Imazaquin
    ЯдЯтаӯЯшЛб ЯдЯтаӯЯшЛб
Introduction: Imazaquin is a imidazole compound used as a selective, pre- and postemergence herbicide. It controls weeds by inhibiting the acetohydroxy acid synthase enzyme responsible for the production of valine, leucine and isoleucine. Activity is first seen in the growing points of susceptible plants where amino acid demands are greatest. The compound is used to control grasses and broadleaved weeds including cocklebur, pigweeds, prickly sida, nightshade, mustard, smartweed, ragweed, velvetleaf, jimsonweed, foxtails, seedling johnsongrass, lambsquarters, sicklepod, morningglory and others. Crops include soybeans, turf and ornamentals.
Common name: Imazaquin
Another name: Imazaquin acid; Scepter Herbicide; Caswell No. 003C; Imazaquin [BSI:ISO]; etc.
Chemical name: (R)-2[4-[(6-chloro-2-benzoxazolyl)oxy]-phenoxy]-propanoic acid
Empirical formula: C17H17N3O3
Structural formula:
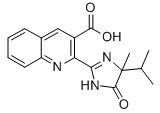
Mol. Weight: 311.34 g/mol
CAS No.: 81335-37-7
Specifications
Leading Imazaquin supplier
Imazaquin 98% TC
Imazaquin 75% WDG
Imazaquin 70% WDG
Imazaquin 15% SL
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Powder: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum etc.
SMALL PACKING
Powder: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized packing label
Imazaquin FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H312 (18.98%): Harmful in contact with skin.
H400 (81.02%): Very toxic to aquatic life.
H410 (81.02%): Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P280: Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection.
P302+P352: IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of water.
P312: Call a POISON CENTER or doctor/... if you feel unwell.
P322: Specific measures (see ...on this label).
363: Wash contaminated clothing before reuse.
P391: Collect spillage.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to an approved waste disposal plant.
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rats is >5000 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rats is >5000 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Acute inhalation toxicity LC50 (4 h) for rats is >5.7 a.i.mg/L. 4) Skin irritation: Non-irritating to slightly irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Eye irritation: Non-irritating to slightly irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Skin sensitization for guinea pig: Non-sensitizing.
NOEL: (18 m) for mice is 150 mg/kg/day. Other An Ames test for mutagenicity was negative.
ADI 0-0.25 mg/kg b.w.
Classification:
WHO Classification: U (Unlikely to present an acute hazard)
EC Risk Classification: Xn - Harmful: R22; N - Dangerous for the environment: R53
US EPA Classification (formulation): III (Caution - Slightly toxic)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: Acute oral LD50 for Mallard is >2150 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: Acute LC50 (96 h) for Rainbow trout is >100 a.i.mg/l. Effects on aquatic invertebrates: Acute EC50 (48 h) for Daphnia magna is >100 a.i.mg/l. Effects on algae: Acute 72 hour EC50 for Pseudokirchneriella subcaptitata is 21.5 a.i.mg/l. Effects on bees: contact acute 48 hour LD50 is >100 a.i.ҰМg/bee, oral acute 48 hour LD50 is >6.5 a.i.ҰМg/bee. Effects on earthworms: Acute 14 day LC50 is >23.5 a.i.mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Imazaquin is metabolically inert in rats. Following oral administration, almost all was excreted in the urine as the unchanged compound within 2 days. No accumulation in blood or tissues. Plants Rapidly metabolised by soya bean plants to inactive compounds, formed by opening of the imidazolinone ring at the ring amide. Soil/Environment Steadily degraded in soil by microbial activity and photolysis, but may remain active in the soil for several weeks to several months, depending on environmental conditions. DT50 60 d; Koc 20.
Usage: Imazaquin was introduced by American Cyanamid Co. (now BASF AG). It is used as pre- and post-emergence particularly for the control of grasses and broad-leaved weeds.
Application: Biochemistry Blocks biosynthesis of branched chain amino acids valine, leucine, and isoleucine through inhibition of acetohydroxy acid synthase, thus causing disruption of protein synthesis, which leads to interference in DNA synthesis and cell growth. Selectivity in soya beans is attributed to rapid detoxification via ring-opening. Mode of action Selective systemic herbicide, absorbed by the roots and foliage, with translocation in the xylem and phloem throughout the plant, and accumulation in the meristematic regions. Uses Pre-planting, pre-emergence or early post-emergence control of broad-leaved weeds in soya beans, at 70-140 g a.e./ha. Also controls or reduces competition from grasses and sedges.
| 






