Hexythiazox 噻螨酮
Introduction: Hexythiazox is a new acaricide which shows excellent control on phytophagous mites. It was discovered and now being developed by Nippon Soda Company Ltd, Tokyo, Japan. Hexythiazox has the distinction of being the first IGR Acaricide. Hexythiazox has novel acaricidal chemistry with marvelous ovicidal, larvicidal and nymphicidal properties, which controls phytophagous mites of different species in different crops.
Common name: Hexythiazox
Another name: Savey; Acarflor; Acariflor; Calibre; Matacar; Nissorun; Ordoval; Cesar; Trevi; etc.
Chemical name:
(4RS,5RS)-5-(4-chlorophenyl)-N-cyclohexyl-4-methyl-2-oxo-1,3-thiazolidine-3-carboxamide
Empirical formula: C17H21ClN2O2S
Structural formula:
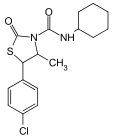
Mol. Weight: 352.88 g/mol
CAS No.: 78587-05-0
Specifications
Leading Hexythiazox supplier
Hexythiazox 98% TC
Hexythiazox 5% EC
Hexythiazox 100 g/L EC
Hexythiazox 5% WP
Hexythiazox 10% WP
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Powder: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum etc.
SMALL PACKING
Powder: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized packing label
Hexythiazox FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H400: Very toxic to aquatic life.
H410: Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P391: Collect spillage.
P501: Dispose of contents/container in accordance with national regulations.
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rats is >5000 mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rats is >5000 mg/kg. 3) Acute inhalation toxicity LC50 (4 h) for rats is >2.0 mg/l. 4) Skin irritation: Non-irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Eye irritation: Slightly irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Skin sensitization for guinea pig: Not a skin sensitiser.
NOEL: NOEL (2 y) for rats is 3.2 mg/kg bw per day, (2 y) for mice is 6.7 mg/kg bw per day, (1 y) for dogs is 2.9 mg/kg bw per day, Other Not genotoxic or mutagenic, not teratogenic.
ADI (JMPR) 0-0.03 mg/kg b.w.[1991, 2008]
Classification:
WHO Classification: U (Unlikely to present an acute hazard)
EC Risk Classification: N - Dangerous for the environment: R50, R53
US EPA Classification (formulation): IV (Caution - Not acutely toxic)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: Acute oral LD50 for Mallard is >2000 mg/kg. Effect on fish: Acute LC50 (96 h) for Rainbow trout is 0.04 mg/l. Effects on aquatic invertebrates: Acute EC50 (48 h) for Daphnia magna is >0.47 mg/l. Effects on algae: Acute EC50 (72 h) for Scenedemus subspicatus is >0.4 mg/l. Effects on bees: Contact acute (48 h) LD50 is >200 μg/bee, Oral acute (48 h) LD50 is >112 μg/bee. Effects on earthworms: Acute 14 day LC50 is >105 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
If released to air, a vapor pressure of 2.55×10-8 mm Hg at 20 deg C indicates hexythiazox will exist in both the vapor and particulate phases in the atmosphere. Vapor-phase hexythiazox will be degraded in the atmosphere by reaction with photochemically-produced hydroxyl radicals; the half-life for this reaction in air is estimated to be 11 hours. Particulate-phase hexythiazox will be removed from the atmosphere by wet and dry deposition. Hexythiazox contains chromophores that absorb at wavelengths >290 nm and, therefore, may be susceptible to direct photolysis by sunlight. Hexythiazox undergoes direct photolysis in aquatic systems with a half-life of 16.6 days for its primary photodegradation and 24.6 days for degradation of the total toxic residues. If released to soil, hexythiazox is expected to have no mobility based upon a Koc of 6,200. Volatilization from moist soil surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon an estimated Henry's Law constant of 2.4×10-8 atm-cu m/mole. Hexythiazox is not expected to volatilize from dry soil surfaces based upon its vapor pressure. Hexythiazox has reported half-lives in aerobic soils of 17 to 43 days suggesting that primary biodegradation may be important under certain environmental conditions in soil. If released into water, hexythiazox is expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon the Koc. Hexythiazox has reported half-lives in aquatic systems of 30 to 40 days suggesting that primary biodegradation may be important under certain environmental conditions in water. Volatilization from water surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon this compound's estimated Henry's Law constant. A measured BCF of 1,600 suggests bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is very high. Hydrolysis is not expected to be an important environmental fate process since this compound lacks functional groups that hydrolyze under environmental conditions (pH 5 to 9).
Usage: Hexythiazox was developed by Nippo Soda Co. Ltd.. Hexythiazox is an acaricide used for the control of eggs and larvae of many mites on a wide variety of food crops.
Application: Mode of action Non-systemic acaricide with contact and stomach action. Good translaminar activity. Has ovicidal, larvicidal, and nymphicidal activity. Not active against adults, but eggs laid by treated females are non-viable. Uses Control of eggs and larvae of many phytophagous mites (particularly Panonychus, Tetranychus, and Eotetranychus spp.) on fruit, citrus, vegetables (all at 150-300 g/ha), vines and cotton.
| 






