Azocyclotin 三唑锡
Introduction: Azocyclotin is an organotin acaricide. It has a low aqueous solubility, is non-volatile and is not expected to leach to groundwater. Data is limited but is not expected to be persistent in soil systems but may be persistent in aquatic systems under certain conditions. It is highly toxic to mammals and also has a high potential to bioaccumulate. It is thought to be a skin, eye and respiratory system irritant. It is highly toxic to fish and aquatic invertebrates and moderately toxic to birds, honeybees and earthworms.
Common name: Azocyclotin
Another name: Peropal; 1-(Tricyclohexylstannyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole; BAY bue 1452; Azocyclotin [BSI:ISO]; UNII-V4YRQ367KE; (1H-1,2,4-Triazolyl)tricyclohexylstan nane; HSDB 6559; Tri(cyclohexyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yltin; etc.
Chemical name: tri(cyclohexyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yltin
Empirical formula: C20H35N3Sn
Structural formula:
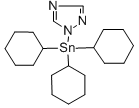
Mol. Weight: 436.22 g/mol
CAS No.: 41083-11-8
Specifications
Leading Azocyclotin supplier
Azocyclotin 95% TC
Azocyclotin 25% WP
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Powder: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum etc.
SMALL PACKING
Powder: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized packing label
Azocyclotin FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H301: Toxic if swallowed.
H315: Causes skin irritation.
H318: Causes serious eye damage.
H330: Fatal if inhaled.
H335: May cause respiratory irritation.
H400: Very toxic to aquatic life.
H410: Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P260: Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray.
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P280: Wear protective gloves/eye protection/face protection.
P284: Wear respiratory protection.
P301+P310: IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician.
P305+P351+P338: IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continue rinsing.
P310: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician.
P320: Specific treatment is urgent (see ... on this label).
P330: Rinse mouth.
P405: Store locked up.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to.
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rats is 80 mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rats is >5000 mg/kg. 3) Acute inhalation toxicity LC50 (4 h) for rats is 0.02 mg/l. 4) Skin irritation (rabbits): Corrosive. 5) Eye irritation (rabbits): Not tested but taken to be corrosive. 6) Skin sensitization for guinea pig: Not a skin sensitiser.
NOEL: NOEL (2 y) for rats is 0.26 mg/kg bw per day, (2 y) for mice is 2.12 mg/kg bw per day. Other Azocyclotin is unlikely to be carcinogenic in rodents. Azocyclotin was not genotoxic in an extensive range of tests for genotoxicity in vitro and in vivo. Not teratogenic or fetotoxic.
ADI (JMPR) 0-0.003 mg/kg b.w.[2005]
Classification:
WHO Classification: II (Moderately hazardous)
EC Risk Classification: T+ - Very toxic: R26; T - Toxic: R25; Xn - Harmful: R41; Xi - Irritant: R37/38; N - Dangerous for the environment: R50, R53.
US EPA Classification (formulation): I (Danger - Highly toxic)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: Acute oral LD50 for Japanese quail is 144 mg/kg. Effect on fish: Acute LC50 (96 h) for Rainbow trout is 0.004 mg/l. Effects on aquatic invertebrates: Acute EC50 (48 h) for Daphnia magna is 0.04 mg/l. Effects on algae: Acute EC50 (72 h) for Scenedemus subspicatus is 0.16 mg/l. Effects on bees: acute (48 h) LD50 is 100 μg/bee. Effects on earthworms: Acute 14 day LC50 is 806 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
If released to air, a vapor pressure of 4.5×10-13 mm Hg at 25℃ indicates azocyclotin will exist solely in the particulate phase in the ambient atmosphere. Particulate-phase azocyclotin will be removed from the atmosphere by wet and dry deposition. If released to soil, azocyclotin is expected to have no mobility based upon an estimated Koc of 18,000. Volatilization from moist soil surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon an estimated Henry's Law constant of 2.1×10-12 atm-cu m/mole. The pKa of azocyclotin is 5.36, indicating that this compound will partially exist in the protonated form in the environment and cations generally adsorb to organic carbon and clay more strongly than their neutral counterparts. If released into water, azocyclotin is expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon the estimated Koc. Volatilization from water surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon this compound's estimated Henry's Law constant. The pKa of azocyclotin is 5.36 indicating that this compound will partially exist in the protonated form in the environment and cations generally adsorb to organic carbon and clay more strongly than their neutral counterparts.
Usage: Azocyclotin was developed by Bayer. It is an organotin acaricide used mainly for Phytophagous mite control.
Application: Biochemistry Inhibitor of oxidative phosphorylation; disruptor of ATP formation. Mode of action Long-acting acaricide with contact action. Uses Control of all motile stages of spider mites on fruit (including citrus), vines, hops, cotton, vegetables, and ornamentals.
| 






