Thiabendazole
    азҫъБй азҫъБй
Introduction: Thiabendazole is a systemic benzimidazole fungicide used to control fruit and vegetable diseases such as mold, rot, blight and stain. It is also active against storage diseases and Dutch Elm disease. In livestock, thiabendazole is also applied to treat roundworms. Thiabendazole is also used medicinally as a chelating agent to bind metals.
Common name: Thiabendazole
Another name: Mintezol; Equizole; Tiabendazol; Mintesol; Omnizole; Thibenzole; Thiabendazol; Bovizole; Minzolum; Thiabenzole; Thibenzol; 2-(4-Thiazolyl) benzimidazole; Testo; Lombristop; Bioguard; Eprofil; Mertect; etc.
Chemical name: 2-(thiazol-4-yl)benzimidazole
Empirical formula: C10H7N3S
Structural formula:
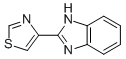
Mol. Weight: 201.25 g/mol
CAS No.: 148-79-8
Specifications
Leading Thiabendazole supplier
Thiabendazole 98% TC
Thiabendazole 50% SC
Thiabendazole 45% SC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Powder: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum etc.
SMALL PACKING
Powder: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized packing label
Thiabendazole FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H400 (99.71%): Very toxic to aquatic life.
H410 (99.71%): Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P391: Collect spillage.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to an approved waste disposal plant.
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rats is >5000 mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rats is >5000 mg/kg. 3) Acute inhalation toxicity LC50 (4 h) for rats is >0.53 mg/L. 4) Skin irritation: Non-irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Eye irritation: Non-irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Skin sensitization for guinea pig: Not a skin sensitizer.
NOEL: (2 y) for rats is 10 mg/kg/day; (1 y) for dogs is 10 mg/kg/day. Other Not carcinogenic. Not genotoxic.
ADI (JMPR) 0-0.2 mg/kg b.w. [2005]
Classification:
WHO Classification: III (Slightly hazardous)
EC Risk Classification: N - Dangerous for the environment: R50, R53
US EPA Classification (formulation): III (Caution - Slightly toxic)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: Acute oral LD50 for Bobwhite quail is >2250 mg/kg. Effect on fish: Acute LC50 (96 h) for Rainbow trout is 0.55 mg/l. Effects on aquatic invertebrates: Acute EC50 (48 h) for Daphnia magna is 0.81 mg/l. Effects on algae: Acute 72 hour EC50 for Raphidocelis subcapitata is 9.0 mg/l. Effects on bees: contact acute 48 hour LD50 is >34 ҰМg/bee, oral acute 48 hour LD50 is >4.0 ҰМg/bee. Effects on earthworms: Acute 14 day LC50 is >1000 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals When administered orally, thiabendazole is rapidly absorbed; up to 90% of the total dose is eliminated (about 65% in urine and 25% in faeces) within 24 h, in both sexes. The compound is rapidly distributed to tissues, with highest levels found in the heart, lungs, spleen, kidneys, and liver. The compound is essentially completely cleared from the body within 7 days in both dose groups. Thiabendazole undergoes hydroxylation at the 5-position. Plants The residue on all crops treated pre- or post-harvest is parent thiabendazole. Soil/Environment Soil DT50 >1 y (1 mg/kg, harsh conditions), 33 d (20 ЎгC, 40% MWC, 0.1 mg/kg soil), 120 d (20 ЎгC, 40% MWC, 1 mg/kg soil). Aqueous photolysis DT50 29 h (pH 5).
Usage: Thiabendazole was introduced by Merck & Co.. It is a mainly post-harvest fungicide used to control a wide range of diseases for fruit and other crops.
Application: Biochemistry Inhibits mitosis by binding to tubuline and thus severely impairs fungal growth and development Mode of action Systemic fungicide with protective and curative action. Thiabendazole forms a protective deposit on the treated surface of fruit and tubers. Uses As a mainly post-harvest fungicide for the control of Aspergillus, Botrytis, Ceratocystis, Cercospora, Cladosporium, Colletotrichum, Corticium, Diaporthe, Diplodia, Fusarium, Gibberella, Gloeosporium, Oospora, Penicillium, Phoma, Podosphaera leucotricha, Rhizoctonia, Sclerotinia, Septoria, Thielaviopsis, Venturia inaequalis, Verticillium spp., etc., in avocados (2 g/l), bananas (0.2-0.4 g/l), chicory, citrus fruit (2.2 g/l), mangoes (2 g/l), mushrooms, ornamentals, pome fruit (1.1 g/l) and potatoes (30 g/ton). Also used for seed treatment and stem injection application.
| 






