DAMINOZIDE 丁酰肼
Introduction: A hydrazide plant growth regulator-internode elongation to produce more compact plants for use in certain ornamentals including azealeas, bedding plants and plugs, chrysanthemums, foliage plants, hydrangers; Tree fruit including peaches, cherries, prunes, pears.
Common name: Daminozide
Another name: Kylar, ALAR, DMASA, Aminozide, N-(Dimethylamino)succinamic acid, SADH, B-Nine, Dimas, diaminozide, Aminozid, Dazide, etc.
Chemical name: N-(dimethylamino)succinamic acid
Empirical formula: C6H12N2O3
Structural formula:
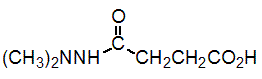
Mol. Weight: 160.17 g/mol
CAS No.: 1596-84-5
Specifications
Leading Daminozide supplier
Daminozide 95% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Solid: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
SMALL PACKING
Solid: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Customerized packing label
Daminozide FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H315 (100%): Causes skin irritation.
H319 (100%): Causes serious eye irritation.
Precautionary statement(s)
P264: Wash ... thoroughly after handling.
P280: Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection.
P302+P352: IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of water.
P305+P351+P338: IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses if present and easy to do - continue rinsing.
P321: Specific treatment (see ... on this label).
P332+P313: IF SKIN irritation occurs: Get medical advice/attention.
P337+P313: IF eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/attention.
P362: Take off contaminated clothing.
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rat: >5000 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rabbit: >5000 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rat: >2.1 a.i.mg/L. 4) Non-irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Severe irritant to eye (rabbits). 6) Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs).
NOEL: (1 y) for dogs is 188 mg/kg b.w. daily, for rats is 5 mg/kg b.w. daily. Non-oncogenic in 2 y feeding trials in rats and mice at 10 000 mg/kg diet. NOEL for teratogenicity and embryotoxicity in rabbits was 300 mg/kg diet. In 3-generation reproductive study, NOAEL for rats was 50 mg/kg b.w. daily. Non-mutagenic in in vivo test.
ADI (JMPR): 0.5 mg/kg bw [1991]
Classification:
Toxicity class WHO (a.i.): U (Unlikely to present an acute hazard)
US EPA Classification (formulation): IV (Caution - Not acutely toxic)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: low toxicity to birds, acute oral LD50 is >2250 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: low toxicity to fish, acute 96 hour LC50 for Bluegill sunfish is 149 a.i.mg/L. Effect on aquatic invertebrates: moderate toxicity to aquatic invertebrates, acute 48 hour EC50 for Daphnia magna is 75.5 a.i.mg/L. Effect on algae: low toxicity to algae, acute 72 hour EC50 for Chlorella spp. is 180 a.i.mg/L. Effect on honeybees: low toxicity to honeybees, acute 48 hour LD50 is >200 a.i.μg/bee. Effect on earthworms: moderate low toxicity to earthworms, acute 14 day LC50 for Eisenia foetida is >1000 a.i.mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Daminozide's production may result in its release to the environment through various waste streams; it's use as a plant growth regulator will result in its direct release to the environment. If released to air, a vapor pressure of 2×10-4 mm Hg at 23 deg C indicates daminozide will exist solely as a vapor in the ambient atmosphere. Vapor-phase daminozide will be degraded in the atmosphere by reaction with photochemically-produced hydroxyl radicals; the half-life for this reaction in air is estimated to be 32 hours. If released to soil, daminozide is expected to have very high mobility based upon an estimated Koc of 4. Daminozide has a pKa of 4.68 suggesting this compound will primarily exist as an anion in moist soils and water surfaces. Volatilization from moist soil is not expected since anions do not volatilize, and volatilization from dry soil surfaces is not expected based on the vapor pressure of this compound. In greenhouse studies, the persistence half-life of daminozide was found to range from 3 to 4 days in four different soils under aerobic conditions. Volatilization from water surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process because this compound will exist primarily as an anion in water and anions will not volatilize. No measurable hydrolysis of daminozide was noted at pH 5-9, but sensitized photolysis was observed, suggesting that photolysis in sunlit surface waters may occur. An estimated BCF of 3 suggests the potential for bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is low.
Usage: Plant growth regulator reported by J. A. Riddell et al. (Science, 1962, 136, 391). Introduced by Uniroyal Chemical Co., Inc. (now Crompton Corp.) in c. 1965. Patents: US 3240799; US 3334991. Manufacturers: Crompton; Fine; Sannong; Tide. Biochemistry: Interferes with gibberellic acid biosynthesis.
Application: Absorbed by the leaves, with translocation throughout the plant. To produce more compact plants (by inhibition of internodal elongation) of chrysanthemums, azaleas, hydrangeas, poinsettias, and other ornamentals. Applied at 0.106-0.425 kg/ha.
| 






