FLOCOUMAFEN
  ·ъКуБй, ·ьКуНӘ, ·ъКуНӘ ·ъКуБй, ·ьКуНӘ, ·ъКуНӘ
Introduction: A rodenticide especially useful against rodents that have become resistant to other anticoagulants.
Common name: Flocoumafen
Another name: Flocoumafene, Stratgem, Storm, etc.
Chemical name: 4-hydroxy-3-[(1RS,3RS;1RS,3SR)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-3-[4-(4-trifluoromethylbenzyloxy)phenyl]-1-naphthyl]coumarin
Empirical formula: C33H25F3O4
Structural formula:
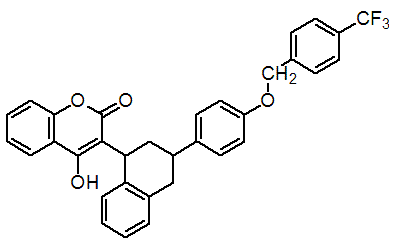
Mol. Weight: 542.54 g/mol
CAS No.: 90035-08-8
Specifications
Leading Flocoumafen supplier
Flocoumafen 98% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Solid: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
SMALL PACKING
Solid: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Customerized packing label
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H300: Fatal if swallowed.
H310: Fatal in contact with skin.
H330: Fatal if inhaled.
H372: Causes damage to organs through prolonged or repeated exposure.
H410: Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P260: Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapors/spray.
P262: Do not get in eyes, on skin, or on clothing.
P264: Wash ... thoroughly after handling.
P270: Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product.
P271: Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area.
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P280: Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection.
P284: [In case of inadequate ventilation] Wear respiratory protection.
P301+P310: IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER/doctor/...
P302+P350: IF ON SKIN: Gently wash with plenty of soap and water.
P304+P340: IF INHALED: Remove person to fresh air and keep comfortable for breathing.
P310: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician.
P314: Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell.
P320: Specific treatment is urgent (see ... on this label).
P321: Specific treatment (see ... on this label).
P322: Specific measures (see ...on this label).
P330: Rinse mouth.
P361: Take off immediately all contaminated clothing.
P363: Wash contaminated clothing before reuse.
P391: Collect spillage.
P403+P233: Store in a well-ventilated place. Keep container tightly closed.
P405: Store locked up.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to ...
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rat: 0.25 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rat: 0.87 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rat: 0.0008 a.i.mg/L. 4) Not a skin irritant (rabbits). 5) Not a eye irritant (rabbits). 6) Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs).
Classification:
Toxicity class WHO (a.i.): Ia (Extremely hazardous)
US EPA Classification (formulation): I (Danger - Highly toxic)
EC Risk Classification: T+ - Very toxic: R26/27/28; T - Toxic: R48/23/24/25; N - Dangerous for the environment: R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: moderate toxicity to birds, acute LD50 for Japanese quail is >300 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: high toxicity to fish, acute 96 hour LC50 for Rainbow trout is 0.091 a.i.mg/L. Effect on aquatic invertebrates: moderate toxicity to aquatic invertebrates, acute 48 hour EC50 for Daphnia magna is 0.66 a.i.mg/L. Effect on algae: moderate toxicity to algae, acute 72 hour EC50 for Raphidocelis subcapitata is 1.1 a.i.mg/L.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Flocoumafen's production may result in its release to the environment through various waste streams; it's use as a rodenticide will result in its direct release to the environment. If released to air, a vapor pressure of 1.0ЎБ10-12 mm Hg at 25 deg C indicates flocoumafen will exist solely in the particulate phase in the ambient atmosphere. Particulate-phase flocoumafen will be removed from the atmosphere by wet and dry deposition. If released to soil, flocoumafen is expected to have slight mobility based upon an estimated Koc of 4,100. Volatilization from moist soil surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon an estimated Henry's Law constant of 7.3ЎБ10-13 atm-cu m/mole. If released into water, flocoumafen is expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon the estimated Koc. Volatilization from water surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon this compound's estimated Henry's Law constant. An estimated BCF of 400 suggests the potential for bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is high. Hydrolysis is not expected to be an important environmental fate process since this compound lacks functional groups that hydrolyze under environmental conditions.
Usage: Rodenticide reported by D. J. Bowler et al. (Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Pests Dis., 1984, 2, 397). Introduced by Shell International Chemical Co., Ltd (now BASF AG). Manufacturers: BASF. Biochemistry: Second-generation indirect anticoagulant. Inhibits the metabolism of vitamin K1, and thus depletes vitamin K1-dependent clotting factors in plasma. Blocks formation of prothrombin.
Application: Control of rodents including Mus musculus, Rattus norvegicus, R. rattus, Arvicanthis niloticus, Bandicota spp., Praomys natalensis, R. argentiventer, R. rattus diardii, R. losea, R. tiomanicus and Sigmodon hispidus. Effective against rodents which have become resistant to other anticoagulant rodenticides. In addition to use around buildings, it is effective in controlling rodents in field and plantation crops including cocoa, cotton, oilpalm, rice and sugar cane.
| 






