Imazethapyr
    ЯдІЭСМ ЯдІЭСМ
Introduction: Imazethapyr is an imidazole compound used as a selective herbicide. It is applied preplant incorporated, preemergence, at cracking, and postemergence. The compound controls weeds by reducing the levels of three branched-chain aliphatic amino acids, isoleucine, leucine and valine, through the inhibition of aceto- hydroxyacid synthase, an enzyme common to the biosynthetic pathway for these amino acids. This inhibition causes a disruption in protein synthesis which, in turn, leads to an interference in DNA synthesis and cell growth. The compound is used to control grasses and broadleaved weeds including barnyardgrass, crabgrass, cocklebur, panicums, pigweeds, nightshade, mustard, smartweed, velvetleaf, jimsonweed, foxtails, seedling johnsongrass, lambsquarters, morningglory and others. Tolerant crops include soybeans, peanuts, dry and edible beans, peas, alfalfa and imidazolinone resistant/tolerant corn. Additional research is being conducted on other leguminous crops.
Common name: Imazethapyr
Another name: Pursuit; 5-ethyl-2-(4-isopropyl-4-methyl-5-oxo-4,5-dihydro- 1H-imidazol-2-yl)nicotinic acid; Pivot; Imazethapyr [ANSI:BSI:ISO]; etc.
Chemical name: 5-ethyl-2-[(RS)-4-isopropyl-4-methyl-5-oxo-2-imidazolin-2-yl]nicotinic acid
Empirical formula: C15H19N3O3
Structural formula:
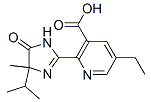
Mol. Weight: 289.33 g/mol
CAS No.: 81335-77-5
Specifications
Leading Imazethapyr supplier
Imazethapyr 97% TC
Imazethapyr 70% WP
Imazethapyr 10% SL
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Powder: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum etc.
SMALL PACKING
Powder: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized packing label
Imazethapyr FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H400 (100%): Very toxic to aquatic life.
H410 (100%): Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P391: Collect spillage.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to an approved waste disposal plant.
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rats is >5000 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rats is >2000 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Acute inhalation toxicity LC50 (4 h) for rats is 3.27 a.i.mg/L. 4) Skin irritation: Slightly irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Eye irritation: Slightly irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Skin sensitization for guinea pig: Non-sensitizing.
NOEL: (2 y) for rats is 500 mg/kg/day; (18 m) for mice is 750 mg/kg/day; (1 y) for dogs is 25 mg/kg/day. Other Non-mutagenic in the Ames test.
ADI 0-0.44 mg/kg b.w.
Classification:
WHO Classification: U (Unlikely to present an acute hazard)
EC Risk Classification: Xn - Harmful: R21/22; Xi - Irritant: R36/38; N - Dangerous for the environment: R52
US EPA Classification (formulation): III (Caution - Slightly toxic)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: Acute oral LD50 for Mallard is 2150 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: Acute LC50 (96 h) for Rainbow trout is 340 a.i.mg/l. Effects on aquatic invertebrates: Acute EC50 (48 h) for Daphnia magna is 1000 a.i.mg/l. Effects on algae: Acute 72 hour EC50 for Raphidocelis subcapitata is 71 a.i.mg/l. Effects on bees: contact acute 48 hour LD50 is >100 a.i.ҰМg/bee, oral acute 48 hour LD50 is >24.6 a.i.ҰМg/bee. Effects on earthworms: Acute 14 day LC50 is 10000 a.i.mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In rats, following oral administration, 95% was excreted in urine and faeces within 48 hrs. Residue levels in blood, liver, kidney, muscle, and fat tissues were <0.01 ppm after 48 hours. Plants Rapidly metabolised in non-susceptible plants, soya beans, maize, alfalfa. The primary metabolic route in all crops tested is oxidative hydroxylation at the a-carbon atom of the ethyl substituent on the pyridine ring. Soil/Environment DT50 lab. (aerobic, 20Ўж) 158 d. Photolytic degradation DT50 (pH7, 22-24Ўж) 2.1 d.
Usage: Imazethapyr was introduced by American Cyanamid Co. (now BASF AG). It is a herbicide used to control a variety of broad-leaved weeds and grasses in numerous crops.
Application: Biochemistry Branched chain amino acid synthesis (ALS or AHAS) inhibitor. Hence reduces levels of valine, leucine and isoleucine, leading to disruption of protein and DNA synthesis. Selectivity in soya benas and peanuts is attributed to rapid detoxification via hydroxylation and glycosylation. Mode of action Systemic herbicide, absorbed by the roots and foliage, with translocation in the xylem and phloem, and accumulation in the meristematic regions. Uses Control of many major annual and perennial grass and broad-leaved weeds in most major crops, at 2-4 oz/a. Applied pre-plant incorporated, pre-emergence, or post-emergence. Phytotoxicity Non-phytotoxic to soya beans and other leguminous crops, when used as directed.
| 






