CHLORPYRIFOS
    ¶ҫЛАтз ¶ҫЛАтз
Introduction: Chlorpyrifos is a broad spectrum organophosphorus insecticide and acaricide used to control soil and foliage pests including scale, wooly aphid, leaf roller, caterpillars, corn earworm, armyworm, cutworms, rootworms, cockroaches, flea beetles, flies, termites, fire ants in Cereals including barley, wheat, Cotton; Fruit including apples, pears, grapes, pineapples, bananas, strawberries, mango; Tomatoes; Nuts; Vegetables inclding carrots, cabbages, cauliflower, Brussel sprouts.
Common name: Chlorpyrifos
Another name: Chlorpyriphos, Dursban, Trichlorpyrphos, Lorsban, Brodan, Coroban, Chlorpyrifos-ethyl, Pyrinex, Clorpyrifos, Killmaster, Bonidel, Danusban, Lentrek, Piridane, Geodinfos, Spannit, Stipend, Tafaban, Durmet, Equity, Terial, Zidil, Suscon blue, Suscon green, suSCon, Dursban F, Dursban R, Lock-On, Dursban 4E, Chlorpyriphos-ethyl, Dowco 179, Ethyl chlorpyriphos, Dursban 10CR, Detmol U.A., Dhanusban.
Chemical name: O,O-diethyl O-3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridyl phosphorothioate
Empirical formula: C9H11Cl3NO3PS
Structural formula:
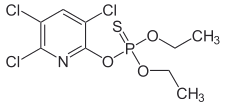
Mol. Weight: 350.58 g/mol
CAS No.: 2921-88-2
Specifications
Leading Chlorpyrifos supplier
Chlorpyrifos 480 g/L EC
Chlorpyrifos 97% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Powder: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum ect.
SMALL PACKING
Powder: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized packing label
Chlorpyrifos FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H301: Toxic if swallowed.
H400: Very toxic to aquatic life.
H410: Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P264: Wash ... thoroughly after handling.
P270: Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product.
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P301+P310: IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER/doctor/...
P321: Specific treatment (see ... on this label).
P330: Rinse mouth.
P391: Collect spillage.
P405: Store locked up.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to ...
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rat: 66 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rat: >1250 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rat: 0.1 a.i. mg/L. 4) Slightly - irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Moderately- irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). No effects on reproduction occurred in a three-generation study with rats fed dietary doses as high as 1 mg/kg/day. Available evidence suggests that chorpyrifos is not teratogenic, mutagenic and carcinogenic. Chlorpyrifos primarily affects the nervous system through inhibition of cholinesterase, an enzyme required for proper nerve functioning.
ADI: 0.01 mg/kg b.w. [1999, 2004]
Classification:
Toxicity class WHO (a.i.): II (Moderately hazardous)
US EPA Classification (formulation): II (Warning - Moderately toxic)
EC Risk Classification: T - Toxic: R25; Xn - Harmful: R21, R43; N - Dangerous for the environment: R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: high toxicity to birds, acute oral LD50 for Colinus virginianus is 39.2 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: high toxicity to fish, acute 96 hour LC50 for Rainbow trout is 0.025 a.i.mg/L. Effect on aquatic invertebrates: high toxicity to aquatic invertebrates, acute 48 hour EC50 for Daphnia magna is 0.00010 a.i.mg/L. Effect on algae: moderate toxicity to algae, acute 72 hour EC50 is 0.48 a.i.mg/L. Effect on honeybees: high toxicity to honeybees, contact acute 48 hour LD50 is 0.059 a.i.ҰМg/bee; Oral acute 48 hour LD50 is 0.25 a.i.ҰМg/bee. Effect on earthworms: moderate toxicity to earthworms, acute 14 day LC50 for Eisenia foetida is129 a.i.mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Chlorpyrifos' production may result in its release to the environment through various waste streams; its use as an insecticide will result in its direct release to the environment. If released to air, a vapor pressure of 2.02ЎБ10-5 mm Hg at 25 deg C indicates chlorpyrifos will exist in both the vapor and particulate phases in the atmosphere. Vapor-phase chlorpyrifos will be degraded in the atmosphere by reaction with photochemically-produced hydroxyl radicals; the half-life for this reaction in air is estimated to be 5 hours. Particulate-phase chlorpyrifos will be removed from the atmosphere by wet or dry deposition. Chlorpyrifos absorbs light greater than 295 nm and photolysis has been observed in air. The summer photolysis half-life is estimated as 4.2 days with the winter photolysis half-life estimated as 9.7 days. If released to soil, chlorpyrifos is expected to have low to no mobility based upon a measured Koc range of 995 to 31,000. Volatilization from moist soil surfaces may be an important fate process based upon a Henry's Law constant of 3.55ЎБ10-5 atm-cu m/mole. A 0.64% volatilization after 3.2 days indicates that chlorpyrifos volatilizes slowly from soil. Field dissipation half-lives can range from 4-139 days. Half-lives can typically range from 33-56 days for soil incorporated applications and 7-15 days for surface applications. The primary route of degradation is transformation to 3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-ol, which is subsequently degraded to organochlorine compounds and carbon dioxide. If released into water, chlorpyrifos is expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon the Koc. Volatilization from water surfaces is expected to be an important fate process based upon this compound's Henry's Law constant. Estimated volatilization half-lives for a model river and model lake are 2.2 and 21.5 days, respectively. However, volatilization from water surfaces is expected to be attenuated by adsorption to suspended solids and sediment in the water column. Measured BCF values of 58 to 2880 suggest bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is moderate to very high. Direct photo-transformation of chlorpyrifos was observed in buffer solutions and river waters, under both natural and artificial lighting conditions with approximate 50% conversion after 30-40 days. The hydrolysis half-lives at 25 deg C in aqueous buffers at pH 5, pH 7 and pH 9 were 72, 72 and 16 days respectively. Biodegradation is expected to be an important fate process. Occupational exposure to chlorpyrifos may occur through inhalation and dermal contact with this compound at workplaces where chlorpyrifos is produced or used. Monitoring and use data indicate that the general population may be exposed to chlorpyrifos via inhalation of ambient air, ingestion of food and drinking water, and dermal contact with this compound.
Usage: Chlorpyrifos was introduced in 1965 by Dow Chemical Company. It acts on the nervous system of insects by inhibiting acetylcholinesterase. It is used on crops, animals, and buildings to kill a number of pests including insects and worms.
Application: To achieve the best control effect, recommend to use at the beginning of larvae or hatching stage. Field crops using preparations against the amount of water per acre 45 to 60 kg, fruit tree according to the size of the old use preparations against the amount of water in 200-200 kg per acre. Windy day or rain in 1 hour, do not administer. Sensitive for melons (special in greenhouses), lettuce in seedling stage, celery and tobacco, when applying pesticide should avoid liquids drifting on the crops, to prevent the adr. In the fruit trees flowering period should not be used.
|







