Teflubenzuron 伏虫隆
Introduction: Teflubenzuron is an insecticide used to control a range of pests including whiteflies, caterpillars, codling moth, leafminers, thrips, pear psylla, beetles mainly on Apples; Pears; Greenhouse crops including tomatoes, aubergine, cucumber, melon, pepper. Also used to control sea lice in fisheries.
Common name: Teflubenzuron
Another name: Calicide, Diaract, Tefluron, Nomolt, Dart, UNII-FS9P57VL74, CME 134, HOE 522, OMS 3009, MK 139, AC 291898, MLS000756919, FS9P57VL74, Ektobann.
Chemical name: 1-(3,5-dichloro-2,4-difluorophenyl)-3-(2,6-difluorobenzoyl)urea
Empirical formula: C14H6Cl2F4N2O2
Structural formula:
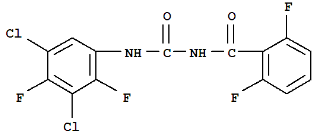
Mol. Weight: 381.11 g/mol
CAS No.: 83121-18-0
Specifications
Leading Teflubenzuron supplier
Teflubenzuron 50 g/L SC
Teflubenzuron 150 g/L SC
Teflubenzuron 94% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Powder: 25KG/Bag, 25KG/Drum, 50KG/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum ect.
SMALL PACKING
Powder: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized Packing label
Teflubenzuron FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H372: Causes damage to organs through prolonged or repeated exposure.
H400: Very toxic to aquatic life.
H410: Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P260: Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapors/spray.
P264: Wash ... thoroughly after handling.
P270: Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product.
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P314: Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell.
P391: Collect spillage.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to ...
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rat: >5038 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rabbit: >2000 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rat: >5.04 a.i. mg/L. 4) Non- irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Non-irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). There was no evidence of toxicity and no effects on reproductive performance. The results of tests for the genotoxicity of teflubenzuron revealed no evidence for mutagenicity or clastogenicity. No toxicologically significant findings were found.
ADI (JMPR): 0.005 mg/kg b.w.[2016]
Classification:
Toxicity class WHO (a.i.): U (Unlikely to present an acute hazard)
US EPA Classification (formulation): IV (Caution - Not acutely toxic)
EC Risk Classification: Carcinogen category 3: R40
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: low toxicity to birds, acute oral LD50 for Bobwhite quail is >2250 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: high toxicity to fish, acute 96 hour LC50 for Bluegill sunfish is >0.0065 a.i.mg/L. Effect on aquatic invertebrates: high toxicity to aquatic invertebrates, acute 48 hour EC50 for Daphnia magna is >0.0028 a.i.mg/L. Effect on algae: moderate toxicity to algae, acute 72 hour EC50 is >0.02 a.i.mg/L. Effect on honeybees: moderate toxicity to honeybees, contact acute 48 hour LD50 is 100 a.i.μg/bee; oral acute 48 hour LD50 is 72 a.i.μg/bee. Effect on earthworms: moderate toxicity to earthworms, acute 14 day LC50 is >500 a.i.mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
The degradation of teflubenzuron in aerobic soil occurred at a moderately rapid rate with a half-life (DT-50) of 29 days and a DT-90 of 108 days. After the change to anaerobic conditions the rate of 14CO2 evolution slowed considerably but the overall rate of degradation did not change, indicating that the initial steps in the degradation route were not affected by the change in conditions. The proportions of the radioactive products recovered after 90 days from the anaerobic and aerobic soils were different. Only 3% of the applied radioactivity was evolved as 14CO2 in the anaerobic phase of the experiment compared with 24% from the aerobic soils over the same time period. The bound residue was higher in the anaerobic than the aerobic soil. Adsorption/desorption in soil: The proportions of teflubenzuron adsorbed after the 6-h treatment period were 96.9% from sand, 98.8% from sandy loam, 99.1% from silt loam and 99.4% from clay loam, showing very strong adsorption of the compound to all the soils tested. Teflubenzuron itself shows practically no tendency to migrate once it is applied to soil. This is attributable to the very low solubility of the compound in water, and strong adsorption with very little leaching in all types of soil tested.
Usage: Teflubenzuron was first report by H. M. Becher et al, and developed by Celamerck GmbH & Co.(Shell Agrar GmbH). Teflubenzuron works by interfering with the synthesis of insect chitin, which is essential to their growth and development.
Application: Eflubenzuron is used to control a wide range of insect pests and mites in fruit, vegetable, cereal and seed crops. It is also occasionally used to control sealice infestations in salmon. Prevention objects were Diptera: Apple stoneflies, Hesse Gall Midge; Lepidoptera: American white moth, codling moth, Apple small leaf rollers, corn borer, small sugarcane borer, coffee leaf miner, Soybean Hornarmyworm. 7 a.i.g/L can be used to control codling moth; 10 mg/kg can be used to control American white moth.
| 






