TRIAZOPHOS 三唑磷
Introduction: Triazophos is an insecticide, nematicide and acaricide for the control of a range of insects including aphids, thrips, midges, beetles, sawflies, apple suckers, fruit flies, spidermites, scale insects in rice, fruit trees, vineyards, sugarcane, corn, tobacco, potatoes and ornamentals.
Common name: Triazophos
Another name: Hostathion, Methoxone, Triazofosz (Hungarian), Hostation.
Chemical name: O,O-diethyl O-1-phenyl-1H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl phosphorothioate
Empirical formula: C12H16N3O3PS
Structural formula:
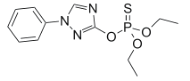
Mol. Weight: 313.3 g/mol
CAS No.: 24017-47-8
Specifications
Leading Triazophos supplier
Triazophos 400 g/L EC
Triazophos 90% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Powder: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum ect.
SMALL PACKING
Powder: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized Packing label
Triazophos FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H301: Toxic if swallowed.
H312: Harmful in contact with skin.
H331: Toxic if inhaled.
H400: Very toxic to aquatic life.
H410: Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P261: Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapors/spray.
P264: Wash ... thoroughly after handling.
P270: Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product.
P271: Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area.
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P280: Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection.
P301+P310: IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER/doctor/...
P302+P352: IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of water.
P304+P340: IF INHALED: Remove person to fresh air and keep comfortable for breathing.
P311: Call a POISON CENTER or doctor/...
P312: Call a POISON CENTER or doctor/... if you feel unwell.
P321: Specific treatment (see ... on this label).
P322: Specific measures (see ...on this label).
P330: Rinse mouth.
P363: Wash contaminated clothing before reuse.
P391: Collect spillage.
P403+P233: Store in a well-ventilated place. Keep container tightly closed.
P405: Store locked up.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to ...
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rat: 66 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rat: >2000 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rat: 0.53 a.i. mg/L. 4) Non- irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Strong- irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). No component of this product present at levels greater than or equal to 0.1% is identified as probable, possible or confirmed human carcinogen by IARC.
ADI (JMPR): 0.001 mg/kg b.w.[1993, 2002]
Classification:
Toxicity class WHO (a.i.): Ib(Highly hazardous)
EC Risk Classification: T - Toxic: R23/25; Xn - Harmful: R21; N - Dangerous for the environment: R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: high toxicity to birds, acute oral LD50 for Colinus virginianus is 8.3 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: high toxicity to fish, acute 96 hour LC50 for Rainbow trout is 0.038 a.i.mg/L. Effect on aquatic invertebrates: high toxicity to aquatic invertebrates, acute 48 hour EC50 for Daphnia magna is 0.0026 a.i.mg/L. Effect on algae: moderate toxicity to algae, acute 72 hour EC50 for Scenedemus subspicatus is 9.1 a.i.mg/L. Effect on honeybees: moderate toxicity to honeybees, contact acute 48 hour LD50 is 59.8 a.i.μg/bee. Effect on earthworms: moderate toxicity to earthworms, acute 14 day LC50 for Eisenia foetida is 466 a.i.mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Triazophos's production may result in its release to the environment through various waste streams; its use as an insecticide, acaricide and nematicide will result in its direct release to the environment. If released to air, a vapor pressure of 2.9×10-6 mm Hg at 30 deg C indicates triazophos will exist in both the vapor and particulate phases in the atmosphere. Vapor-phase triazophos will be degraded in the atmosphere by reaction with photochemically-produced hydroxyl radicals; the half-life for this reaction in air is estimated to be 4 hours. Particulate-phase triazophos will be removed from the atmosphere by wet or dry deposition. Triazophos does not contain chromophores that absorb at wavelengths >290 nm and, therefore, is not expected to be susceptible to direct photolysis by sunlight when in the vapor-phase. If released to soil, triazophos is expected to have moderate mobility based upon a Koc of 355. Volatilization from moist soil surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon an estimated Henry's Law constant of 3.1×10-8 atm-cu m/mole. Triazophos has measured biodegradation half-lives of 2 to 87 days in various soils under different environmental conditions. If released into water, triazophos is expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon the Koc. Triazophos had a half-life of 27 days in seawater and <35 to 47 days in surface water, however, no distinction was made between losses due to biodegradation, hydrolysis, adsorption, or photolysis. Volatilization from water surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon this compound's estimated Henry's Law constant. An estimated BCF of 74 suggests the potential for bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is moderate. Hydrolysis half-lives of 30-250 days were measured for triazophos in water at 25 deg C and photodegradation half-lives of 21 days and 67 days were measured for river water and sea water, respectively. Occupational exposure to triazophos may occur through inhalation and dermal contact with this compound at workplaces where triazophos is produced or used. Monitoring data indicate that the general population may be exposed to triazophos via ingestion of food containing residues.
Usage: The production of triazofos began in the 1980s as a Hoechst patent by the company Bayer.
Application: Triazofos interacts with several enzymes and signalling pathways according to various bio-assay results:inhibits vitamin D receptor (VDR). acts as a small molecule disruptors of the mitochondrial membrane potential. acts as a disruptor of small molecule activators of the human pregnane X receptor (PXR) signalling pathway. acts as a genotoxic compound against isogenic chicken DT40 cell lines. acts as a small molecule antagonist of the oestrogen receptor alpha (Er-alpha) signalling pathway. acts as a small molecule that activates the Aryl (AHR) hydrocarbon receptor signalling pathway. acts as a small molecule antagonist of the constitutive androstane receptor (CAR) signalling pathway. It was used to control aphids, beetles, borers, bugs, foliar-feeding larvae, fruit flies, leafhoppers, leafminers, free-living nematodes, scales, soil insects, thrips, mites and white flies in fruits, vegetable and ornamentals. The triazofos of 1250 ml/ha was most effective against leafhoppers, whiteflies and shoot and fruit borer of brinjal.
| 






