mice 7000mg / kg, rat-acute percutaneous LD50 1000mg / kg; rat-acute inhalation LC50 1846mg / m3. No irritation effect on rabbit eyes and skin. Guinea pig sensitization test result is negative. The sub-acute oral no-effect dose for rat is 3mg / kg; rabbits subcutaneous sub-acute no-effect daily dose of rabbit is 1000mg / kg; chronic oral no-effect dose for rat is 50mg / kg. No teratogenic, carcinogenic, mutagenic effects were found. Carp LC50 300mg / L (96h); safe for birds and bees; sensitive to silkworms.
|
|
Toxicity classification
|
low toxicity
|
|
Acute Toxicity
|
Oral - Rat LD50:> 8500 mg / kg; Oral - Mouse LD50:> 8500 mg / kg
|
|
Flammability Hazard Characteristics
|
Combustion produces toxic nitrogen oxides, chlorides and fluoride gases.
|
|
Storage and transportation
|
warehouse ventilated, low temperature and drying; separate storage and transportation of food raw materials
|
|
Extinguishing agent
|
dry powder, foam, sand
|
|
Uses
|
Chlorfluazuron is benzoyl(pyridiyloxyphenyl)urea based pesticide that acts as a chitin synthesis inhibitor. Chlorfluazuron is commonly used in agriculture as an insect growth regulator for controlling the major insect pests in crops
|
|
Uses
|
Chlorfluazuron is used for the control of Heliothis, Spodoptera, Bemisia tabaci and other chewing insects on cotton, and Plutella and Thrips on vegetables. It is also used on fruit, potatoes, ornamentals and tea.
|
|
Metabolic pathway
|
Only limited information is available in the open literature on the metabolism of chlorfluazuron.
|
|
Degradation
|
Chlorfluazuron is reported to be hydrolytically stable (PM).
|
|
|
|
Chlorfluazuron Preparation Products And Raw materials
|
|
|
|
|







