Carbendazim 多菌灵
Introduction: Carbendazim is a widely used, broad-spectrum benzimidazole fungicide and a metabolite of benomyl. It is also employed as a casting worm control agent in amenity turf situations such as golf greens, tennis courts etc. and in some countries is licensed for that use only. The fungicide is used to control plant diseases in cereals and fruits, including citrus, bananas, strawberries, pineapples, and pomes.
Common name: Carbendazim
Another name: Carbendazole; Mecarzole; Bavistin; Carbendazime; Carbendazol; Bavistan; Derosal; Thicoper; Medamine; Funaben; BMK (fungicide); Carbendazym; Equitdazin; Garbenda; Kemdazin; Supercarb; Agrizim; Battal; etc.
Chemical name: methyl benzimidazol-2-ylcarbamate
Empirical formula: C9H9N3O2
Structural formula:
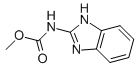
Mol. Weight: 191.21 g/mol
CAS No.: 10605-21-7
Specifications
Leading Carbendazim supplier
Carbendazim 98% TC
Carbendazim 50% WP
Carbendazim 500 g/L SC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Powder: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum etc.
SMALL PACKING
Powder: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized packing label
Carbendazim FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H340 (99.83%): May cause genetic defects.
H360 (99.65%): May damage fertility or the unborn child.
H400 (98.96%): Very toxic to aquatic life.
H410 (93.96%): Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P201: Obtain special instructions before use.
P202: Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood.
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P281: Use personal protective equipment as required.
P308+P313: IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention.
P391: Collect spillage.
P405: Store locked up.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to an approved waste disposal plant.
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rats is >10000 mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rats is >2000 mg/kg. 3) Acute inhalation toxicity LC50 (4 h) for rats is >5.8 mg/L. 4) Skin irritation: Non-irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Eye irritation: Non-irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Skin sensitization for guinea pig: Non-sensitiser.
NOEL: (2 y) for rats is 22 mg/kg/day; (18 m) for mice is 22.5 mg/kg/day; (2 y) for dogs is 2.6 mg/kg/day. Other Not carcinogenic.
ADI (JMPR) 0-0.03 mg/kg b.w. [1995, 2005]
Classification:
WHO Classification: U (Unlikely to present an acute hazard)
EC Risk Classification: Mutagenic category 2: R46; Reproduction risk category 2: R60, R61; N - Dangerous for the environment: R50, R53
US EPA Classification (formulation): III (Caution - Slightly toxic)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: Acute oral LD50 for Japanese quail is >2250 mg/kg. Effect on fish: Acute LC50 (96 h) for Rainbow trout is 0.19 mg/l. Effects on aquatic invertebrates: Acute EC50 (48 h) for Daphnia magna is 0.15 mg/l. Effects on algae: Acute 72 hour EC50 for Scenedemus subspicatus is >7.7 mg/l. Effects on bees: contact acute 48 hour LD50 is >50 μg/bee, oral acute 48 hour LD50 is >756 μg/bee. Effects on earthworms: Acute 14 day LC50 is 5.4 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 149 (WHO, 1993). EHC 149 concludes that, although highly toxic to aquatic organisms, low bioavailability in surface waters makes it unlikely this toxicity will occur in the field. Animals In male rats, following a single oral administration of 3 mg/kg, 66% was eliminated in the urine within 6 hours. Plants Readily absorbed by plants. One degradation product is 2-aminobenzimidazole. Soil/Environment 2-Aminobenzimidazole has been found as a minor metabolite. DT50 in soil 8-32 d under outdoor conditions. Carbendazim decomposes in the environment, DT50 6-12 mo on bare soil, 3-6 mo on turf, and 2-25 mo in water under aerobic and anaerobic conditions, respectively. It is mainly decomposed by micro-organisms. Koc 200-250.
Usage: Carbendazim was introduced by BASF AG, and Hoechst AG (now Bayer CropScience). It is a fungicide used to control a a range of diseases including Septoria, Fusarium and Sclerotina. Can also be a pesticide transformation product.
Application: Biochemistry Inhibits beta-tubulin synthesis. Mode of action Systemic fungicide with protective and curative action. Absorbed through the roots and green tissues, with translocation acropetally. Acts by inhibiting development of the germ tubes, the formation of appressoria, and the growth of mycelia. Uses Control of Septoria, Fusarium, Erysiphe and Pseudocercosporella in cereals; Sclerotinia, Alternaria and Cylindrosporium in oilseed rape; Cercospora and Erysiphe in sugar beet; Uncinula and Botrytis in grapes; Cladosporium and Botrytis in tomatoes; Venturia and Podosphaera in pome fruit and Monilia and Sclerotinia in stone fruit. Application rates vary from 120-600 g/ha, depending on crop. A seed treatment (0.6-0.8 g/kg) will control Tilletia, Ustilago, Fusarium and Septoria in cereals, and Rhizoctonia in cotton. Also shows activity against storage diseases of fruit as a dip (0.3-0.5 g/l).







