Propamocarb Hydrochloride
    ЛӘГ№НюСОЛбСО ЛӘГ№НюСОЛбСО
Introduction: Propamocarb hydrochloride is a carbamate pesticide. Carbamate pesticides are derived from carbamic acid and kill insects in a similar fashion as organophosphate insecticides. They are widely used in homes, gardens and agriculture. The first carbamate, carbaryl, was introduced in 1956 and more of it has been used throughout the world than all other carbamates combined. Because of carbaryl's relatively low mammalian oral and dermal toxicity and broad control spectrum, it has had wide use in lawn and garden settings. Most of the carbamates are extremely toxic to Hymenoptera, and precautions must be taken to avoid exposure to foraging bees or parasitic wasps. Some of the carbamates are translocated within plants, making them an effective systemic treatment.
Common name: Propamocarb Hydrochloride
Another name: W-110639; Propyl [3-(dimethylamino)propyl]carbamate hydrochloride; CHEBI:81735; Carbamic acid, [3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-, propyl ester, monohydrochloride; etc.
Chemical name: propyl 3-(dimethylamino)propylcarbamate hydrochloride
Empirical formula: C9H21ClN2O2
Structural formula:
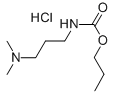
Mol. Weight: 224.73 g/mol
CAS No.: 25606-41-1
Specifications
Leading Propamocarb Hydrochloride supplier
Propamocarb Hydrochloride 97% TC
Propamocarb Hydrochloride 69% TC
Propamocarb Hydrochloride 722 g/L AS
Propamocarb Hydrochloride 35% AS
Propamocarb Hydrochloride 66.5% AS
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Powder: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum etc.
SMALL PACKING
Powder: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized packing label
Propamocarb Hydrochloride FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H317 (94.59%): May cause an allergic skin reaction.
Precautionary statement(s)
P261: Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapors/spray.
P272: Contaminated work clothing should not be allowed out of the workplace.
P280: Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection.
P302+P352: IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of water.
P321: Specific treatment (see ... on this label).
P333+P313: IF SKIN irritation or rash occurs: Get medical advice/attention.
P363: Wash contaminated clothing before reuse.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to an approved waste disposal plant.
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rats is >1330 mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rats is >2000 mg/kg. 3) Acute inhalation toxicity LC50 (4 h) for rats is >5.01 mg/L. 4) Skin irritation: Non-irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Eye irritation: Slightly irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Skin sensitization for guinea pig: Not a sensitizer.
NOEL: (2 y) for male rats is 43 mg/kg/day, for female rats is 55 mg/kg/day. Other Not carcinogenic.
ADI 0-0.29 mg/kg b.w.
Classification:
WHO Classification: U (Unlikely to present an acute hazard)
EC Risk Classification: Xn - Harmful: R43; N - Dangerous for the environment: R52
US EPA Classification (formulation): IV (Caution - Not acutely toxic)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: Acute oral LD50 for Mallard is >1842 mg/kg. Effect on fish: Acute LC50 (96 h) for Rainbow trout is >99 mg/l. Effects on aquatic invertebrates: Acute EC50 (48 h) for Daphnia magna is >100 mg/l. Effects on algae: Acute 72 hour EC50 for Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata is >85 mg/l. Effects on bees: contact acute 48 hour LD50 is >100 ҰМg/bee, oral acute 48 hour LD50 is >84 ҰМg/bee. Effects on earthworms: Acute 14 day LC50 is >660 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Propamocarb hydrochloride is relatively non-persistent, is stable to photodegradation in water, is photodegradable on soil with a half-life of 35 days, degrades fairly rapidly by microbial-mediated metabolism, is persistent to anaerobic metabolism, dissipates rapidly under field conditions, has limited hydrolytic potential and bioconcentration in fish, and has variable mobility from mobile to relatively immobile. Volatilization is not considered a probable route of dissipation. Abiotic hydrolysis is not a significant dissipation process. However, base-catalyzed hydrolysis may occur at extremely slow rates.
Usage: Propamocarb hydrochloride was discovered and developed by Shering AG. It is a fungicide for specific control of Phycomycetes and effective against Phytophthora spp. and Pythium spp.
Application: Propamocarb hydrochloride is a versatile, effective, and safe carbamate fungicide with specific activity against numerous Oomycete species, causing seed, seedling, root, foot, and stem rots and foliar diseases in numerous edible crops and ornamental plants. The mode of action is different from that of other Oomycete fungicides, and propamocarb hydrochloride effectively controls strains that have developed resistance to other fungicides. Propamocarb hydrochloride is used to control the plant disease "damping-off" and has fungicidal activity against Pythium spp. and Phytophthora spp. Current use sites include ornamental lawns and turf, ornamental sod farms (turf), ornamental herbaceous plants, ornamental woody shrubs and vines.
| 






