DIMETHOATE 乐果
Introduction: Dimethoate is an insecticide and acaricide used to control a wide range of pests including Aphididae, Coleoptera and Lepidoptera, such as aphids, thrips, whiteflies, leaf & plant hoppers, fruit flies, grasshoppers, jassids, spidermites in fruit including apples, pears, citrus, alfalfa, corn, cotton, pecans, safflower, sorghum, soybean, sugarbeet, turnips, beetroot, tobacco, cereals including wheat, rye and triticale. Dimethoate also is a pesticide transformation product.
Common name: Dimethoate
Another name: Phosphamide, Rogor, Aadimethoal, Fosfamid
Chemical name: 2-dimethoxyphosphinothioylthio-N-methylacetamide
Empirical formula: C5H12NO3PS2
Structural formula:
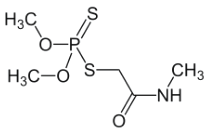
Mol. Weight: 229.26 g/mol
CAS No.: 60-51-5
Specifications
Leading Dimethoate supplier
Dimethoate 400 g/L EC
Dimethoate 98% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Powder: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum ect.
SMALL PACKING
Powder: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized packing label
Dimethoate FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H302: Harmful if swallowed.
H312: Harmful in contact with skin.
Precautionary statement(s)
P264: Wash ... thoroughly after handling.
P270: Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product.
P280: Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection.
P301+P312: IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER/doctor/... IF you feel unwell.
P302+P352: IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of water.
P312: Call a POISON CENTER or doctor/... if you feel unwell.
P322: Specific measures (see ...on this label).
P330: Rinse mouth.
P363: Wash contaminated clothing before reuse.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to ...
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rat: 245 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rat: >2000 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rat: 1.68 a.i. mg/L. 4) Mildly- irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Mildly - irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). When mice were given 9.5 to 10.5 mg/kg/day dimethoate in their drinking water, there was decreased reproduction, pup survival, and growth rates of surviving pups. Adults in this study exhibited reduced weight gain, but their survival was not affected. Impaired reproductive function in humans is not likely under normal conditions. Dimethoate is teratogenic in cats and rats, It is not likely that teratogenic effects will be seen in humans under normal circumstances. Mutagenic effects due to dimethoate exposure were seen in mice. Mutagenic effects are unlikely in humans under normal circumstances. An increase in malignant tumors was reported in rats given oral doses of 5, 15 or 30 mg/kg/day dimethoate for over a year. Carcinogenic effects in humans are unlikely.
ADI (JMPR): 0.002 mg/kg b.w.[2003, 1996]
Classification:
Toxicity class WHO (a.i.): II (Moderately hazardous)
US EPA Classification (formulation): II (Warning - Moderately toxic)
EC Risk Classification: Xn - Harmful: R21/22
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: high toxicity to birds, acute oral LD50 for Colinus virginianus is 10.5 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: moderate toxicity to fish, acute 96 hour LC50 for Rainbow trout is 30.2 a.i.mg/L. Effect on aquatic invertebrates: moderate toxicity to aquatic invertebrates, acute 48 hour EC50 for Daphnia magna is 2 a.i.mg/L. Effect on algae: low toxicity to algae, acute 72 hour EC50 for Raphidocelis subcapitata is 90.4 a.i.mg/L. Effect on honeybees: high toxicity to honeybees, contact acute 48 hour LD50 is 0.1 a.i.μg/bee; Oral acute 48 hour LD50 is 0.1 a.i.μg/bee. Effect on earthworms: moderate toxicity to earthworms, acute 14 day LC50 for Eisenia foetida is 31 a.i.mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Dimethoate's production may result in its release to the environment through various waste streams; its use as a contact and systemic insecticide will result in its direct release to the environment. If released to air, a vapor pressure of 1.87×10-5 mm Hg at 25 deg C indicates dimethoate will exist in both the vapor and particulate phases in the atmosphere. Vapor-phase dimethoate will be degraded in the atmosphere by reaction with photochemically-produced hydroxyl radicals; the half-life for this reaction in air is estimated to be 5 hours. Particulate-phase dimethoate will be removed from the atmosphere by wet or dry deposition. Due to a lack of absorbance of wavelengths of light above 290 nm, dimethoate is not expected to be susceptible to direct photolysis by sunlight. If released to soil, dimethoate is expected to have very high mobility based upon Koc values of 5.2-50. Volatilization of dimethoate from moist soil surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process given an estimated Henry's Law constant of 2.4×10-10 atm-cu m/mole. Microbially-mediated oxidative and hydrolytic degradation is the major degradation pathway in aerobic soil with a half-life of 2.2 days reported. Soil half-lives of 7 and 11 days were reported. However, a half-life of 122 days has also been measured in soil. If released into water, dimethoate is not expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon the Koc values. Dimethoate may be subject to biodegradation in natural waters based on a half-life of 8 weeks for degradation in raw river water. Volatilization from water surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon this compound's estimated Henry's Law constant. BCFs of 1.1-2.4 and 2.7-6 suggest bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is low. Dimethoate hydrolyzes very slowly in sterile buffered solutions at pHs 5 and 7 with half-lives of 156 and 68 days respectively, but hydrolyzes rapidly to desmethyl dimethoate and dimethylthiophosphoric acid with a half-life of 4.4 days at pH 9. Occupational exposure to dimethoate may occur through inhalation and dermal contact with this compound at workplaces where dimethoate is produced or used. Monitoring and use data indicate that the general population may be exposed to dimethoate via inhalation of ambient air, ingestion of food and contaminated drinking water, and dermal contact with this compound and other products containing dimethoate.
Usage: Dimethoate is a widely used organophosphate insecticide and acaricide. It was patented and introduced in the 1950s by American Cyanamid. Like other organophosphates, dimethoate is an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor which disables cholinesterase, an enzyme essential for central nervous system function. It acts both by contact and through ingestion. It is readily absorbed and distributed throughout plant tissues, and is degraded relatively rapidly.
Application: Control of a wide range of Acari, Aphididae, Aleyrodidae, Coccidae, Coleoptera, Collembola, Diptera, Lepidoptera, Pseudococcidae and Thysanoptera in cereals, citrus, coffee, cotton, fruit, grapes, olives, pastures, beetroot, potatoes, pulses, tea, tobacco, ornamentals, ornamental shrubs, and vegetables. Also used for control of flies in animal houses. Typical application rates for cereals 340-680, citrus 2100, olives 720, beetroot 84-600, vegetables 330 -600 (all in a.i.g/ha per application).
| 






