CYPERMETHRIN 氯氰菊酯
Introduction: Cypermethrin is an insecticide used to control a broad spectrum of pests including aphid vectors of BYDV, summer aphids, weevils, caterpillars, yellow cereal fly, flea beetles, blossom beetles, pod midge in cereals including wheat, barley, oats, rye, triticale, vegetables including peas & beans, brassicas, oilseed rape, sugarbeet, fodder beet and mangels, potatoes, apples, pears and grassland.
Common name: Cypermethrin
Another name: Ammo, Arrivo, Barricade, Basathrin, CCN52, Cymbush, Cymperator, Cynoff, Cypercopal, Cyperguard 25EC, Cyperhard Tech, Cyperkill, Cypermar, Demon, Flectron, Fligene CI, Folcord, Kafil, NRDC 149, Polytrin, PP383, Ripcord, Siperin, Stockade and Super.
Chemical name: (RS)-α-cyano-3-phenoxybenzyl (1RS,3RS;1RS,3SR)-3-(2,2- dichlorovinyl)-2,2-dimethylcyclopropanecarboxylate
Empirical formula: C22H19Cl2NO3
Structural formula:
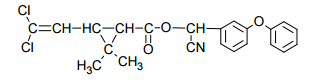
Mol. Weight: 416.3 g/mol
CAS No.: 52315-07-8
Specifications
Leading Cypermethrin supplier
Cypermethrin 50 g/L EC
Cypermethrin 100 g/L SC
Cypermethrin 100 g/L EC
Cypermethrin 250 g/L EC
Cypermethrin 93% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Powder: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum ect.
SMALL PACKING
Powder: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized Packing label
Cypermethrin FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H301 (100%): Toxic if swallowed.
H332 (36.22%): Harmful if inhaled.
H335 (100%): May cause respiratory irritation.
H373 (100%): Causes damage to organs through prolonged or repeated exposure. H400 (99.46%): Very toxic to aquatic life.
H410 (100%): Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P260: Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapors/spray.
P261: Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapors/spray.
P264: Wash ... thoroughly after handling.
P270: Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product.
P271: Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area.
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P301+P310: IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER/doctor/...
P304+P312: IF INHALED: Call a POISON CENTER/doctor/... if you feel unwell.
P304+P340: IF INHALED: Remove person to fresh air and keep comfortable for breathing.
P312: Call a POISON CENTER or doctor/... if you feel unwell.
P314: Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell.
P321: Specific treatment (see ... on this label).
P330: Rinse mouth.
P391: Collect spillage.
P403+P233: Store in a well-ventilated place. Keep container tightly closed.
P405: Store locked up.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to ...
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rat: 287 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rat: >2000 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rat: 3.56 a.i. mg/L. 4) Slightly- irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Slightly- irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). There was no evidence of carcinogenicity, genotoxic, reproductive toxicity, teratogenic; Pyrethroids like cypermethrin may cause adverse effects on the central nervous system.
ADI (JMPR): 0.02mg/kg b.w.[2006]
Classification:
Toxicity class WHO (a.i.): II (Moderately hazardous)
US EPA Classification (formulation): II(Warning - Moderately toxic)
EC Risk Classification: T - Toxic: R22; Xn - Harmful: R48/22; Xi - Irritant: R37; N - Dangerous for the environment: R50, R53 Note: for cis/trans ratio 40:60
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: low toxicity to birds, acute oral LD50 for Mallard ducks >9520 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: high toxicity to fish, acute 96 hour LC50 for Rainbow trout is 0.00151 a.i.mg/L. Effect on aquatic invertebrates: high toxicity to aquatic invertebrates, acute 48 hour EC50 for Daphnia magna is 0.00021 a.i.mg/L. Effect on algae: moderate toxicity to algae, acute 72 hour EC50 for Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata is >0.0667 a.i.mg/L. Effect on honeybees: high toxicity to honeybees, contact acute 48 hour LD50 is 0.023 a.i.μg/bee; Oral acute 48 hour LD50 is 0.172 a.i.μg/bee. Effect on earthworms: moderate toxicity to earthworms, acute 14 day LC50 for Eisenia foetida is >100 a.i.mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Cypermethrin's production may result in its release to the environment through various waste streams; its use as an insecticide will result in its direct release to the environment. If released to air, a vapor pressure of 1.7×10-9 mm Hg at 20 deg C indicates cypermethrin will exist solely in the particulate phase in the atmosphere. Particulate-phase cypermethrin will be removed from the atmosphere by wet or dry deposition. If released to soil, cypermethrin is expected to have no mobility based upon Koc values of 20,800 to 503,000. Volatilization from moist soil surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon an estimated Henry's Law constant of 2.4×10-7 atm-cu m/mole. Cypermethrin degrades rapidly in soil under aerobic conditions with half-lives of 4.1 to 17.6 days for trans-cypermethrin and 12.5 to 56.4 days for cis-cypermethrin. If released into water, cypermethrin is expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon the Koc values. Cypermethrin is expected to biodegrade in water with half-lives of 11.6 to 30.4 days at 15 to 19 deg C, pH 7.7, and biological oxygen demand of 2.2 mg/L. Volatilization from water surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon this compound's estimated Henry's Law constant. BCFs of 420 in golden ide fish, 430 in rainbow trout and 468 in bluegill suggest bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is high. The abiotic hydrolysis half-life of cypermethrin was 63 weeks at pH 7. The photodegradation half-lives of the cis- and trans-isomers of cypermethrin in distilled water solution ranged from 2.6 to 3.6 days in sunlight and >10 days in dark controls; the half-lives in river and seawater ranged from 0.6 to 1.0 days. Occupational exposure to cypermethrin may occur through inhalation of dust particles and dermal contact with this compound at workplaces where cypermethrin is produced or used. Monitoring data indicate that the general population may be exposed to cypermethrin via inhalation of ambient air and ingestion of food containing cypermethrin residues.
Usage: Cypermethrin is a pyrethroid insecticide. It was first synthesized in 1974. Then it was producted by Mitchell, ICI, FMC,Ciba-Geigy, Japanese sumitomo and British shell in 1975. Non-systemic insecticide with contact and stomach action. Also exhibits anti-feeding action. Good residual activity on treated plants.
Application: Uses Control of a wide range of insects, especially Lepidoptera, but also Coleoptera, Diptera, Hemiptera, and other classes, in fruit (including citrus), vines, vegetables, potatoes, cucurbits, lettuce, capsicums, tomatoes, cereals, maize, soya beans, cotton, coffee, cocoa, rice, pecans, oilseed rape, beet, ornamentals, forestry, etc. Control of flies and other insects in animal houses; and mosquitoes, cockroaches, houseflies and other insect pests in public health. Also used as an animal ectoparasiticide. 50-60 mg/kg 50 g/L EC can be used to control of peach moth in apple trees.
| 






