Pyrimethanil
    аЧГ№°· аЧГ№°·
Introduction: Pyrimethanil is a broad spectrum fungicide often applied to seeds. It inhibits methionine biosynthesis, thus affecting protein formation and subsequent cell division. Pyrimethanil works best on young fungus infestations.
Common name: Pyrimethanil
Another name: 4,6-dimethyl-N-phenyl-2-pyrimidinamine; 4,6-dimethyl-N- phenylpyrimidin-2-amine; Pyrimethanil [ISO]; 2-Anilino-4,6-dimethylpyrimidine; etc.
Chemical name: N-(4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)aniline
Empirical formula: C12H13N3
Structural formula:
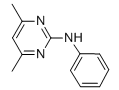
Mol. Weight: 199.11 g/mol
CAS No.: 53112-28-0
Specifications
Leading Pyrimethanil supplier
Pyrimethanil 95% TC
Pyrimethanil 98% TC
Pyrimethanil 40% SC
Pyrimethanil 40% WP
Pyrimethanil 20% SC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Powder: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum etc.
SMALL PACKING
Powder: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized packing label
Pyrimethanil FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H411 (100%): Toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P391: Collect spillage.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to an approved waste disposal plant.
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rats is 4149 mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rats is >5000 mg/kg. 3) Acute inhalation toxicity LC50 (4 h) for rats is >1.98 mg/L (nose only). 4) Skin irritation: Non-irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Eye irritation: Slightly irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Skin sensitization for guinea pig: Not a sensitizer (Magnussen & Kligman and Buehler test).
NOEL: (2 y) for rats is 17 mg/kg/day; (80 w) for mice is 20 mg/kg/day; (1 y) for dogs is 80 mg/kg/day. Other Not carcinogenic. Not genotoxic.
ADI (JMPR) 0-0.2 mg/kg b.w. [2007]
Classification:
WHO Classification: III (Slightly hazardous)
EC Risk Classification: N - Dangerous for the environment: R51, R53
US EPA Classification (formulation): IV (Caution - Not acutely toxic)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: Acute oral LD50 for Mallard is >2000 mg/kg. Effect on fish: Acute LC50 (96 h) for Rainbow trout is 10.56 mg/l. Effects on aquatic invertebrates: Acute EC50 (48 h) for Daphnia magna is 2.9 mg/l. Effects on algae: Acute 72 hour EC50 for Raphidocelis subcapitata is 1.2 mg/l. Effects on bees: contact acute 48 hour LD50 is >100 ҰМg/bee, oral acute 48 hour LD50 is >100 ҰМg/bee. Effects on earthworms: Acute 14 day LC50 is 313 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Rapidly absorbed, extensively metabolised and rapidly excreted in all species examined. No evidence of accumulation, even on repeated dosing. Metabolism proceeds by oxidation to phenolic derivatives which are excreted as glucuronide or sulfate conjugates. Plants Little metabolism occurs in fruit; residues at maturity consist essentially of unchanged parent compound only. For this reason, a crop residue monitoring method has been developed for the direct determination of pyrimethanil itself. Soil/Environment DT50 in laboratory studies 27-82 d; field studies indicate rapid degradation, DT50 7-54 d. Koc 265-751. Low potential for leaching to groundwater; field studies show minimal movement of pyrimethanil into deeper soil layers. Pyrimethanil disappears rapidly from surface water and moderately adsorbs to the sediment, from which it is further degraded.
Usage: Pyrimethanil was introduced by Schering (now Bayer CropScience). It is a fungicide used to control fungal pathogens on fruit, vegetables and ornamentals.
Application: Biochemistry Proposed inhibitor of methionine biosynthesis, leading to inhibition of the secretion of enzymes necessary for infection. Mode of action Protectant (in Botrytis) and both protective and curative action (in Venturia). Uses Control of grey mould (Botrytis cinerea) on vines, fruit, vegetables and ornamentals. Control of leaf scab (Venturia inaequalis or V. pirina) on pome fruit. Phytotoxicity May be phytotoxic in closed systems at 380% r.h. on certain species.
| 






