4-CPA
  ¶ФВИұҪСхТТЛб ¶ФВИұҪСхТТЛб
Introduction: Like plant growth regulator, 4-CPA is absorbed by plant via root, stem,leaf, bloom and fruit. 4-CPA is used to prevent abscission of bloom and fruit, inhibit rooting of beans,promote fruit set, induce formation of seedless fruit. 4-CPA is also used for ripening and fruit thinning. At high dosage, 4-CPA also has herbicidal effect.
Common name: 4-CPA
Another name: 4-CHLOROPHENOXYACETIC ACID, Sure-Set, Tomatotone, Tomato Fix, Tomato hold, Marks 4-cpa, etc.
Chemical name: 2-(4-chlorophenoxy)acetic acid
Empirical formula: C8H7ClO3
Structural formula:
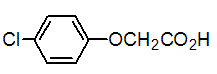
Mol. Weight: 186.59 g/mol
CAS No.: 122-88-3
Specifications
Leading 4-CPA supplier
4-CPA 98% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Solid: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
SMALL PACKING
Solid: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Customerized packing label
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H302: Harmful if swallowed.
Precautionary statement(s)
P264: Wash ... thoroughly after handling.
P270: Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product.
P301+P312: IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER/doctor/... IF you feel unwell.
P330: Rinse mouth.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to ...
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rat: 2200 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rat: >2000 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rat: 10.6 a.i.mg/L. 4) Irritation to eye (rabbits). 5) No Irritation to skin (rabbits). 6) Skin sensitiser: not applicable.
No ingredient of this product present at levels greater than or equal to 0.1% is identified as probable, possible or confirmed human carcinogen by IARC.
ADI: 0.022 mg/kg b.w./day.
Classification:
Toxicity class WHO (a.i.): III (Slightly hazardous)
US EPA Classification (formulation): III (Caution - Slightly toxic)
EC Risk Classification: Xn; R22
ECOTOXICOLOGY
LC50 for Lepomis macrochirus (Bluegill) is >180 ppm/96 hr; static/diethanolamine salt; 2% AI formulated product. LD50 for Salmo trutta (Sea trout) is 147 mg/L/24 hr /Conditions of bioassay not specified.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
4-Chlorophenoxyacetic acid's production may result in its release to the environment through various waste streams; it's use as a plant growth regulator and as an aid in setting fruit will result in its direct release to the environment. If released to air, an estimated vapor pressure of 3.2ЎБ10-4 mm Hg at 25 deg C indicates 4-chlorophenoxyacetic acid will exist solely as a vapor in the ambient atmosphere. Vapor-phase 4-chlorophenoxyacetic acid will be degraded in the atmosphere by reaction with photochemically-produced hydroxyl radicals; the half-life for this reaction in air is estimated to be 35 hours. 4-Chlorophenoxyacetic acid was degraded 30% upon exposure to natural sunlight over the course of 24 hours, suggesting photodegradation in air is an important environmental fate process. If released to soil, 4-chlorophenoxyacetic acid is expected to have very high mobility based upon an estimated Koc of 18. The pKa of 4-chlorophenoxyacetic acid is 3.56, which indicates it will exist primarily as an anion under environmental conditions. Volatilization from moist soil surfaces will not be an important fate process because anions do not volatilize. 4-Chlorophenoxyacetic acid is not expected to volatilize from dry soil surfaces based upon its estimated vapor pressure. The half-life of 4-chlorophenoxyacetic acid in a clay loam soil under field conditions was 20 days. If released into water, 4-chlorophenoxyacetic acid is not expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon the estimated Koc value. Volatilization will not be an important fate process in water since anions do not volatilize. 4-Chlorophenoxyacetic acid is resistant to aqueous environmental hydrolysis; however, photolysis in sunlit surface waters may be an important fate process since it absorbs light greater than 290 nm. An estimated BCF of 3 suggests the potential for bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is low.
Usage: Plant growth regulator introduced by Dow Chemical Co. (now Dow AgroSciences). Manufacturers: Ishihara Sangyo.
Application: To improve fruit setting on tomato (by spraying the flowers, at 15-30 ppm) and inhibit sprout formation in mung beans. Also used for fruit thinning in peaches.
| 






