| Phenthoate 稻丰散稻丰散
Introduction: Phenthoate is an insecticide used to control common insects including Aphids, Houseflies, blowflies, Scale insects, leafhoppers, mealybugs, mosquitoes in rice; vegetables including brassicas, eggplant, peppers, radish, turnips; carrot; soybean; potatoes; tea; citrus.
Common name: Phenthoate
Another name: Fenthoate, Dimephenthioate, Dimephenthoate, Cidial, Phendal, Elsan, Dimefenthoat, Cidemul, Papthion, Tsidial, Tagson, Tanone, dl-Papthion, d-Papthion, l-Papthion, Montecatini L-561, Dimethenthoate, Bayer 18510, Cidial ULV, Elsan ULV, Phenthoate 50 EC, ENT 27386GC, Caswell No. 427B, Phenthoate [BSI:ISO].
Chemical name: S-α-ethoxycarbonylbenzyl O,O-dimethyl phosphorodithioate
Empirical formula: C12H17O4PS2
Structural formula:
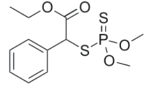
Mol. Weight: 320.36 g/mol
CAS No.: 2597-03-7
Specifications
Leading Phenthoate supplier
Phenthoate 500 g/L EC
Phenthoate 90% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Powder: 25KG/Bag, 25KG/Drum, 50KG/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum ect.
SMALL PACKING
Powder: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized Packing label
Phenthoate FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H302: Harmful if swallowed.
H312: Harmful in contact with skin.
H400: Very toxic to aquatic life.
H410: Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P264: Wash ... thoroughly after handling.
P270: Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product.
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P280: Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection.
P301+P312: IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER/doctor/... IF you feel unwell.
P302+P352: IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of water.
P312: Call a POISON CENTER or doctor/... if you feel unwell.
P322: Specific measures (see ...on this label).
P330: Rinse mouth.
P363: Wash contaminated clothing before reuse.
P391: Collect spillage.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to ...
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rat: 249 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rabbit: 72.0 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rat: 3.17 a.i. mg/L. 4) Prolonged skin contact may cause temporary irritation. 5) Direct contact with eyes may cause temporary irritation. 6) Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). No data available to indicate product or any components present at greater than 0.1% are mutagenic or genotoxic. This product is not considered to be a carcinogen by IARC, ACGIH, NTP, or OSHA.
ADI (JMPR): 0.003 mg/kg b.w.[1984]
Classification:
Toxicity class WHO (a.i.): II (Moderately hazardous)
US EPA Classification (formulation): II (Warning - Moderately toxic)
EC Risk Classification: Xn - Harmful: R21/22; N - Dangerous for the environment: R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: moderate toxicity to birds, acute oral LD50 for Phasianidae is 300 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: moderate toxicity to fish, acute 96 hour LC50 for Cyprinidae is 2.5 a.i.mg/L. Effect on aquatic invertebrates: high toxicity to aquatic invertebrates, acute 48 hour EC50 for Daphnia magna is 0.0017 a.i.mg/L. Effect on honeybees: high toxicity to honeybees, acute 48 hour LD50 is 0.306 a.i.μg/bee.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Phenthoate has been identified in pond water, soil samples, forest air, and in various types of food. If released to soil, phenthoate is expected to have slight mobility. Volatilization of phenthoate is not expected to be important from moist soil surfaces but may occur from dry soil surfaces. The field half-life of phenthoate in soil has been determined to be 35 days. Calculated half-lives of phenthoate on foliage are 1.9, 1.5, 3.1, and 3.6 days on citrus, citrus, lemon, and orange crops, respectively. According to a Japanese MITI biodegradation test, phenthoate is not expected to be an important fate process in soil or water. However, soil biodegradation studies have shown that biodegradation in soil can occur within 30-75 days. If released to water, phenthoate would adsorb to suspended solids and sediment. Phenthoate would be essentially non-volatile from water surfaces. Experimental BCF values for phenthoate of 3.7-29 and 7.1-34 (carp), 36 (topmouth gudgeon), and 713 (willow shiners) suggest that phenthoate will bioconcentrate in aquatic organisms. Phenthoate has estimated base-catalyzed hydrolysis half-lives of 2.4 years at pH of 8, and 24 years at a pH of 7. If released to the atmosphere, phenthoate will exist as a vapor. Vapor-phase phenthoate is degraded in the atmosphere by reaction with photochemically produced hydroxyl radicals with an estimated half-life of about 5 hours. Particulate-phase phenthoate may be physically removed from the air by wet and dry deposition. The half-life for the photochemical conversion of phenthoate by sunlight is 11 minutes. Occupational exposure to organophosphorus pesticides, such as phenthoate, can occur through ingestion, inhalation, and dermal contact.
Usage: Phenthoate has the contact and stomach toxicity, sucking action without inner. In addition, also has a long residual period, quick and strong, safety to crops characteristics.
Application: Efficient, broad-spectrumorganophosphorus insecticide, ovicidal and acaricidal agent. Such as the prevention and treatment of yellow rice borer Chilo suppressalis, in egg hatching peak, with 50% EC 15 ~ 30 mL/100 m2 to 7.5 ~ 10.5 kg spray water. The same concentration and dose can be used for preventing and controlling rice planthopper and leafhopper, Helicoverpa armigera, Pieris rapae, diamondback moth, aphids, cotton leafhopper, Spodoptera litura and thrips. Can be used for controlling rice, citrus, fruit trees, cotton, vegetables, tea, oil crops, rice yellow borer Sesamia inferens, Chilo suppressalis, leafhopper, Planthopper and other pests. Use of the product is highly efficient, broad-spectrum, low toxicity and non absorbable organicphosphorus insecticide, ovicidal and acaricidal agent, used for a variety ofpest control of rice, fruit trees, cotton, vegetables, oil crops.
|







