CINOSULFURON
  ГС»ЗВЎ ГС»ЗВЎ
Introduction: A triazinylsulfonylurea herbicide used for post-emergence control of many weeds including european water plaintain, annual sedge, aquatic ferns, pond weeds, parrowhead, duck potato, water hyacinth, etc. in Tropical & temporal rice crops field.
Common name: Cinosulfuron
Another name: UNII-53HYL452SB, etc.
Chemical name: 1-(4,6-dimethoxy-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)-3-[2-(2-methoxyethoxy)phenylsulfonyl]urea
Empirical formula: C15H19N5O7S
Structural formula:
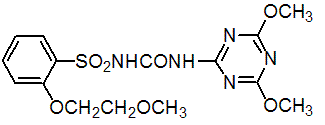
Mol. Weight: 413.4 g/mol
CAS No.: 94593-91-6
Specifications
Leading Cinosulfuron supplier
Cinosulfuron 20% WP
Cinosulfuron 92% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Solid: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
SMALL PACKING
Solid: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Customerized packing label
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
The substance does not meet the criteria for classification.
Precautionary statement(s)
Prevention.
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rat: >5000 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rat: >2000 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rat: 5.0 a.i. mg/L. 4) Non-irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Non-irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Non-sensitising to skin (guinea pigs). NOEL: (2 y) for rats is 400, mice is 60 ppm; (1 y) for dogs is 2500 ppm.
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: moderate toxicity to birds, acute oral LD50 for Japanese quail is 2000 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: moderate toxicity to fish, acute 96 hour LC50 for Rainbow trout is 100 a.i.mg/L. Effect on aquatic invertebrates: low toxicity to aquatic invertebrates, acute 48 hour EC50 for Daphnia magna is 2500 a.i.mg/L. Effect on algae: moderate toxicity to algae, acute 72 hour EC50 for Scenedemus subspicatus is 4.8 a.i.mg/L. Effect on honeybees: moderate toxicity to honeybees, oral acute 48 hour LD50 is 100 a.i.ҰМg/bee. Effect on earthworms: moderate toxicity to earthworms, acute 14 day LC50 for Eisenia foetida is 1000 a.i.mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals: Hydrolysis of methoxy groups and cleavage of the sulfonylurea bridge. It is rapidly excreted (80-100% within 24 h). Plants: In plants, rapid degradation by cleavage of the sulfonylurea bridge. Soil/Environment In soil, degrades (a) by O-dealkylation in both ring systems, forming the corresponding phenol, mono- and di- hydroxytriazine and (b) by cleavage of the sulfonylurea bridge; degradation proceeds further to form bound residues and CO2; DT50 in soil (lab.) c. 20 d, in paddy fields c. 3 d. No potential for bioaccumulation. Koc c. 20, indicating that cinosulfuron may leach; column data show however that rapid degradation prevents leaching. In paddy fields under natural conditions, cinosulfuron dissipates rapidly due to photolysis and, to a lesser extent, by adsorption to soil.
Usage: Herbicide reported by M. Quadranti et al. (Proc. 11th Conf. Asian Pacific Weed Sci. Soc., 1987, 1, 117). Introduced by Ciba-Geigy AG (now Syngenta AG). Patents: US 4479821; EP 44807. Manufacturers: Syngenta. Branched chain amino acid synthesis (ALS or AHAS) inhibitor. Acts by inhibiting biosynthesis of the essential amino acids valine and isoleucine, hence stopping cell division and plant growth. Selectivity derives from rapid metabolism in the crop. Metabolic basis of selectivity in sulfonylureas reviewed (M. K. Koeppe & H. M. Brown, Agro-Food-Industry, 6, 9-14 (1995)).
Application: Absorbed primarily by shoots and roots, and translocated to actively growing meristematic tissue. Applied post-emergence to control many weeds, including Alisma, annual Cyperus, Eleocharis, Marsilea, Potamogeton and Sagittaria spp., Monochoria vaginalis and Sphenoclea zeylanica in transplanted, direct seeded, wet-sown and water-sown, and dry-sown flooded rice crops, at 20-80 g/ha. Also used in tropical plantation crops. For full weed spectrum, may need to be combined with a grass herbicide in tank-mix or sequential treatment. Phytotoxicity No varietal restrictions for rice.
| 






