DITHIANON 二噻农
Introduction: Dithianon is a dicarbonitrile fungicide for control of scab and other foliar diseases excluding powdery mildew on apples, pears, grapes (table & wine), blackcurrants, etc. Protectant with some curative activity. Multi-site activity.
Common name: Dithianon
Another name: Dithianone, Delan, Merkdelan, Thynon, Delan-col, Delan WP, Delan (fungicide)
Chemical name: 5,10-dihydro-5,10-dioxonaphtho[2,3-b]-1,4-dithiine-2,3-dicarbonitrile
Empirical formula: C14H4N2O2S2
Structural formula:
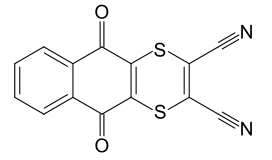
Mol. Weight: 296.32 g/mol
CAS No.: 3347-22-6
Specifications
Leading Dithianon supplier
Dithianon 500 g/L SC
Dithianon 75% WP
Dithianon 95% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Solid: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum ect.
SMALL PACKING
Solid: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized packing label
Dithianon FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H302: Harmful if swallowed.
H400: Very toxic to aquatic life.
H410: Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P264: Wash ... thoroughly after handling.
P270: Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product.
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P301+P312: IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER/doctor/... IF you feel unwell.
P330: Rinse mouth.
P391: Collect spillage.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to ...
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rat: 300 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rat: >2000 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rat: 0.31 a.i. mg/L. 4) moderately- irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Caused skin sensitization in animal studies. Mutagenicity tests revealed no genotoxic potential. Long term administration of organotoxic doses revealed a carcinogenic effect. In long-term studies in mice in which the substance was given by feed, a carcinogenic effect was not observed. Animal studies gave no indication of a developmental toxic effect at doses that were not toxic to the parental animals.
ADI (JMPR): 0.01 mg/kg b.w.[2010]
Classification:
Toxicity class WHO (a.i.): II (Moderately hazardous)
US EPA Classification (formulation): III (Caution - Slightly toxic)
EC Risk Classification: Carcinogen category 3: R40; T - Toxic: R23; Xn - Harmful: R22, R41, R43; Xi - Irritant: R66; N - Dangerous for the environment: R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: moderate toxicity to birds, acute oral LD50 for Bobwhites quail is 309 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: moderate toxicity to fish, acute 96 hour LC50 for Rainbow trout is 0.07 a.i.mg/L. Effect on aquatic invertebrates: moderate toxicity to aquatic invertebrates, acute 48 hour EC50 for Daphnia magna is 0.26 a.i.mg/L. Effect on algae: moderate toxicity to algae, acute 72 hour EC50 is 0.09 a.i.mg/L. Effect on honeybees: low-moderate toxicity to honeybees, contact acute 48 hour LD50 is > 100 a.i.μg/bee, oral acute 48 hour LD50 is >25.4 a.i.μg/bee. Effect on earthworms: moderate toxicity to earthworms, acute 14 day LC50 is 578 a.i.mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Dithianon's former production and use in the US as a fungicide may have resulted in its direct release to the environment. If released to air, a vapor pressure of 2.03×10-11 mm Hg at 25 deg C indicates dithianon will exist solely in the particulate phase in the atmosphere. Particulate-phase dithianon will be removed from the atmosphere by wet or dry deposition. Dithianon may undergo direct photolysis in the environment based on an aqueous photolysis half-life of 19 hours. If released to soil, dithianon is expected to have low mobility based upon an estimated Koc of 840. Biodegradation data were not available. However the compound was shown to be unstable under alkaline conditions. Volatilization from moist soil surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon an estimated Henry's Law constant of 5.7×10-11 atm-cu m/mole. Dithianon is not expected to volatilize from dry soil surfaces based upon its vapor pressure. If released into water, dithianon is expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon the estimated Koc. Volatilization from water surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon this compound's estimated Henry's Law constant. An estimated BCF of 85 suggests the potential for bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is moderate. A hydrolysis half-life range of <1 to 12.3 days has been reported for dithianon. Occupational exposure and general population exposure should be low or non-existent since dithianon is no longer produced or used in the US (October, 1989). (SRC)
Usage: Fungicide popularized by Merch at first in 1962 , then by Shell Agrar Gmbh (now Syngenta AG), Patent: BP857383.
Application: Dithianonis used to control many foliar diseases (but not powdery mildews), includingscab on pome fruit; Stigmina carpophila, Coccomyces hiemalis and scab oncherries; Monilia spp., rust and leaf curl on peaches and apricots; leaf spotand rust on currants; Didymella applanata on raspberries; Mycosphaerella fragariae and Diplocarpon earliana on strawberries; Plasmopara viticola onvines; downy mildew on hops; scab and Phomopsis citri on citrus fruit;Ascochyta chrysanthemi on chrysanthemums under glass; Glomerella cingulata oncoffee; Marssonina leaf spot on poplars; etc. Applied at 1400 g/ha (hops), 525g/ha (pome and stone fruit), 560 g/ha (vines).
| 






