Fenobucarb(BPMC) 仲丁威
Introduction: Fenobucarb is a carbamate pesticide. Carbamate pesticides are derived from carbamic acid and kill insects in a similar fashion as organophosphate insecticides. They are widely used in homes, gardens and agriculture. It has had wide use in lawn and garden settings. Most of the carbamates are extremely toxic to Hymenoptera.
Common name: Fenobucarb
Another name: Osbac, Bassa, BPMC, Baycarb, Fenobcarb, Barizon, Carvil, Hopcin, Bayer 41367C, Bayer 41637, Geocarb 50EC, Fenobucarb [BSI:ISO]
Chemical name: (RS)-2-sec-butylphenyl methylcarbamate
Empirical formula: C12H17NO2
Structural formula:
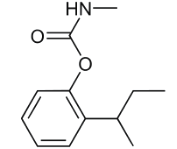
Mol. Weight: 207.27 g/mol
CAS No.: 3766-81-2
Specifications
Leading Fenobucarb supplier
Fenobucarb 500 g/L EC
Fenobucarb 95% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Powder: 25 kg/Bag, 25 kg/Drum, 50 kg/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200 L/Drum, 20 L/Drum, 10 L/Drum ect.
SMALL PACKING
Powder: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500mL/Bottle, 250mL/Bottle, 100mL/Bottle, 50mL/Bottle etc.
Customerized Packing label
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H302: Harmful if swallowed.
H400: Very toxic to aquatic life.
H410: Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P264: Wash ... thoroughly after handling.
P270: Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product.
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P301+P312: IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER/doctor/... IF you feel unwell.
P330: Rinse mouth.
P391: Collect spillage.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to ...
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rat: 620 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rat: ˃5000 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rat: 0.37 a.i. mg/L. 4) Slight irritating effect to skin (rabbit). 5) Slight irritant to eye (rabbit). 6) Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). NOEL (2 y) for rats 4.1 mg/kg b.w. daily (100 mg/kg diet).
Classification:
Toxicity class WHO (a.i.): II (Moderately hazardous)
US EPA Classification (formulation): II (Warning - Moderately toxic)
EC Risk Classification: Xn - Harmful: R22; N - Dangerous for the environment; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: low toxicity to birds, acute LD50 for Bobwhite quail is 2250 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: moderate toxicity to fish, acute 96 hour LC50 for Cyprinoid is 1.7 a.i.mg/L. Effect on aquatic invertebrates: moderate toxicity to aquatic invertebrates, acute 48 hour EC50 for Daphnia magna is 0.1 a.i.mg/L. Effect on earthworms: moderate toxicity to earthworms, acute 14 day LC50 is 10.7 a.i.mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 64 (WHO, 1986; a review of carbamate insecticides in general). Animals 2-(2-Hydroxy-1-methylpropyl)-phenyl N-methylcarbamate is a metabolite. Metabolism of carbamate insecticides is reviewed (M. Cool & C. K. Jankowski in "Insecticides"). Plants As for animals. Soil/Environment Soil Kom 125 (Utsunomia soil, 5.2% o.m.), 661 (Niigata soil, 1.8% o.m.); DT50 6-30 d and 6-14 d under paddy and upland conditions, respectively.
Usage: History Insecticide reported by R. L. Metcalf et al. (J. Econ. Entomol., 1962, 55, 889). Introduced by Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd, by Kumiai Chemical Industry Co., Ltd and Mitsubishi Chemical Industries (now Mitsubishi Chemical Corp., who sold their agrochemical business to Nihon Nohyaku Co., Ltd in 2002) jointly, and by Bayer AG (who no longer manufacture or market it); registered in Japan and first marketed in 1968.
Application: Biochemistry Cholinesterase inhibitor. Mode of action Non-systemic insecticide with contact action. Uses Control of leafhoppers, planthoppers, thrips, and weevils on rice, tea, sugar cane, wheat, cucurbits, aubergines, and capsicums. Control of bollworms and aphids on cotton, at 0.5-1.0 kg/ha; control of leafhoppers, at 0.6-1.2 kg/ha.
| 






