IMAZAMOX
    јЧСхЯдІЭСМ јЧСхЯдІЭСМ
Introduction: A post-emergence herbicide used to control weeds including grass and broadleaf weeds, common reed (phragmites australis), flowering rush (butomus umbellatus), curly-leaf pond weed (potamogeton crispus) in aquatic situations; edible legumes; soybeans; alfalfa; sunflowers; winter osr.
Common name: Imazamox
Another name: Pulsar, Raptor, Imazamox [ISO], Raptor (herbicide), (+-)-Imazamox, HSDB 7013, AC 299263, CL 299263, etc.
Chemical name: 2-[(RS)-4-isopropyl-4-methyl-5-oxo-2-imidazolin-2-yl]-5-methoxymethylnicotinic acid
Empirical formula: C15H19N3O4
Structural formula:
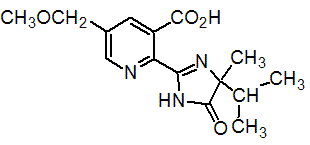
Mol. Weight: 305.34 g/mol
CAS No.: 114311-32-9
Specifications
Leading Imazamox supplier
Imazamox 25 g/L SC
Imazamox 40 g/L AS
Imazamox 97% TC
Imazamox 98% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Solid: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum ect.
SMALL PACKING
Solid: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized packing label
Imazamox FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H400 (100%): Very toxic to aquatic life.
H410 (100%): Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P391: Collect spillage.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to ...
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rat: >5000 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rat: >4000 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rat: >6.3 a.i.mg/L. 4) Slight skin irritant (rabbits). 5) Moderate eye irritant (rabbits). 6) Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs).
NOEL: (1 y) for dogs is 1165 mg/kg b.w. daily. Negative in Ames, micronucleus aberration and CHO/HGPRT tests.
ADI(JMPR): 3 mg/kg b.w. [2014]
Classification:
EC Risk Classification: N - Dangerous for the environment: R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: moderate toxicity to birds, acute oral LD50 for Bobwhite quail is >1846 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: low toxicity to fish, acute 96 hour LC50 for Rainbow trout is >122 a.i.mg/L. Effect on aquatic invertebrates: low toxicity to aquatic invertebrates, acute 48 hour EC50 for Daphnia magna is >100 a.i.mg/L. Effect on algae: low toxicity to algae, acute 72 hour EC50 for Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata is >29.1 a.i.mg/L. Effect on honeybees: moderate toxicity to honeybees, contact acute 48 hour LD50 is >58 a.i.ҰМg/bee, oral acute 48 hour LD50 is >40 a.i.ҰМg/bee. Effect on earthworms: moderate toxicity to earthworms, acute 14 day LC50 for Eisenia foetida is >901 a.i.mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Imazamox's production may result in its release to the environment through various waste streams; it's use as a herbicide will result in its direct release to the environment. If released to air, a vapor pressure of less than 1.0ЎБ10-7 mm Hg at 20 deg C indicates imazamox will exist solely in the particulate phase in the ambient atmosphere. Particulate-phase imazamox will be removed from the atmosphere by wet and dry deposition. If released to soil, imazamox is expected to have very limited leaching based on field studies and remain in the top 30 cm (12 inches) of soil. Volatilization from moist soil surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon an estimated Henry's Law constant of 9.15ЎБ10-19 atm-cu m/mole. Imazamox is primarily degraded by microbes in soil. Field dissipation half-lives range from 15 to 130 days with typical representative half-lives of 20 to 50 days. If released into water, some adsorption to suspended solids and sediment may occur. Volatilization from water surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon this compound's estimated Henry's Law constant. An estimated BCF of 3.16 suggests the potential for bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is low. Photodegradation in shallow water can occur (surface half-life of about 7 hours). Aqueous hydrolysis is not expected to be an important environmental fate process. Occupational exposure to imazamox may occur through inhalation of dust and dermal contact with this compound at workplaces where imazamox is produced or used. (SRC)
Usage: EUP first granted in 1995; US unconditional registration in 2001. Manufacturers: BASF. Biochemistry: Branched chain amino acid synthesis (ALS or AHAS) inhibitor. Selectivity in soya beans and peanuts is attributed to rapid detoxification via demethylation and glycosylation (B. Tecle et al., Proc. 1997 Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Weeds, 2,605).
Application: Post-emergence herbicide, absorbed through both foliage and roots and translocated to growing points. Plants wilt and turn brown. For post-emergence weed control in soya beans and other legumes grown in rotation with sugar beet and other crops where more persistent imidazolinones are not suited and in crops tolerant to imazamox, such as 'Clearfield' wheat, rape and sunflowers. Application rates 0.032-0.05 lb/a.
| 






