TEBUFENPYRAD
    ЯБтэ°· ЯБтэ°·
Introduction: Tebufenpyrad is a contact and stomach action acaricide used to control all stages of Tetranychus, Panonychus, Oligonychus and Eotetranychus spp. including european red mite, fruit tree red spider mite and the two spotted spider mite, aphids on fruit trees including apples, pears, strawberries, Commercial greenhouses, Ornamentals including roses, hopsand other crops.
Common name: Tebufenpyrad
Another name: Pyranica; Tebufenpyrad [ISO]; MK239; MK 239, AC 801757, HSDB 7271, CHEBI:9422, UNII-IRU3P7ZB3F.
Chemical name: N-(4-tert-butylbenzyl)-4-chloro-3-ethyl-1-methylpyrazole-5- carboxamide
Empirical formula: C18H24ClN3O
Structural formula:
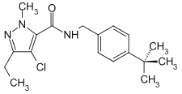
Mol. Weight: 333.8 g/mol
CAS No.: 119168-77-3
Specifications
Leading Tebufenpyrad supplier
Tebufenpyrad 10% WP
Tebufenpyrad 20% WP
Tebufenpyrad 20% WDG
Tebufenpyrad 300 g/L SC
Tebufenpyrad 92% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Powder: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum ect.
SMALL PACKING
Powder: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized packing label
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H301: Toxic if swallowed.
H317: May cause an allergic skin reaction.
H332: Harmful if inhaled.
H373: Causes damage to organs through prolonged or repeated exposure.
H410: Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P260: Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapors/spray.
P261: Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapors/spray.
P264: Wash ... thoroughly after handling.
P270: Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product.
P271: Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area.
P272: Contaminated work clothing should not be allowed out of the workplace.
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P280: Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection.
P301+P310: IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER/doctor/...
P302+P352: IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of water.
P304+P312: IF INHALED: Call a POISON CENTER/doctor/... if you feel unwell.
P304+P340: IF INHALED: Remove person to fresh air and keep comfortable for breathing.
P312: Call a POISON CENTER or doctor/... if you feel unwell.
P314: Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell.
P321: Specific treatment (see ... on this label).
P330: Rinse mouth.
P333+P313: IF SKIN irritation or rash occurs: Get medical advice/attention.
P363: Wash contaminated clothing before reuse.
P391: Collect spillage.
P405: Store locked up.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to ...
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rat: >202 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rat: >2000 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rat: 2.7 a.i. mg/L. 4) Non-irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Minimal-irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). In accordance with the EPA Draft Guidelines for Carcinogen Risk Assessment (July 1999), the Cancer Assessment Review Committee classified tebufenpyrad into the category Ў°Suggestive Evidence of Carcinogenicity, but Not Sufficient to Assess Human Carcinogenic PotentialЎұ.
ADI: 0.01mg/kg b.w.
Classification:
Toxicity class WHO (a.i.): II (Moderately hazardous)
EC Risk Classification: Xn - Harmful: R20, R22, R43; N - Dangerous for the environment: R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: low toxicity to birds, acute LD50 for Colinus virginianus is >2000 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: high toxicity to fish, acute 96 hour LC50 for Rainbow trout is 0.023 a.i.mg/L. Effect on aquatic invertebrates: high toxicity to aquatic invertebrates, acute 48 hour EC50 for Daphnia magna is 0.046 a.i.mg/L. Effect on algae: moderate toxicity to algae, acute 72 hour EC50 for Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata is 0.052 a.i.mg/L. Effect on honeybees: moderate toxicity to honeybees, contact acute 48 hour LD50 is 6.7 a.i.ҰМg/bee; Oral acute 48 hour LD50 is 60.3 a.i.ҰМg/bee. Effect on earthworms: moderate toxicity to earthworms, acute 14 day LC50 for Eisenia foetida is 20.5 a.i.mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Tebufenpyrad's production may result in its release to the environment through various waste streams; its use as an acaricide will result in its direct release to the environment. If released to air, a vapor pressure of <7.3ЎБ10-8 mm Hg at 20 deg C indicates tebufenpyrad will exist solely in the particulate phase in the atmosphere. Particulate-phase tebufenpyrad will be removed from the atmosphere by wet or dry deposition. If released to soil, tebufenpyrad is expected to have low to no mobility based upon reported Koc values of 1380 to 8310. Volatilization from moist soil surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon an estimated Henry's Law constant of <1.2ЎБ10-8 atm-cu m/mole. Specific biodegradation data were unavailable, but tebufenpyrad had reported soil dissipation half-lives in laboratory studies of 19 to 56 days and in the field as 2 to 50 days. If released into water, tebufenpyrad is expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon the Koc values. Volatilization from water surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon this compound's estimated Henry's Law constant. An estimated BCF of 830 suggests the potential for bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is high. Tebufenpyrad is reported to be stable to hydrolysis at environmental pHs and has an aqueous photolysis half-life of 187 days at pH 7 and 25 deg C. Occupational exposure to tebufenpyrad may occur through inhalation and dermal contact with this compound at workplaces where tebufenpyrad is produced or used. Limited monitoring data indicate that the general population may be exposed to tebufenpyrad via ingestion of food.
Usage: Tebufenpyrad was discovered and developed by Mitsubishi chemical corporation of Japan in 1987.
Application: Tebufenpyrad is registered for use on ornamental plants grown in commercial greenhouses. An application rate of 0.8 to 3.4 fluid ounces of product (0.02 to 0.08 pounds active ingredient) per 100 gallons sprayed to obtain uniform and complete coverage of foliage. Applications may be repeated at 5 to 7 day intervals to maintain control. 3 to 4 treatments may be needed
| 






