CHLORTHAL-DIMETHYL
  өРІЭЛчЈ¬ВИМӘЛб¶юјЧхҘ өРІЭЛчЈ¬ВИМӘЛб¶юјЧхҘ
Introduction: A residual benzoic acid herbicide for pre-emergent control of annual grasses and some annual broad-leaved weeds including barnyardgrass, bindweed, nightshade, chickweed, crabgrass, fat-hen, pigweed, redshank, fescue, stinging nettle, petty spurge, ryegrass, etc. in vegetables including brassicas, peas & beans, onions, carrots, turnips; strawberries; cotton; lucerne; ornamentals and lawns.
Common name: Chlorthal-dimethyl
Another name: dacthal, DIMETHYL TETRACHLOROTEREPHTHALATE, Dacthalor, Fatal, Chlorthal-methyl, Tetral, Tetrachloroterephthalic acid dimethyl ester
Dimethyl 2,3,5,6-tetrachloroterephthalate, DAC 4, Chlorthal dimethyl ester, Daktal [Czech], UNII-ZU3X5G2QLR, DCPA (VAN), Chlorthal dimethyl, Diformic Acid Chlorotitanate, Daktal, Chlorothal, Chlorothal-methyl
Chemical name: dimethyl tetrachloroterephthalate
Empirical formula: C8H6Cl4O4
Structural formula:
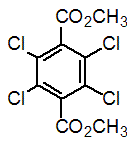
Mol. Weight: 331.96 g/mol
CAS No.: 1861-32-1
Specifications
Leading Chlorthal-dimethyl supplier
Chlorthal-dimethyl 90% WDG
Chlorthal-dimethyl 95% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Solid: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
SMALL PACKING
Solid: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Customerized packing label
Chlorthal-dimethyl FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H411 Toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P273 Avoid release to the environment.
P391 Collect spillage.
P501 Dispose of contents/ container to an approved waste disposal plant.
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rat: >5000 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rat: >2000 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rat: >4.48 a.i. mg/L. 4) Mild irritant to skin (rabbits). 5) slight irritant to eyes (rabbits). 6) Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). NOEL: (2 y) for mice is 142, rats is 1 mg/kg daily.
ADI: 0.01 mg/kg b.w. [Rat, Sf=100]
Classification:
Toxicity class WHO (a.i.): III (Slightly hazardous)
US EPA Classification (formulation): IV (Caution - Not acutely toxic)
EC Risk Classification: Xn - Harmful: R22; Xi - Irritant: R36/38
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: low toxicity to birds, acute oral LD50 for Bobwhites quail is >2250 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: moderate toxicity to fish, acute 96 hour LC50 for Rainbow trout is >4.7 a.i.mg/L. Effect on aquatic invertebrates: moderate toxicity to aquatic invertebrates, acute 48 hour EC50 for Daphnia magna is >4.6 a.i.mg/L. Effect on algae: low toxicity to algae, acute 72 hour EC50 for Scenedemus subspicatus is >10 a.i.mg/L. Effect on honeybees: low toxicity to honeybees, contact acute 48 hour LD50 is >100 a.i.ҰМg/bee; oral acute 48 hour LD50 is >100 a.i.ҰМg/bee. Effect on earthworms: moderate toxicity to earthworms, acute 14 day LC50 for Eisenia foetida is >500 a.i.mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Dimethyl tetrachloroterephthalate is released directly to the environment during its use as a pre-emergence herbicide for the control of annual grasses and some annual broad-leaved weeds. If released to the atmosphere, dimethyl tetrachloroterephthalate will exist in both the vapor phase and the particulate phase based on an experimental vapor pressure of 2.5ЎБ10-6 mm Hg. In the vapor phase, it should react slowly with hydroxyl radicals with an estimated half-life of 36 days. Particulate phase dimethyl tetrachloroterephthalate may be removed physically from air by wet and dry deposition. Dimethyl tetrachloroterephthalate is expected to be essentially immobile in soil based on an estimated Koc of 5900; it may bind strongly to organic matter or clay in the soil. This compound will biodegrade with products of monomethyl tetrachloroterephthalate and tetrachloroterephthalic acid. Half-lives ranging from 11 to 289 days depending on the soil temperature and moisture conditions (optimal conditions, 20-30 deg C, 0.2 kg H2O/kg soil) have been reported. Volatilization of dimethyl tetrachloroterephthalate from moist soil surfaces is also possible. During a 21 day period, 36-52% of the total measured dimethyl tetrachloroterephthalate loss from soil was accounted for by volatilization and 26% by breakdown in soil. Photodegradation on soil surfaces may occur with a half-life of 5 hours (reaction products include monomethyl tetrachloroterephthalate, tetrachloroterephthalic acid, and 1,2,4,5-tetrachlorobenzene). In water, dimethyl tetrachloroterephthalate should bind strongly to particulate matter and sediment in the water column based on an estimated Koc value of 5900. Biodegradation may occur based on evidence from several soil studies. Dimethyl tetrachloroterephthalate should bioconcentrate in aquatic organisms based on an estimated BCF value of 1300; this compound has been detected in fish at several locations. Exposure to dimethyl tetrachloroterephthalate by the general population is through the ingestion of leafy and root vegetables and fish, the drinking of well water, and, in some agricultural areas, by the inhalation of air. (SRC)
Usage: Herbicide reported by P. H. Schuldt et al. (Proc. Northeast. Weed Control Conf., 1960, p. 42). Chlorthal-dimethyl introduced by Diamond Alkali Co. (later ISK Biosciences Corp.). Patents: US 2923634. Manufacturers: Amvac. Microtubule assembly inhibition.
Application: Selective non-systemic herbicide, absorbed by the coleoptiles (grasses) and hypocotyls. Kills germinating seeds. Pre-emergence control of annual grasses and some annual broad-leaved weeds in onions, garlic, leeks, tomatoes, lettuce, cucurbits, capsicums, aubergines, brassicas, potatoes, sweet potatoes, horseradish, field beans, soya beans, cotton, strawberries, ornamentals, established turf, and other crops. Applied at 6.9-11.5 kg formulation/ha for sandy-sandy soil, 11.5 -16.1 kg formulation/ha for heavy silt loam. Phytotoxicity Phytotoxic to beet, spinach, flax, and trefoil.
|







