CAPTAN
    ҝЛҫъөӨ ҝЛҫъөӨ
Introduction: Captan is a nonsystemic phthalimide fungicide used to control diseases of many fruit, ornamental, and vegetable crops. It improves fruit finish by giving it a healthy, bright colored appearance. It is used in agricultural production as well as by the home gardener. A major use of captan is in apple production.
Common name: Captan
Another name: Agrox, Captal, Captec, Captol, Captonex, Clomitane, Merpan, Meteoro, Orthocide, Phytocape, Sepicap, Sorene, and Vancide 89
Chemical name: N-(trichloromethylthio)cyclohex-4-ene-1,2-dicarboximide
Empirical formula: C9H8Cl3NO2S
Structural formula:
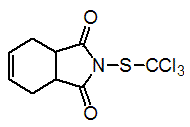
Mol. Weight: 300.61 g/mol
CAS No.: 133-06-2
Specifications
Leading Captan supplier
Captan 80% WP
Captan 80% WDG
Captan 95% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Solid: 25KG/Bag, 25KG/Drum, 50KG/Drum etc.
SMALL PACKING
Solid: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Customerized Packing label
Captan FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H317: May cause an allergic skin reaction.
H318: Causes serious eye damage.
H331: Toxic if inhaled.
H351: Suspected of causing cancer.
H400: Very toxic to aquatic life.
Precautionary statement(s)
P201: Obtain special instructions before use.
P202: Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood.
P261: Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapors/spray.
P271: Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area.
P272: Contaminated work clothing should not be allowed out of the workplace.
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P280: Wear protective gloves/ eye protection/ face protection.
P281: Use personal protective equipment as required.
P302+P352: IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of water.
P304+P340: IF INHALED: Remove person to fresh air and keep comfortable for breathing.
P305+P351+P338: IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses if present and easy to do - continue rinsing.
P308+P313: IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention.
P310: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician.
P311: Call a POISON CENTER or doctor/...
P321: Specific treatment (see ... on this label).
P333+P313: IF SKIN irritation or rash occurs: Get medical advice/attention.
P363: Wash contaminated clothing before reuse.
P391: Collect spillage.
P403+P233: Store in a well-ventilated place. Keep container tightly closed.
P405: Store locked up.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to ...
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rat: >2000 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rat: >2000 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rat: 0.67 a.i. mg/L. 4) Corrosive to eyes (rabbit) 5) mildly irritating to skin (rabbit). 6) Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). NOEL (2 y) for rats is 2000, dogs is 4000 mg/kg diet. No carcinogenic, teratogenic, or mutagenic effects observed.
ADI(JMPR): 0.1 mg/kg b.w. [2004]
Classification:
Toxicity class WHO (a.i.): U (Unlikely to present an acute hazard)
US EPA Classification (formulation): IV (Caution - Not acutely toxic)
EC Risk Classification: Carcinogen category 3: R40; T - Toxic: R23; Xn - Harmful: R43, R41; N - Dangerous for the environment: R50
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: low toxicity to birds, acute oral LD50 for Mallard ducks is >2000 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: moderate toxicity to fish, acute 96 hour LC50 for Rainbow trout is 0.186 a.i.mg/L. Effect on aquatic invertebrates: moderate toxicity to aquatic invertebrates, acute 48 hour EC50 for Daphnia magna is 7.1 a.i.mg/L. Effect on algae: moderate toxicity to algae, acute 72 hour EC50 for Raphidocelis subcapitata is 1.18 a.i.mg/L. Effect on honeybees: low toxicity to honeybees, contact acute 48 hour LD50 is >200 a.i.ҰМg/bee, oral acute 48 hour LD50 is >100 a.i.ҰМg/bee. Effect on earthworms: moderate toxicity to earthworms, acute 14 day LC50 for Eisenia foetida is >519 a.i.mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Captan's production may result in its release to the environment through various waste streams; its use as a fungicide will result in its direct release to the environment. If released to air, a vapor pressure of 9.0ЎБ10-8 mm Hg at 25 deg C indicates captan will exist in both the vapor and particulate phases. Vapor-phase captan will be degraded in the atmosphere by reaction with photochemically-produced hydroxyl radicals and ozone; the half-lives for these reactions in air are estimated to be 4.4 and 4.1 hours, respectively. Particulate-phase captan will be removed from the atmosphere by wet and dry deposition. Captan does not contain chromophores that absorb at wavelengths >290 nm and, therefore, is not expected to be susceptible to direct photolysis by sunlight. If released to soil, captan is expected to have very high to moderate mobility based upon Koc values of 33-600. Volatilization from moist soil surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon a Henry's Law constant of 7.0ЎБ10-9 atm-cu m/mole. Captan is not expected to volatilize from dry soil surfaces based upon its vapor pressure. In field studies using sterile and unsterile soil at pH 7.2 and 50% moisture content, captan, applied to a sandy loam, clay loam and sandy loam soil amended with peat had a reported half-life of 12-20, 5.5-5.9 and 7.7-8.9 days, respectively. If released into water, captan is expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon the Koc range. Captan is hydrolyzed with half-lives of 18.8 hrs, 4.9 hrs and 8.3 min measured in water at pH values of 5, 7 and 9, respectively. Based on the rapid hydrolysis of captan, biodegradation in water is not expected to be an important fate process. Volatilization from water surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon this compound's Henry's Law constant. A reported BCF of 126 in bluegill sunfish suggests bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is moderate. Occupational exposure to captan may occur through inhalation and dermal contact with this compound at workplaces where captan is produced or used. Monitoring data indicate that the general population may be exposed to captan primarily via ingestion of fruit containing residual pesticide. Limited monitoring data indicate exposure may occur via dermal contact with consumer products containing captan, inhalation of ambient air, and ingestion of contaminated drinking water. (SRC)
Usage: Fungicide reported by A. R. Kittleston (Science, 1952, 115, 84). Introduced by Standard Oil Development Co., later by Chevron Chemical Co. Manufacturers: Arvesta; Crystal; Drexel; Makhteshim-Agan; Rallis; Sharda.
Application: Control of a wide range of fungal diseases, e.g. scab, black rot, botryosphaeria rot, bitter rot, bull's eye rot, botrytis rot of pome fruit; shot-hole of stone fruit; peach leaf curl; brown rots of cherries, apricots, peaches, plums, and citrus fruit; downy mildew and black rot of vines; early and late blights of potatoes and tomatoes; Alternaria blight and leaf spot of carrots; anthracnose and downy mildew of cucurbits; leaf spot diseases of ornamentals; anthracnose and leaf spot diseases of tomatoes; brown patch on turf; Botrytis spp. on many crops; etc. Used on a large number of other crops. Applied at 2-4.5 lb/a. Used as a seed treatment or root dip for control of Pythium, Phoma, Rhizoctonia spp., etc. on maize, ornamentals, vegetables, oilseed rape, and other crops.
| 






