Bromadiolone
    деөРВЎ деөРВЎ
Introduction: Bromadiolone is an anti-coagulant coumarin-derivative rodenticide mainly used for indoor applications such as houses, commercial buildings or industrial sites to control of rats and mice.
Common name: Bromadiolone
Another name: Broprodifacoum, Bromadiolon, Bromatrol, Maki, Bromone, Contrac, Contrac, Boldo, Temus, Sup'operats, Super-rozol, Boot hill, Super-caid, Bromore, Contrax, Topidion, Eradic, Rafix, Super-Cald, Broprodifacoum [South Africa].
Chemical name: 3-[3-[4-(4-Bromophenyl)phenyl]-3-hydroxy-1-phenylpropyl]-2-hydroxychromen-4-one
Empirical formula: C30H23BrO4
Structural formula:
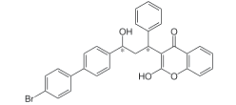
Mol. Weight: 527.41 g/mol
CAS No.: 28772-56-7
Specifications
Leading Bromadiolone supplier
Bromadiolone 0.25% TK
Bromadiolone 0.005% GR
Bromadiolone 98% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Powder: 25KG/Bag, 25KG/Drum, 50KG/Drum etc.
SMALL PACKING
Powder: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Customerized Packing label
Bromadiolone FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H300: Fatal if swallowed.
H310: Fatal in contact with skin.
H330: Fatal if inhaled.
H360D: May damage the unborn child.
H372: Causes damage to organs through prolonged or repeated exposure.
H400: Very toxic to aquatic life.
H410: Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P201: Obtain special instructions before use.
P202: Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood.
P260: Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapors/spray.
P262: Do not get in eyes, on skin, or on clothing.
P264: Wash ... thoroughly after handling.
P270: Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product.
P271: Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area.
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P280: Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection.
P281: Use personal protective equipment as required.
P284: [In case of inadequate ventilation] Wear respiratory protection.
P301+P310: IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER/doctor/...
P302+P350: IF ON SKIN: Gently wash with plenty of soap and water.
P304+P340: IF INHALED: Remove person to fresh air and keep comfortable for breathing.
P308+P313: IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention.
P310: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician.
P314: Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell.
P320: Specific treatment is urgent (see ... on this label).
P321: Specific treatment (see ... on this label).
P322: Specific measures (see ...on this label).
P330: Rinse mouth.
P361: Take off immediately all contaminated clothing.
P363: Wash contaminated clothing before reuse.
P391: Collect spillage.
P403+P233: Store in a well-ventilated place. Keep container tightly closed.
P405: Store locked up.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to ...
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rat: >0.56 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rat: >1.30 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rat: 0.0043 a.i. mg/L. 4) Non-irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Slightly-irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). In feeding studies on rats, the only effect found has been that associated with anticoagulant action. In a 12-week feeding study on rats, the maximum tolerated dose was 10 µg/kg body weight per day. Mutagenicity and teratogenicity studies have not shown any mutagenic, embryotoxic, or teratogenic effects.
ADI: Not relevant
Classification:
Toxicity class WHO (a.i.): Ia (Extremely hazardous)
US EPA Classification (formulation): I (Danger - Highly toxic)
EC Risk Classification: Xn - Harmful: R21, R22
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: moderate toxicity to birds, acute oral LD50 for Bobwhite quail is 138 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: moderate toxicity to fish, acute 96 hour LC50 for Rainbow trout is >8.0 a.i.mg/L. Effect on aquatic invertebrates: moderate toxicity to aquatic invertebrates, acute 48 hour EC50 for Daphnia magna is 2 a.i.mg/L. Effect on algae: moderate toxicity to algae, acute 72 hour EC50 for Scenedemus subspicatus is 0.017 a.i.mg/L. Effect on earthworms: high toxicity to earthworms, acute 14 day LC50 is >4.74 a.i.mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Bromadiolone's production may result in its release to the environment through various waste streams; its use as a rodenticide will result in its direct release to the environment. If released to air, a vapor pressure of 1.6ЎБ10-10 mm Hg at 25 deg C indicates bromadiolone will exist solely in the particulate phase in the ambient atmosphere. Particulate-phase bromadiolone will be removed from the atmosphere by wet and dry deposition. Bromadiolone is susceptible to rapid direct photolysis in sunlight. If released to soil, bromadiolone is expected to have low to no mobility based upon an observed Koc range of 1,563 to 41,600. Volatilization from moist soil surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon an estimated Henry's Law constant of 8.9ЎБ10-12 atm-cu/mole. Bromadiolone is not expected to volatilize from dry soil surfaces based upon its vapor pressure. Photodegradation on soil surfaces exposed to sunlight is expected to occur. Using OECD 301B (CO2 evolution method), bromadiolone showed 0% degradation after 28 days, indicating that biodegradation is not an important environmental process in soil or water. If released into water, bromadiolone is expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon the Koc values. Volatilization from water surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon this compound's estimated Henry's Law constant. An estimated BCF range of 125 to >513 suggests the potential for bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is high. Bromadiolone is stable to hydrolysis at environmental pH ranges. Photolysis of bromadiolone in aqueous solution is rapid with a half-life of 12 hours or less. Occupational exposure to bromadiolone may occur through dust inhalation and dermal contact with this compound at workplaces where bromadiolone is produced or used. The general population may be exposed to bromadiolone via dermal contact with products containing bromadiolone.
Usage: Bromadiolone was developed by S. A. Lipha in France. M. Grand reported the rat-killing activity of Bromadiolone in 1976.
Application: In the places where mice often appear, put it along the foot of a wall or shadows. Outside, put it nearby mouseholes or mousepassages. 10 to 20 g per m2, the stack distance is 5 m. The more the quantity of mice, the more the quantity of stack shall be taken. The death time is 2 to 11 days. If has water in circumstances, it will improve the effect of deratization.
| 






