PENDIMETHALIN
    ¶юјЧОмАЦБй ¶юјЧОмАЦБй
Introduction: A herbicide used to control most annual grasses including barnyardgrass, goosegrass, crab grass, signal grass and common buffalo grass; annual broad-leaved weeds including pigweed, goosefoot and purslane in wheat & other small grain cereals; corn; soybeans; maize; fruit; vegetables including beans & peas, carrots; turf & lawns; potatoes; vineyards; peanuts.
Common name: Pendimethalin
Another name: Penoxaline, Prowl, Herbadox, Penoxalin, Phenoxalin, Accotab, Stomp, Way Up, Penoxyn, Sipaxol, Go-Go-San, Tendimethalin, Pendimax, Acumen, Most Micro, etc.
Chemical name: N-(1-ethylpropyl)-2,6-dinitro-3,4-xylidine
Empirical formula: C13H19N3O4
Structural formula:
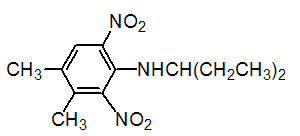
Mol. Weight: 281.31 g/mol
CAS No.: 40487-42-1
Specifications
Leading Pendimethalin supplier
Pendimethalin 330 g/L EC
Pendimethalin 40% EC
Pendimethalin 500 g/L EC
Pendimethalin 95% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Solid: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum ect.
SMALL PACKING
Solid: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized packing label
Pendimethalin FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H317: May cause an allergic skin reaction.
H400: Very toxic to aquatic life.
H410: Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P261: Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapors/spray.
P272: Contaminated work clothing should not be allowed out of the workplace.
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P280: Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection.
P302+P352: IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of water.
P321: Specific treatment (see ... on this label).
P333+P313: IF SKIN irritation or rash occurs: Get medical advice/attention.
P363: Wash contaminated clothing before reuse.
P391: Collect spillage.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to ...
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for mouse: 4665 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rat: >5000 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rat: >6.73 a.i.mg/L. 4) Non-irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Non-irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs).
NOEL: In 2 y feeding trials, rats receiving 100 mg/kg diet showed no ill-effects.
ADI(JMPR): 0.1 mg/kg b.w. [2016]
Classification:
Toxicity class WHO (a.i.): II (Moderately hazardous)
US EPA Classification (formulation): III (Caution - Slightly toxic)
EC Risk Classification: Xn - Harmful: R43; N - Dangerous for the environment: R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: moderate toxicity to birds, acute oral LD50 for Mallard ducks is 1421 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: moderate toxicity to fish, acute 96 hour LC50 for Rainbow trout is 0.196 a.i.mg/L. Effect on aquatic invertebrates: moderate toxicity to aquatic invertebrates, acute 48 hour EC50 for Daphnia magna is 0.147 a.i.mg/L. Effect on algae: high toxicity to algae, acute 72 hour EC50 for Selenastrum capricornutum is 0.004 a.i.mg/L. Effect on honeybees: low-moderate toxicity to honeybees, contact acute 48 hour LD50 is 100 a.i.ҰМg/bee, oral acute 48 hour LD50 is >101.2 a.i.ҰМg/bee. Effect on earthworms: low toxicity to earthworms, acute 14 day LC50 for Eisenia foetida is >1000 a.i.mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Pendimethalin's production may result in its release to the environment through various waste streams; its use as an herbicide to control annual grasses and broadleaf weeds on a variety of grains, cotton and other crops will result in its direct release to the environment. If released to air, a vapor pressure of 9.4ЎБ10-6 mm Hg at 25 deg C indicates pendimethalin will exist in both the vapor and particulate phases in the atmosphere. Vapor-phase pendimethalin will be degraded in the atmosphere by reaction with photochemically-produced hydroxyl radicals; the half-life for this reaction in air is estimated to be 13 hours. Particulate-phase pendimethalin will be removed from the atmosphere by wet or dry deposition. Pendimethalin absorbs UV radiation at wavelengths >290 nm and therefore may be susceptible to direct photolysis by sunlight. If released to soil, pendimethalin is expected to have no mobility based upon Koc values ranging from 6,500 to 43,863. Volatilization from moist soil surfaces is expected to be an important fate process based upon a Henry's Law constant of 8.56ЎБ10-7 atm-cu m/mole. However, adsorption to soil is expected to attenuate volatilization. Pendimethalin is not expected to volatilize from dry soil surfaces based upon its vapor pressure. Biodegradation rates may be attenuated by the strong adsorption to soil with difficult desorption from the soil resulting in no bioavailablity. A soil half-life of 3-4 months has been reported indicating that biodegradation is not an important environmental fate process in soil. If released into water, pendimethalin is expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon the Koc. Using water from two nursery recycling ponds, pendimethalin exhibited first-order half-lives of 26.9 to 37.4 days at 10 deg C and 16.4 to 29.1 days at 22 deg C in non-sterile water, indicating that biodegradation may be an important environmental fate process in water. Volatilization from water surfaces is expected to be an important fate process based upon this compound's Henry's Law constant. Estimated volatilization half-lives for a model river and model lake are 72 and 530 days, respectively. However, volatilization from water surfaces is expected to be attenuated by adsorption to suspended solids and sediment in the water column. A measured BCF of 5,100 suggests bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is very high. Hydrolysis is not expected to be an important environmental fate process since this compound lacks functional groups that hydrolyze under environmental conditions.
Usage: Herbicide reported by P. L. Sprankle (Proc. Br. Weed Control Conf., 12th, 1974, 2, 825). Introduced by American Cyanamid Co. (now BASF AG). Patents: BE 816837; US 4199669. Manufacturers: BASF; Feinchemie Schwebda; Rallis; Sundat. Biochemistry: Microtubule assembly inhibition.
Application: Selective herbicide, absorbed by the roots and leaves. Affected plants die shortly after germination or following emergence from the soil. Control of most annual grasses and many annual broad-leaved weeds, at 0.6-2.4 kg/ha, in cereals, onions, leeks, garlic, fennel, maize, sorghum, rice, soya beans, peanuts, brassicas, carrots, celery, black salsify, peas, field beans, lupins, evening primrose, tulips, potatoes, cotton, hops, pome fruit, stone fruit, berry fruit (including strawberries), citrus fruit, lettuce, aubergines, capsicums, established turf, and in transplanted tomatoes, sunflowers, and tobacco. Applied pre-plant incorporated, pre-emergence, pre-transplanting, or early post-emergence. Also used for control of suckers in tobacco. Phytotoxicity Injury to maize may occur if used as a pre-plant, soil-incorporated treatment.
| 






