Kasugamycin 春雷霉素
Introduction: Kasugamycin (Ksg) is an aminoglycoside antibiotic that was originally isolated in 1965, from Streptomyces kasugaensis, a Streptomyces strain found near the Kasuga shrine in Nara, Japan. Kasugamycin was discovered by Hamao Umezawa, who also discovered kanamycin and bleomycin, as a drug that prevent growth of a fungus causing rice blast disease. It was later found to inhibit bacterial growth also. It exists as a white, crystalline substance with the chemical formula C14H28ClN3O10 (kasugamycin hydrochloride). It is also known as kasumin.
Common name: Kasugamycin
Another name: Kasuminl; HSDB 6695; BRN 1403823; CHEBI:81419; etc.
Chemical name: 2-amino-2-[(2R,3S,5S,6R)-5-amino-2-methyl-6-[(2S,3S,5S,6R)- 2,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxycyclohexyl]oxyoxan-3-yl]iminoacetic acid
Empirical formula: C14H25N3O9
Structural formula:
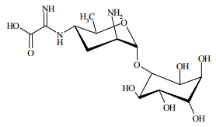
Mol. Weight: 379.36 g/mol
CAS No.: 6980-18-3
Specifications
Leading Kasugamycin supplier
Kasugamycin 70% TC
Kasugamycin 6% WP
Kasugamycin 3% SL
Kasugamycin 2% SL
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Powder: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum etc.
SMALL PACKING
Powder: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized packing label
Kasugamycin FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H315: Causes skin irritation
H360: May damage fertility or the unborn child
H373: May cause damage to blood system, lung, through prolonged or repeated exposure
H412: Harmful to aquatic life with long lasting effects
Precautionary statement(s)
P201: Obtain special instructions before use.
P202: Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood.
P260: Do not breathe dust.
P264: Wash hands thoroughly after handling.
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P280: Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection.
P302+P352: IF ON SKIN: Wash with plenty of soap and water.
P308+P313: IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention.
P314: Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell.
P332+P313: If skin irritation occurs: Get medical advice/attention.
P362+P364: Take off contaminated clothing and wash it before reuse.
P405: Store locked up.
P501: Dispose of contents/container in accordance with related laws
and local/regional regulations.
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rats is >5000 mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rats is >2000 mg/kg (Kasugamycin hydrochloride hydrate). 3) Acute inhalation toxicity LC50 (4 h) for rats is >2.07 mg/L (Kasugamycin hydrochloride hydrate). 4) Skin irritation: Non-irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Eye irritation: Non-irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Skin sensitization for guinea pig: Non-sensitizing.
NOEL: (2 y) for rats is 11 mg/kg diet. Other Not carcinogenic. Not genotoxic.
ADI 0-0.1 mg/kg b.w.
Classification:
WHO Classification: U (Unlikely to present an acute hazard)
EC Risk Classification: Harmful: R22
US EPA Classification (formulation): No concensus across products or no products available
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: Acute oral LD50 for Bobwhite quail is >4000 mg/kg. Effect on fish: Acute LC50 (96 h) for Carp is >40 mg/l. Effects on aquatic invertebrates: Acute EC50 (48 h) for Daphnia magna is >40 mg/l. Effects on bees: contact acute 48 hour LD50 is >40 μg/bee.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Kasugamycin hydrochloride hydrate orally administered to rabbits was mostly excreted in the urine within 24 h. When injected intravenously to dogs, it was mostly excreted within 8 h. After oral administration to rats at 200 mg/kg, no residues were detected in eleven organs or blood; 96% of administered dose remained in the digestive tract 1 h after administration. Plants Degraded to kasugamycinic acid and kasuganobiosamine; finally degraded to ammonia, oxalic acid, CO2 and water. Soil/Environment Degradation proceeds as in plants.
Usage: Kasugamycin was introduced by the Institute of Microbial Chemistry and by Hokko Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. It is an aminoglycoside antibiotic used, normally as the hydrochloride salt, against bacteria and some fungi.
Application: (kasugamycin hydrochloride hydrate) Biochemistry Protein synthesis inhibitor. Inhibits binding of Met-RNA to the mRNA-30S complex, thereby preventing amino acid incorporation. Mode of action Systemic fungicide and bactericide with protective and curative action. Inhibits hyphal growth of Pyricularia oryzae on rice, preventing lesion development; comparatively weak inhibitory action to spore germination, appressoria formation on the plant surface or penetration into the epidermal cell. Rapidly taken up into plant tissue and translocated. In contrast, against Cladosporium fulvum on tomatoes, inhibition of sporulation is strong, but inhibition of hyphal growth is weak. Uses Control of fungal and bacterial diseases affecting rice, vegetables and fruit. On rice, it controls diseases caused by Pyricularia oryzae and Burkholderia glumae (bacterial grain rot), with ground and aerial applications, at 20-30 g/ha, and seedling diseases caused by various bacterial pathogens, at 0.3-0.6 g/box. In sugar beet, it controls Cercospora beticola, at 80-100 g/ha. Also used to control plant diseases in various crops: Pseudomonas syringae pv. lachrymans in cucumbers, at 30-60 g/ha; Colletotrichum lagenarium in melons and water melons; Cladosporium fulvum and Corynebacterium michiganense in tomatoes, at 20-40 g/ha; Mycovellosiella spp. in aubergines; Cercospora spp. in celery; Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora in potatoes, carrots and onions; Pseudomonas syringae pv. coronafaciens (halo blight) in kidney beans, at 40-60 g/ha; Xanthomonas spp. in paprika; Venturia sp. in apples; Pseudomonas marginalis pv. marginalis in kiwifruit; etc.
| 






