Picloram
  ¶ҫЭ¬¶Ё ¶ҫЭ¬¶Ё
Introduction: Picloram, in the pyridine family of compounds, is a systemic herbicide used for general woody plant control. It also controls a wide range of broad- leaved weeds excepting mustards (crucifers). Most grasses are resistant to picloram so it is used in range management programs. Picloram is formulated either as an acid (technical product) or as a potassium salt. The materials in this document refer to the acid form unless otherwise indicated.
Common name: Picloram
Another name: 4-Amino-3,5,6-trichloropyridine-2-carboxylic acid; 4-Amino-3,5,6- trichloropicolinic acid; Tordon; Borolin; etc.
Chemical name: 4-amino-3,5,6-trichloropyridine-2-carboxylic acid
Empirical formula: C6H3Cl3N2O2
Structural formula:
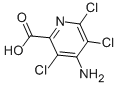
Mol. Weight: 241.46 g/mol
CAS No.: 1918-02-1
Specifications
Leading Picloram supplier
Picloram 92% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Powder: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum etc.
SMALL PACKING
Powder: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized packing label
Picloram FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H319 (21.49%): Causes serious eye irritation.
H400 (39.67%): Very toxic to aquatic life.
H410 (41.32%): Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
H412 (38.84%): Harmful to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P264: Wash ... thoroughly after handling.
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P280: Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection.
P305+P351+P338: IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses if present and easy to do - continue rinsing.
P337+P313: IF eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/attention.
P391: Collect spillage.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to an approved waste disposal plant.
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rats is 4012 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rats is >2000 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Acute inhalation toxicity LC50 (4 h) for rats is >0.035 a.i.mg/L. 4) Skin irritation: Non-irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Eye irritation: Slightly irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Skin sensitization for guinea pig: Non-sensitizing.
NOEL: (2 y) for rats is 20 mg/kg/day. Other Not mutagenic.
ADI 0-0.3 mg/kg b.w.
Classification:
WHO Classification: U (Unlikely to present an acute hazard)
EC Risk Classification: N - Dangerous for the environment: R51, R53
US EPA Classification (formulation): I (Danger - Highly toxic)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: Acute oral LD50 for Mallard is >1944 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: Acute LC50 (96 h) for Rainbow trout is 8.8 a.i.mg/l. Effects on aquatic invertebrates: Acute EC50 (48 h) for Daphnia magna is 44.2 a.i.mg/l. Effects on algae: Acute 72 hour EC50 for Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata is 60.2 a.i.mg/l. Effects on bees: contact acute 48 hour LD50 is >100 a.i.ҰМg/bee, oral acute 48 hour LD50 is >74 a.i.ҰМg/bee. Effects on earthworms: Acute 14 day LC50 is >4475 a.i.mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
In heavy clay soil, picloram has a half life of slightly over two months. However, when more organic material is present, the half life of the compound nearly doubles. Breakdown by soil microorganisms occurs slowly, resulting in the formation of carbon dioxide (CO2) and the release of a chloride ion. The compound is mobile and relatively persistent in soil and can therefore leach to groundwater. Picloram has been detected in the groundwater of seven states. In water, the action of sunlight is an important mechanism leading to the breakdown of the product. Herbicide levels in farm ponds which were 1 ppm at the time of spraying reached 10 ppb in 100 days primarily due to dilution and the action of sunlight. The movement of picloram in runoff after heavy rainfall may occur. Picloram is readily absorbed by plant roots, less so by the foliage, and is readily translocated throughout plants. It remains stable and intact in plants.
Usage: Picloram was introduced by Dow Chemical. It is a persistent herbicide for the control of broad-leaved weeds on non-crop and utility areas.
Application: Mode of action Selective, systemic absorbed by roots and leaves and translocated. Synthetic auxin. Uses Picloram is a systemic herbicide used for general woody plant control. It also controls a wide range of broad-leaved weeds and undesirable brush.
| 






