Phosalone
    ·ьЙұБтБЧ ·ьЙұБтБЧ
Introduction: Phosalone was introduced in 1963 by Rhone-Poulenc company as a nonsystemic insecticide and acaricide for use on deciduous fruit trees, market garden crops, cotton, potatoes and rape. It is a broad-spectrum pesticide with rapid killing ability. Approximately 12-20 days control may be expected. Phosalone is a member of the organophosphate family of insecticides. It is used as both an insecticide and acaricide. It comes in emulsifiable concentrate, wettable powder and dust formulations. It is used on nut crops, citrus, pome fruits, stone fruits, grapes, potatoes, artichokes, roses and arborvitae. It is active against the red spider mite on apples and pears. It controls a wide range of caterpillars and beetles on crops of economic importance as well as a number of hemiptera and hymenoptera.
Common name: Phosalone
Another name: Fosalon; Benzophosphate; Azofene; fosalon; fozalone; phoazlone; Zolone etc.
Chemical Name (IUPAC): S-6-chloro-2,3-dihydro-2-oxo-1,3-benzoxazol-3-ylmethyl O,O-diethyl phosphorodithioate
Structural formula:
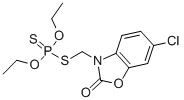
Empirical formula: C12H15ClNO4PS2
Mol. Weight: 367.8
CAS No.: 2310-17-0
Specifications
Leading Phosalone supplier
Phosalone 95% TC
Phosalone 35% EC
Packing
BULK PACKING
Powder: 25KG/Bag, 25KG/Drum, 50KG/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum ect.
SMALL PACKING
Powder: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized Packing label
Phosalone FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H400: Very toxic to aquatic life.
H410: Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P391: Collect spillage.
P501: Dispose of contents/container in accordance with local regulation.
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rats is 120 mg/kg. 2) Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats is 1530 mg/kg. 3) Acute inhalation toxicity LC50 for rats is 1.26 mg/l. 4) Skin irritation: Non-irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Eye irritation: Slightly irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Skin sensitization for guinea pig: Not a skin sensitiser.
NOEL: NOEL (2 y) for rats is 44 mg/kg diet, for mice is 23 mg/kg diet; NOEL (90 d) for dogs is 8.6 mg/kg diet. Other Not mutagenic or genotoxic. Not teratogenic in either the rats or rabbits. Not carcinogenic in lifetime feeding studies in rats and mice.
ADI (JMPR) 0-0.02 mg/kg b.w. [1997, 2001].
Classification:
WHO Classification: II (Moderately hazardous)
EC Risk Classification: T - Toxic: R25; Xn - Harmful: R20/21, R43; N - Dangerous for the environment: R50, R53.
US EPA Classification (formulation): II (Warning - Moderately toxic).
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: Acute oral LD50 for mallards is >2150 mg/kg, for pheasants is 290 mg/kg. Effect on fish: Acute LC50 (96 h) for Rainbow trout is 0.63 mg/l. Effects on aquatic invertebrates: Acute EC50 (48 h) for Daphnia magna is 0.00074 mg/l. Effects on algae: Acute EC50 (72 h) for Scenedemus subspicatus is 1.1 mg/l. Effects on bees: Contact acute (48 h) LD50 is 4.4 ҰМg/bee, Oral acute (48 h) LD50 is 102 ҰМg/bee. Effects on earthworms: Acute 14 day LC50 is 22.5 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Breakdown of Chemical in Soil and Groundwater: Phosalone rapidly degraded (t1/2 = 3-7 days) in flooded Metapeake loam and Monmouth fine sandy loam. Mineralization to carbon dioxide accounted for only 10% of the loss. The primary degradative pathway proceeded by oxidation of phosalone to give phosalone oxon. Subsequent cleavage of the O,O-diethyl methyl phosphorodithioate linkage gave 6-chloro-2- benzoxazolinone. Phosalone is stable at pH 5 and 7, but is hydrolyzed at a pH of 9 with a half-life of 9 days. Phosalone does not move in soil and degrades rapidly when compared to parathion. Aerobic soil metabolism studies demonstrate half-life values of 1-7 days. Field dissipation studies showed half-life values of 1-9 weeks. Phosalone was essentially immobile in a soil column test. Based on this preliminary data, phosalone appears unlikely to contaminate groundwater. Breakdown of Chemical in Surface Water: Phosalone rapidly dissipates in untreated waters. Breakdown of Chemical in Vegetation: Phosalone degrades in plants to chlorbenzoxazolone, formaldehyde, and diethyl phosphorodithioate. It persists on plants about 14 hours, being converted to the corresponding phosphorothioate which is rapidly hydrolyzed. Phosalone is not phytotoxic under normal conditions.
Usage: Phosalone was developed by Rhone-Poulenc company. It is An insecticide and acaricide used to control Coleoptera, Homoptera, Lepidoptera and other pests mainly on potatoes, artichokes, nuts, fruit including citrus, apples, pears, plums, apricots, grapes, nuts, roses, etc.
Application: Biochemistry Cholinesterase inhibitor. Mode of action Non-systemic insecticide and acaricide showing localised penetration of plant cuticle; with contact and stomach action. Uses A non-systemic acaricide and insecticide used primarily in pome and stone fruit trees. Effective against Coleoptera, Homoptera (Aphididae), Lepidoptera (Cydia pomonella) and Thysanoptera on fruit trees. It is selective of most beneficial insects and widely used in integrated pest management programmes. Also used in grapes, oilseed rape, ornamentals, potatoes and vegetables.
| 






