Oxadiargyl
    ұыИІ¶сІЭНӘ ұыИІ¶сІЭНӘ
Introduction: Oxadiargyl acts as protoporphyrinogen IX oxidase inhibitor. It is pre-emergence and early post-emergence herbicide active on broad-leaved weeds (Amaranthus, Bidens, Chenopodium, Malva, Monochoria, Polygonum, Portulaca, Potamogeton, Raphanus, Solanum, Sonchus, Rotala), grasses (Echinochloa, Leptochloa, Brachiaria, Cenchrus, Digitaria, Eleusine, Panicum and wild rice) and annual sedges, in rice, upland crops (sunflower, potato, vegetables and sugar cane) and perennial crops (fruit trees and citrus).
Common name: Oxadiargyl
Another name: Topstar; 5-(tert-Butyl)-3-(2,4-dichloro-5-(prop-2-yn-1-yloxy)phenyl) -1,3,4-oxadiazol-2(3H)-one; RP 020630; EINECS 254-637-6; etc.
Chemical name: 5-tert-butyl-3-[2,4-dichloro-5-(prop-2-ynyloxy)phenyl]-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2(3H)-one
Empirical formula: C15H14Cl2N2O3
Structural formula:
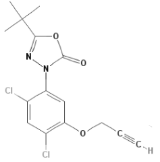
Mol. Weight: 341.2 g/mol
CAS No.: 39807-15-3
Specifications
Leading Oxadiargyl supplier
Oxadiargyl 96% TC
Oxadiargyl 80% WDG&WP
Oxadiargyl 10% OD
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Powder: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum etc.
SMALL PACKING
Powder: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized packing label
Oxadiargyl FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H360 (100%): May damage fertility or the unborn child.
H373 (100%): Causes damage to organs through prolonged or repeated exposure.
H400 (100%): Very toxic to aquatic life.
H410 (100%): Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P201: Obtain special instructions before use.
P202: Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood.
P260: Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapors/spray.
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P281: Use personal protective equipment as required.
P308+P313: IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention.
P314: Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell.
P391: Collect spillage.
P405: Store locked up.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to.
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rats is >802 mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rats is >2000 mg/kg. 3) Acute inhalation toxicity LC50 (4 h) for rats is 5.16 mg/L. 4) Skin irritation: Non-irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Eye irritation: Slightly irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Skin sensitization for guinea pig: Non-sensitizer.
NOEL: (2 y) for rats 0.8 mg/kg/day; (1 y) for dogs 1 mg/kg/day. Other Not carcinogenic. Not genotoxic.
ADI 0-0.008 mg/kg b.w.
Classification:
WHO Classification: NL (Not listed)
EC Risk Classification: Reproduction risk category 3: R63; Xn - Harmful: R48/22; N - Dangerous for the environment: R50, R53
US EPA Classification (formulation): No consensus across products or no products available.
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: Acute oral LD50 (8 d) for Bobwhite quail is >2000 mg/kg. Effect on fish: Acute LC50 (96 h) for Rainbow trout is >0.201 mg/l. Effects on aquatic invertebrates: Acute EC50 (48 h) for Daphnia magna is >0.352 mg/l. Effects on algae: Acute 72 hour EC50 for Scenedesmus subspicatus is 0.001 mg/l. Effects on bees: oral acute 48 hour LD50 is >200 ҰМg/bee. Effects on earthworms: Acute 14 day LC50 is >1000 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Studies on goats and hens demonstrated that oxadiargyl is rapidly excreted; there is no evidence of accumulation in milk, eggs or edible tissues. Plants Studies on lemons, sunflowers and rice demonstrated very low levels of residues at harvest, mainly parent compound (C. R. Leake et al., Proc. 9th IUPAC Int. Congr. Pestic. Chem., London, 1998, 2, 5A-021). Soil/Environment DT50 (lab., aerobic) 18-72 d (20-30 ЎгC), forming two major metabolites (one of which is herbicidal) which are, in turn, steadily degraded, resulting in mineralisation to CO2 and a soil-bound residue. Oxadiargyl dissipates rapidly from water into the sediment phase and is readily degraded under anaerobic conditions. Strongly adsorbed to soil (Koc 1000-3000); oxadiargyl and its two major soil metabolites show low mobility in 4 soil types and are unlikely to leach. Field results were consistent: DT50 9-25 d, mean DT90 90 d; for oxadiargyl and its two major metabolites, DT50 was 9-31 d, DT90 65-234 d; >95% of oxadiargyl residues remained in the top 10 cm of soil, and no residues were found below 30 cm.
Usage: Oxadiargyl was developed by Bayer CropScience. It is a pre-emergence oxadiazolone herbicide for grass and broad-leaved weed control.
Application: Biochemistry Protoporphyrinogen IX oxidase inhibitor. Mode of action Selective herbicide, active mainly pre-emergence; effects begin at germination. It is not absorbed by the plant. Efficacy is not dependent on soil texture and type. Uses Pre-emergence and early post-emergence herbicide active on broad-leaved weeds (Amaranthus, Bidens, Chenopodium, Malva, Monochoria, Polygonum, Portulaca, Potamogeton, Raphanus, Solanum, Sonchus, Rotala), grasses (Echinochloa, Leptochloa, Brachiaria, Cenchrus, Digitaria, Eleusine, Panicum and wild rice) and annual sedges, in rice (at 50-150 g/ha), upland crops (sunflower, potato, vegetables and sugar cane, at 300-500 g/ha) and perennial crops (fruit trees and citrus, at 500-1500 g/ha).
| 






