Esfenvalerate 顺式氰戊菊酯
Introduction: Esfenvalerate has replaced the compound fenvalerate for use in the United States. Much of the data for esfenvalerate is closely applicable to the pesticide fenvalerate because the two compounds contain the same components. The only difference in the two products is the relative proportions of the four separate constituents (isomers). Esfenvalerate has become the principal compound of the two because it results in lower application rates than fenvalerate, is less chronically toxic, and is a more powerful insecticide. The compound contains a much higher percentage of the one insecticidally active isomer (84% for esfenvalerate and 22% for fenvalerate). Esfenvalerate is a synthetic pyrethroid insecticide which is used on a wide range of pests such as moths, flies, beetles, and other insects. It is used on vegetable crops, tree fruits, and nut crops. It may be mixed with a wide variety of other types of pesticides such as carbamate compounds or organophosphates.
Common name: Esfenvalerate
Another name: Fenvalerate (S,S)-isomer; Sumi-alpha; UNII-7F07OXM0PP; Asana
7F07OXM0PP; Halmark; Sumi-alfa; A alpha; Fenvalerate alpha; CHEBI:39346; Sumiciclin Aalpha; Asana XL; Sumicidin A alpha; Fenvalerate A alpha; S-5620A alpha; etc.
Chemical name:
(S)-α-cyano-3-phenoxybenzyl (S)-2-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-methylbutyrate
Empirical formula: C25H22ClNO3
Structural formula:
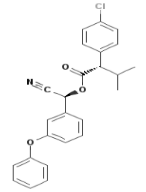
Mol. Weight: 419.91 g/mol
CAS No.: 66230-04-4
Specifications
Leading Esfenvalerate supplier
Esfenvalerate 90% TC
Esfenvalerate 95% TC
Esfenvalerate 5% EC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Powder: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum etc.
SMALL PACKING
Powder: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized packing label
Esfenvalerate FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H301: Toxic if swallowed.
H313: May be harmful in contact with skin.
H316: Causes mild skin irritation.
H317: May cause an allergic skin reaction.
H320: Causes eye irritation.
H330: Fatal if inhaled.
H335: May cause respiratory irritation.
H370: Causes damage to organs.
H373: Causes damage to organs through prolonged or repeated exposure.
H400: Very toxic to aquatic life.
H410: Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P260: Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapors/spray.
P270: Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product.
P280: Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection.
P301+P310: IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER/doctor/...
P302+P352: IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of water.
P305+P351+P338: IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses if present and easy to do - continue rinsing.
P312: Call a POISON CENTER or doctor/... if you feel unwell.
P320: Specific treatment is urgent (see ... on this label).
P330: Rinse mouth.
P363: Wash contaminated clothing before reuse.
P391: Collect spillage.
P405: Store locked up.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to.
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rats is 90 mg/kg 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rats is >5000 mg/kg. 3) Acute inhalation toxicity LC50 (4 h) for rats is >0.48 mg/L. 4) Skin irritation: Non-irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Eye irritation: Slightly irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Skin sensitization for guinea pig: Non-sensitizing.
NOEL: (2 y) for rats is 7.5 mg/kg/day, (18 m) for mice is 4.3 mg/kg/day, (1 y) for dogs is 5 mg/kg/day. Other Not carcinogenic. Not genotoxic.
ADI (JMPR) 0-0.02 mg/kg b.w. [2002]
Classification:
WHO Classification: II (Moderately hazardous)
EC Risk Classification: T - Toxic: R23/25; Xn - Harmful: R43; H - handling risks: R10; N - Dangerous for the environment: R50, R53
US EPA Classification (formulation): II (Warning - Moderately toxic)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: Acute oral LD50 for Bobwhite quail is 1312 mg/kg. Effect on fish: Acute LC50 (96 h) for Rainbow trout is 0.26 mg/l. Effects on aquatic invertebrates: Acute EC50 (48 h) for Daphnia magna is 0.00027 mg/l. Effects on algae: Acute 72 hour EC50 for Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata is 0.0065 mg/l. Effects on bees: Contact acute 48 hour LD50 is 0.06 μg/bee, oral acute 48 hour LD50 is 0.21 μg/bee. Effects on earthworms: Acute 14 day LC50 is 10.6 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Rapid metabolism and elimination occurs in rats and other animals. Primary metabolism involves hydroxylation of 2'- and 4'- hydroxyl moieties, ester cleavage, hydroxylation and oxidation of the alcohol derivatives, oxidation of the cyano moiety and conjugation of the acidic metabolites with sulfate, glycine and glucuronic acid. Plants The major metabolite was decarboxylated fenvalerate. Ester cleavage, hydration of the cyano group to carboxamide and carboxylic acid, hydroxylation of the 2'- and 4'- phenoxy positions, conversion of the alcohol moiety to 3-phenoxybenzyl alcohol and 3-phenoxybenzoic acid, and conjugation of the resulting carboxylic acids and alcohols with sugars, also occur. Soil/Environment In sand (0.38% o.m.), Kd (25 ºC) 4.4; in sandy loam (pH 7.3, 1.1% o.m.), Kd (25 ºC) 6.4, DT50 88 d; in silty loam (pH 5.3, 2.0% o.m.), Kd (25 ºC) 71, DT50 114 d; in clay loam (pH 5.7, 0.2% o.m.), DT50 287 d; in clay loam (pH 6.4, 1.5% o.m.), Kd (25 ºC) 105. Koc 5300.
Usage: Esfenvalerate was introduced by Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd and developed under licence by Shell International Chemical Co., Ltd and E. I. du Pont de Nemours and Co. It is a synthetic pyrethroid insecticide which is used on a wide range of pests such as moths, flies, beetles, and other insects. It is used on vegetable crops, tree fruit, and nut crops.
Application: Biochemistry Voltage dependent sodium channel agonist. Mode of action Insecticide with contact and stomach action. Uses A potent contact and ingested insecticide with a very broad range of activity, especially effective against Coleoptera, Diptera, Hemiptera, Lepidoptera and Orthoptera on cotton, fruit, vegetables and other crops, at 5-25 g/ha. It is effective against strains resistant to organochlorine, organophosphorus and carbamate insecticides. Phytotoxicity Some injury has been noted on crucifers, cucumbers, aubergines, tomatoes, pears and mandarin oranges.
| 






