ACEPHATE 高灭磷, 乙酰甲胺磷
Introduction: Acephate is an organophosphate insecticide used normally as a foliar spray to control chewing and sucking insects such as aphids, leaf miners, lepidopterous larvae, sawflies, thrips on fruit, vegetables, potatoes, sugarbeet, vines, rice, hops, ornamentals, greenhouse crops including peppers, cucumbers.
Common name: Acephate
Another name: Orthene, Acetamidophos, Ortran, Ortril, Acephat, Chevron Orthene, Acephat [German], Acefate
Chemical name: (RS)-N-[methoxy(methylthio)phosphinoyl]acetamide
Empirical formula: C4H10NO3PS
Structural formula:
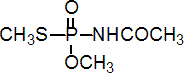
Mol. Weight: 183.17 g/mol
CAS No.: 30560-19-1
Specifications
Leading Acephate supplier
Acephate 400 g/L EC
Acephate 75% SP
Acephate 95% TC
Acephate 97% TC
Acephate 98% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Solid: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum ect.
SMALL PACKING
Solid: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized packing label
Acephate FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H302: Harmful if swallowed.
Precautionary statement(s)
P264: Wash ... thoroughly after handling.
P270: Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product.
P301+P312: IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER/doctor/... IF you feel unwell.
P330: Rinse mouth.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to ...
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rat: 945 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rat: >10000 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rat: 15.0 a.i. mg/L. 4) Slightly irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) minimal-irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). NOEL (2 y) for dogs is 0.75 mg/kg b.w. daily; LOEL for rats is 0.25 mg/kg b.w. daily.
ADI (JMPR): 0.03 mg/kg b.w.[1990]
Classification:
Toxicity class WHO (a.i.): II (Moderately hazardous)
US EPA Classification (formulation): III (Caution - Slightly toxic)
EC Risk Classification: Xn - Harmful: R22
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: moderate toxicity to birds, acute LD50 for Mallard ducks is 350 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: low toxicity to fish, acute 96 hour LC50 for Rainbow trout is 110 a.i.mg/L. Effect on aquatic invertebrates: moderate toxicity to aquatic invertebrates, acute 48 hour EC50 for Daphnia magna is 67.2 a.i.mg/L. Effect on algae: low toxicity to algae, acute 72 hour EC50 is 980 a.i.mg/L. Effect on honeybees: moderate toxicity to honeybees, contact acute 48 hour LD50 is 1.2 a.i.μg/bee. Effect on earthworms: low toxicity to earthworms, acute 14 day LC50 is >22974 a.i.mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Acephate's production may result in its release to the environment through various waste streams; its use as an insecticide will result in its direct release to the environment. If released to air, a vapor pressure of 1.7×10-6 mm Hg at 25 deg C indicates that acephate is expected to exist in both the vapor and particulate-phases in the ambient atmosphere. Vapor-phase acephate is degraded in the atmosphere by reaction with photochemically-produced hydroxyl radicals; the half-life for this reaction in air is estimated to be 34 hours. Particulate-phase acephate will be removed from the atmosphere by wet or dry deposition. Acephate was photolytically stable in aqueous solutions exposed to natural sunlight, suggesting photolysis will not be an important fate process. If released to soil, acephate is expected to have very high mobility based upon a Koc value of 4.7 measured in a clay loam. Volatilization from moist soil surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon an estimated Henry's Law constant of 5×10-13 atm-cu m/mole. Volatilization from dry soil is not expected based upon the vapor pressure. Acephate is non-persistent in the environment with observed half-lives of <3 days in laboratory studies and terrestrial field dissipation studies. If released into water, acephate is not expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon the Koc. Volatilization from water surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon this compound's estimated Henry's Law constant. Acephate was stable to hydrolysis at pH 5 and 7, but degraded with a half-life of 18 days at pH 9. A BCF value of 10 measured in fish suggests that bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is low. Occupational exposure to acephate may occur through inhalation of dust and dermal contact with this compound at workplaces where acephate is produced or used. Monitoring data indicate that the general population may be exposed to acephate via ingestion of food containing acephate. (SRC)
Usage: Insecticide described by J. M. Grayson (Pest Control, 1972, 40, 30). Chemical structure-biological activity relationships of analogues summarised by P. S. Magee (Residue Rev., 1974, 53, 3). Introduced by Chevron Chemical Co. Patents US 3845172. Manufacturers: Aimco; Arvesta; Cheminova; Jingma; Meghmani; Nagarjuna Agrichem; Rallis; Reposo; Sabero; Sannong; Sharda; Shaw Wallace; Sinon; Sumitomo; Sundat; Tekchem; Tide
Application: Uses Control of a wide range of chewing and sucking insects, e.g. aphids, thrips, lepidopterous larvae, sawflies, leaf miners, leafhoppers, cutworms, etc., at 0.5-1.0 kg/ha, in fruit (including citrus), vines, hops, olives, cotton, soya beans, peanuts, macadamia nuts, beet, brassicas, celery, beans, potatoes, rice, tobacco, ornamentals, forestry, and other crops. Of moderate persistence, with residual activity lasting c. 10-21 d. Phytotoxicity Non-phytotoxic to most crops, but marginal leaf burn may occur on Red Delicious apples.
|







