AMETRYN 莠灭净
Introduction: A triazine herbicide used to control most annual weeds including burmuda grass, wiregrass, goosegrass, crabgrass and other grass weeds, broad-leaved weeds including dallisgrass, thistle, purslane, pigweed, cocklebur, lambsquarters, morning in fruit including citrus, bananas; corn; potatoes; sugarbeet.
Common name: Ametryn
Another name: AMETRYNE, Gesapax, Ametrex, Evik, Ametrine, Cemerin, Crisatrine, Doruplant, Amephyt, Trinatox D, Primatol Z 80, Gardopax, Geshpax, Gestene, Topazol, etc.
Chemical name: N2-ethyl-N4-isopropyl-6-methylthio-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamine
Empirical formula: C9H17N5S
Structural formula:
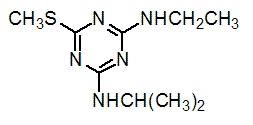
Mol. Weight: 227.12 g/mol
CAS No.: 834-12-8
Specifications
Leading Ametryn supplier
Ametryn 40% WP
Ametryn 50% WP
Ametryn 80% WDG
Ametryn 97% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Solid: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
SMALL PACKING
Solid: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Customerized packing label
Ametryn FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H302: Harmful if swallowed.
H400: Very toxic to aquatic life.
H410: Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P264: Wash ... thoroughly after handling.
P270: Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product.
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P301+P312: IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER/doctor/... IF you feel unwell.
P330: Rinse mouth.
P391: Collect spillage.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to ...
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rat: 1009 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rabbit: >2020 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rat: >5.03 a.i.mg/L. 4) Non-irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Non-irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs).
NOEL: (2 y) for rats is 50, for mice is 10 ppm; (1 y) for dogs is 200 ppm.
ADI: 0.015 mg/kg b.w./day
Classification:
Toxicity class WHO (a.i.): II (Moderately hazardous)
US EPA Classification (formulation): III (Caution - Slightly toxic)
EC Risk Classification: Xn - Harmful: R22; N - Dangerous for the environment: R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: low toxicity to birds, acute oral LD50 for Mallard ducks is >5620 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: moderate toxicity to fish, acute 96 hour LC50 for Rainbow trout is 5 a.i.mg/L. Effect on aquatic invertebrates: moderate toxicity to aquatic invertebrates, acute 48 hour EC50 for Daphnia magna is 28 a.i.mg/L. Effect on algae: high toxicity to algae, acute 72 hour EC50 for Raphidocelis subcapitata is 0.0036 a.i.mg/L. Effect on honeybees: low toxicity to honeybees, oral acute 48 hour LD50 is >100 a.i.μg/bee. Effect on earthworms: moderate toxicity to earthworms, acute 14 day LC50 is 166 a.i.mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Ametryne's production may result in its release to the environment through various waste streams; its use in pre-emergence and post-emergence herbicides will result in its direct release to the environment. If released to air, a vapor pressure of 2.74×10-6 mm Hg at 25 deg C indicates ametryne will exist in both the vapor and particulate phases in the atmosphere. Vapor-phase ametryne will be degraded in the atmosphere by reaction with photochemically-produced hydroxyl radicals; the half-life for this reaction in air is estimated to be 4.5 hours. Particulate-phase ametryne will be removed from the atmosphere by wet and dry deposition. 1,3,5-Triazines, such as ametryne, have a UV absorption band whose tail extends beyond 290 nm and, therefore, may be susceptible to direct photolysis. Using a photoreactor, maintained at pH 6.5 and 15 deg C, ametryne exhibited a half-life of 10.2 hrs. If released to soil, ametryne is expected to have very high to low mobility based upon Koc values ranging from 69 to 530. The pKa of ametryne is 4.10, indicating that this compound will exist partially in the cation form in the environment and cations generally adsorb more strongly to soils containing organic carbon and clay than their neutral counterparts. Volatilization from moist soil surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon an estimated Henry's Law constant of 3.9×10-9 atm-cu m/mole. Ametryne is not expected to volatilize from dry soil surfaces based upon its vapor pressure. Utilizing the Japanese MITI test, 0% of the Theoretical BOD was reached in 4 weeks indicating that biodegradation is not an important environmental fate process in soil or water. However, ametryne has a median half-life in soil of 62 days resulting from microbial degradation, indicating that biodegradation, albeit slow, may be an important environmental fate process in soil under certain conditions. If released into water, ametryne may adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon the Koc values. Volatilization from water surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon this compound's estimated Henry's Law constant. A BCF of 8.3 suggests bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is low. Hydrolysis is not expected to be an important environmental fate process since this compound lacks functional groups that hydrolyze under environmental conditions (pH 5 to 9).
Usage: Herbicide reported by H. Gysin & E. Knüsli (Adv. Pest Control Res., 1960, 3, 289). Introduced by J. R. Geigy S.A. (now Syngenta AG). Patents: GB 814948; CH 337019. Manufacturers: Atanor; Crystal; Hegang Heyou; Hesenta; Makhteshim-Agan; Oxon; Sannong; Syngenta. Photosynthetic electron transport inhibitor at the photosystem II receptor site.
Application: Selective systemic herbicide, absorbed by the leaves and roots, with translocation acropetally in the xylem, and accumulation in the apical meristems. Pre- and post-emergence control of most annual grasses and broad-leaved weeds in pineapples, sugar cane, bananas, citrus fruit, maize, cassava, coffee, tea, sisal, cocoa, oil palms, and on non-crop land. Application rates are in the range 2-4 kg/ha, except when used as a directed spray on maize. Also used as a potato haulm desiccant. Some sugar cane varieties show temporary chlorosis and scorching of lower leaves.
| 






