DIURON 敌草隆
Introduction: A pre-emergence residual herbicide for total control of weeds and mosses in non-crop areas and woody crops.
Common name: Diuron
Another name: DCMU, Dynex, Duran, Dichlorfenidim, Herbatox, Vonduron, Dailon, Karmex, Marmer, Karmex DW, Di-on, Cekiuron, Crisuron, Lucenit, Unidron, Diuron Nortox, Karmex D, Anduron, Ansaron, Dirurol, Durashield, Herburon, Seduron, Bioron, Drexel, Farmco diuron, etc.
Chemical name: 3-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,1-dimethylurea
Empirical formula: C9H10Cl2N2O
Structural formula:
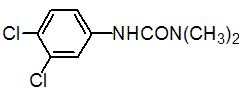
Mol. Weight: 233.09 g/mol
CAS No.: 330-54-1
Specifications
Leading Diuron supplier
Diuron 25% WP
Diuron 50% WP
Diuron 80% WP
Diuron 95% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Solid: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
SMALL PACKING
Solid: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Customerized packing label
Diuron FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H302: Harmful if swallowed.
H351: Suspected of causing cancer.
H373: Causes damage to organs through prolonged or repeated exposure.
H410: Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P201: Obtain special instructions before use.
P202: Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood.
P260: Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapors/spray.
P264: Wash ... thoroughly after handling.
P270: Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product.
P281: Use personal protective equipment as required.
P301+P312: IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER/doctor/... IF you feel unwell.
P308+P313: IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention.
P314: Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell.
P330: Rinse mouth.
P391: Collect spillage.
P405: Store locked up.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to ...
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rat: 437 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rat: >5000 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rat: >0.26/7.1 (aerosol / dust) a.i. mg/L. 4) non-irritating to intact skin (50% aqueous paste) (guinea pigs). 5) Mild eye irritant (WP formulation) (rabbits). 6) Non-sensitising to skin (guinea pigs). NOEL: (2 y) for rats 250, dogs 125 mg/kg diet (H. C. Hodge et al., Food Cosmet. Toxicol., 1967, 5, 513).
Classification:
Toxicity class WHO (a.i.): III (Slightly hazardous)
US EPA Classification (formulation): III (Caution - Slightly toxic)
EC Risk Classification: Carcinogen category 3: R40; Xn - Harmful: R22, R48/22; N - Dangerous for the environment: R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: moderate toxicity to birds, acute oral LD50 for Bobwhite quail is >250 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: moderate toxicity to fish, acute 96 hour LC50 for Cyprinodon variegatus is 6.7 a.i.mg/L. Effect on aquatic invertebrates: moderate toxicity to aquatic invertebrates, acute 48 hour EC50 for Daphnia magna is 5.7 a.i.mg/L. Effect on algae: high toxicity to algae, acute 72 hour EC50 for Scenedemus subspicatus is 0.0027 a.i.mg/L. Effect on honeybees: low toxicity to honeybees, contact acute 48 hour LD50 is >100 a.i.μg/bee; oral acute 48 hour LD50 is >100 a.i.μg/bee. Effect on earthworms: moderate toxicity to earthworms, acute 14 day LC50 for Eisenia foetida is >798 a.i.mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Diuron's production may result in its release to the environment through various waste streams; its use as a pre-emergence herbicide and sugarcane flowering suppressant will result in its direct release to the environment. If released to air, a vapor pressure of 6.90×10-8 mm Hg at 25 deg C indicates diuron will exist solely in the particulate phase in the atmosphere. Particulate-phase diuron will be removed from the atmosphere by wet or dry deposition. The two main absorption bands for diuron are located at 247 nm and 284 nm; absorption is very low but not completely negligible between 320 and 370 nm and therefore diuron may be susceptible to direct photolysis by sunlight. If released to soil, diuron is expected to have moderate to low mobility based upon measured Koc values ranging from 224 to 879. Volatilization from moist soil surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon an estimated Henry's Law constant of 5.0×10-10 atm-cu m/mole. Diuron is not expected to volatilize from dry soil surfaces based upon its vapor pressure. Utilizing the Japanese MITI test, 0% of the theoretical BOD was reached in 4 weeks indicating that biodegradation is not an important environmental fate process; adsorption to humic substances in soil hinders degradation. If released into water, diuron is expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon the Koc. Volatilization from water surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon this compound's estimated Henry's Law constant. Measured BCF values ranging from <2.9 to 14 indicate that bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is low. The rate of diuron hydrolysis is negligible at neutral pH but increases as the conditions become stongly acidic or alkaline, leading to its principle derivative, 3,4-dichloroaniline; a hydrolysis half-life of 4 months has been reported. Occupational exposure to diuron may occur through inhalation of dust and dermal contact with this compound at workplaces where diuron is produced or used. Monitoring data indicate that the general population may be exposed to diuron via inhalation of ambient air, ingestion of food and drinking water, and dermal contact with this compound. (SRC)
Usage: Herbicide reported by H. C. Bucha & C. W. Todd (Science, 1951, 114, 493). Introduced by E. I. du Pont de Nemours Co. (who no longer manufacture or market it). Manufacturers: Ancom; Bayer CropScience; Cedar; Crystal; Drexel; ÉMV; Griffin; Hegang Heyou; Hodogaya; Makhteshim-Agan; Milenia; Nufarm Ltd; Sannong; United Phosphorus. Photosynthetic electron transport inhibitor at the photosystem II receptor site.
Application: Systemic herbicide, absorbed principally by the roots, with translocation acropetally in the xylem. Total control of weeds and mosses on non-crop areas, at 10-30 kg/ha. Selective control of germinating grass and broad-leaved weeds in many crops, including asparagus, tree fruit, bush fruit, citrus fruit, vines, olives, pineapples, bananas, sugar cane, cotton, peppermint, alfalfa, forage legumes, cereals, maize, sorghum, and perennial grass-seed crops, at 0.6-4.8 kg/ha. Phytotoxic residues in soil disappear within 1 season at these lower rates.
| 






