ACETOCHLOR
  ТТІЭ°· ТТІЭ°·
Introduction: Acetochlor is a chloroacetanilide herbicide used mainly pre-emergence or pre-planting to control annual grasses including feathertop chloris, goosegrass, sweet buffalo grass and crab grass; Certain broadleaf weeds including morning glory, marigold, pigweed and cocklebur; Yellow nutsedge in vegetables including cabbage, peas and onions; fruit including citrus, apples, pears, plums, apricots; coffee; corn; sugarbeet; sugarcane; potatoes.
Common name: Acetochlor
Another name: acetochlore, azetochlor, harness, nevirex, acenit, erunit, etc.
Chemical name: 2-chloro-N-ethoxymethyl-6'-ethylacet-o-toluidide
Empirical formula: C14H20ClNO2
Structural formula:
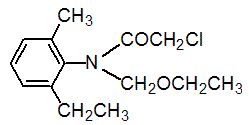
Mol. Weight: 269.77 g/mol
CAS No.: 34256-82-1
Specifications
Leading Acetochlor supplier
Acetochlor 500 g/L EC
Acetochlor 900 g/L EC
Acetochlor 90% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum ect.
SMALL PACKING
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized packing label
Acetochlor FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H350: May cause cancer.
H361: Suspected of damaging fertility or the unborn child.
H372: Causes damage to organs through prolonged or repeated exposure.
H373: Causes damage to organs through prolonged or repeated exposure.
H400: Very toxic to aquatic life.
H410: Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P201: Obtain special instructions before use.
P202: Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood.
P260: Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapors/spray.
P264: Wash ... thoroughly after handling.
P270: Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product.
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P281: Use personal protective equipment as required.
P308+P313: IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention.
P314: Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell.
P391: Collect spillage.
P405: Store locked up.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to ...
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rat: 1929 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rat: >2000 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rat: 3.99 a.i. mg/L. 4) Non- irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Non- irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Contact sensitisation reactions observed in guinea pigs. NOEL: (2 y) for rats is 11 mg/kg b.w. daily; (1 y) for dogs is 2 mg/kg b.w. daily.
ADI (JMPR): 0.01 mg/kg b.w./day [2015]
Classification:
Toxicity class WHO (a.i.): III (Slightly hazardous)
US EPA Classification (formulation): III (Caution - Slightly toxic)
EC Risk Classification: Xn - Harmful: R20, R43; Xi - Irritant: R37/38; N - Dangerous for the environment: R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: moderate toxicity to birds, acute LD50 for Bobwhites quail is 928 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: moderate toxicity to fish, acute 96 hour LC50 for Rainbow trout is 0.36 a.i.mg/L. Effect on aquatic invertebrates: moderate toxicity to aquatic invertebrates, acute 48 hour EC50 for Daphnia magna is 8.6 a.i.mg/L. Effect on algae: high toxicity to algae, acute 72 hour EC50 for Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata is 0.00027 a.i.mg/L. Effect on honeybees: low toxicity to honeybees, contact acute 48 hour LD50 is >200 a.i.ҰМg/bee, oral acute 48 hour LD50 is >100 a.i.ҰМg/bee. Effect on earthworms: moderate toxicity to earthworms, acute 14 day LC50 for Eisenia foetida is 105.5 a.i.mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Acetochlor's production may result in its release to the environment through various waste streams; its use as a herbicide will result in its direct release to the environment. If released to air, a vapor pressure of 1.67ЎБ10-7 mm Hg at 20 deg C indicates acetochlor will exist in both the vapor and particulate phases in the atmosphere. Vapor-phase acetochlor will be degraded in the atmosphere by reaction with photochemically-produced hydroxyl radicals; the half-life for this reaction in air is estimated to be 2.6 hours. Particulate-phase acetochlor will be removed from the atmosphere by wet or dry deposition. An aqueous solution of acetochlor irradiated for 24 hours in a quartz reactor resulted in a light spectrum of the arch at 311-437 nm with the most intensive emission at 360 nm; therefore acetochlor may be susceptible to direct photolysis by sunlight. If released to soil, acetochlor is expected to have high to moderate mobility based upon a Koc range of 98.5 to 335. Volatilization from moist soil surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon an estimated Henry's Law constant of 2.7ЎБ10-10 atm-cu m/mole. Acetochlor was degraded 8 to 15% in a sandy loam over the course of a 48 day incubation period, indicating that biodegradation is an important environmental fate process in soil. If released into water, acetochlor is not expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon the Koc range. The half-life of acetochlor in a sewage sludge was determined to be 17.2 hours, indicating that biodegradation may be an important environmental fate process in water. Volatilization from water surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon this compound's estimated Henry's Law constant. An estimated BCF of 250 suggests the potential for bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is high, provided the compound is not metabolized by the organism. Hydrolysis has been described as first-order with half-lives in river water of 1386, 2310 and 2310 days at pH 4, pH 7 and pH 10, respectively. Occupational exposure to acetochlor may occur through inhalation and dermal contact with this compound at workplaces where acetochlor is produced or used. Monitoring data indicate that the general population residing in the US Corn Belt may be exposed to acetochlor via dermal contact with contaminated water and rainfall. (SRC)
Usage: Herbicide discovered and introduced by Monsanto Co. Manufacturers: Dow AgroSciences; ÉMV; Monsanto; NitrokЁҰmia; Sharda; Sinon; Sundat. Inhibits cell division by blocking protein synthesis; more recent research suggests chloroacetamides may inhibit synthesis of very long chain fatty acids. Maize tolerance of chloroacetamides is due mainly to conjugation with glutathione; P450 metabolism may also be a factor.
Application: Selective herbicide, absorbed mainly by the shoots and secondarily by the roots of germinating plants. Used pre-emergence or pre-plant to control annual grasses, certain annual broad-leaved weeds and yellow nutsedge in maize (at 3 kg/ha), peanuts, soya beans, cotton, potatoes and sugar cane.
| 






