Zineb
    ҙъЙӯРҝ ҙъЙӯРҝ
Introduction: Zineb is a polymeric complex of zinc with the ethylene bis(dithiocarbamate) anionic ligand. It is used as a fungicide to control downy mildews, rusts and redfire disease. Zinc is a metallic element with the atomic number 30. It is found in nature most often as the mineral sphalerite. Though excess zinc in harmful, in smaller amounts it is an essential element for life, as it is a cofactor for over 300 enzymes and is found in just as many transcription factors.
Common name: Zineb
Another name: METIRAM; 12122-67-7; Parzate; Zinc ethylenebisthiocarbamate; ; CHEBI:52498; Zinc ethylenebisdithiocarbamate; Cynkotox; Novozir; zinc ethane-1,2-diylbis(dithiocarbamate); Dithane Z-78; Polikarbatsin; Tritoftorol; Aaphytora; Aphytora; Asporum; Blightox; Blizene; Carbadine; etc.
Chemical name: zinc ethylenebis(dithiocarbamate) (polymeric)
Empirical formula: C4H6N2S4Zn
Structural formula:
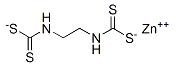
Mol. Weight: 275.78 g/mol
CAS No.: 12122-67-7
Specifications
Leading Zineb supplier
Zineb 85% TC
Zineb 80% WP
Zineb 70% WP
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Powder: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum etc.
SMALL PACKING
Powder: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized packing label
Zineb FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H317 (100%): May cause an allergic skin reaction.
H400 (100%): Very toxic to aquatic life.
H410 (100%): Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P261: Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapors/spray.
P272: Contaminated work clothing should not be allowed out of the workplace.
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P280: Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection.
P302+P352: IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of water.
P321: Specific treatment (see ... on this label).
P333+P313: IF SKIN irritation or rash occurs: Get medical advice/attention.
P363: Wash contaminated clothing before reuse.
P391: Collect spillage.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to ...
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rats is >5200 mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rats is >6000 mg/kg. 3) Acute inhalation toxicity LC50 (4 h) for rats is 0.8 mg/L. 4) Skin irritation: Moderately irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Eye irritation: Moderately irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Skin sensitization for guinea pig: Sensitizing.
NOEL: (1 y) for dogs is 50 mg/kg/day. Other Not carcinogenic. Not genotoxic.
ADI (JMPR) 0-0.03 mg/kg b.w. [1993]
Classification:
WHO Classification: U (Unlikely to present an acute hazard)
EC Risk Classification: Xn - Harmful: R43; Xi - Irritant: R37
US EPA Classification (formulation): IV (Caution - Not acutely toxic).
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: Acute oral LD50 for Mallard ducks is 2000 mg/kg. Effect on fish: Acute LC50 (96 h) for Rainbow trout is 20.8 mg/l. Effects on aquatic invertebrates: Acute EC50 (48 h) for Daphnia magna is 40 mg/l. Effects on algae: Acute 72 hour EC50 for Scenedesmus acutus is 0.51 mg/l. Effects on bees: contact acute 48 hour LD50 is 13.1 ҰМg/bee. Effects on earthworms: Acute 14 day LC50 is 960 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 78 (WHO, 1988; general review of dithiocarbamates). Plants Ethylenethiourea is the major metabolite in plants. Ethylenethiuram monosulfide and presumably ethylenethiuram disulfide and sulfur are also formed.
Usage: Zineb is introduced by Rohm & Haas Co. (now Dow AgroSciences), and by E. I. du Pont de Nemours and Co., (who no longer manufacture or market it). It is used to protect fruit and vegetable crops from a wide range of foliar and other diseases.
Application: Biochemistry Non-specific thiol reactant, inhibiting respiration. Mode of action Foliar fungicide with protective action. Uses Control of downy mildews in vines, hops, lettuce, onions, spinach, brassicas, oilseed rape, tobacco, and ornamentals; rusts in currants, berry fruit, plums, vegetables, and ornamentals (especially carnations and chrysanthemums); red fire disease on vines; potato and tomato blights; leaf spot diseases on currants, berry fruit, olives, and celery; anthracnose on beans, vines, and citrus fruit; scab on apples and pears; shot-hole on stone fruit; Cercospora on bananas; tulip fire; Botrytis; needle cast in forestry; etc. Phytotoxicity Non-phytotoxic, except for zinc-sensitive plants such as tobacco and cucurbits.
| 






