THIACLOPRID 噻虫啉
Introduction: Thiacloprid is a high selective carbamate insecticide with stomach and ovicidal action. Thiacloprid is chloronicotinyl insecticide for use on apples, pears, some citrus crops, brussel sprouts, cabbage, cauliflower, carrot, parsnip, peas, potato, oilseed rape to control sucking and chewing insects such as aphids, pollen beetles, blossom midge, codling moth.
Common name: Thiacloprid
Another name: Calypso, (Z)-thiacloprid,
Chemical name: (Z)-3-(6-chloro-3-pyridylmethyl)-1,3-thiazolidin-2-ylidenecyanamide
Empirical formula: C10H9CIN4S
Structural formula:
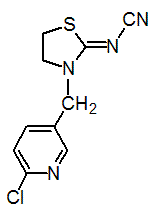
Mol. Weight: 252.72 g/mol
CAS No.: 111988-49-9
Specifications
Leading Thiacloprid supplier
Thiacloprid 240 g/L SC
Thiacloprid 450 g/L SC
Thiacloprid 480 g/L SC
Thiacloprid 95% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Solid: 25KG/Bag, 25KG/Drum, 50KG/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum ect.
SMALL PACKING
Solid: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized packing label
Thiacloprid FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H301: Toxic if swallowed.
H332: Harmful if inhaled.
H336: May cause drowsiness or dizziness.
H351: Suspected of causing cancer.
H360FD: May damage fertility; May damage the unborn child.
H400: Very toxic to aquatic life.
H410: Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P201: Obtain special instructions before use.
P202: Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood.
P261: Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapors/spray.
P264: Wash ... thoroughly after handling.
P270: Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product.
P271: Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area.
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P281: Use personal protective equipment as required.
P304+P312: IF INHALED: Call a POISON CENTER/doctor/... if you feel unwell.
P304+P340: IF INHALED: Remove person to fresh air and keep comfortable for breathing.
P308+P313: IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention.
P312: Call a POISON CENTER or doctor/... if you feel unwell.
P321: Specific treatment (see ... on this label).
P330: Rinse mouth.
P391: Collect spillage.
P403+P233: Store in a well-ventilated place. Keep container tightly closed.
P405: Store locked up.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to ...
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rat: 444 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rat: >2000 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rat: >0.481 a.i. mg/L. 4) Non- irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Non- irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). NOAEL for rats (chronic toxicity, carcinogenicity) is 25 ppm. No primary carcinogenic potential; no primary developmental toxicity in rats and rabbits; no evidence of a genotoxic or mutagenic potential.
ADI (JMPR): 0.01 mg/kg b.w./day [2006]
Classification:
Toxicity class WHO (a.i.): II (Moderately hazardous)
EC Risk Classification: Xn - Harmful: R20/22; N - Dangerous for the environment: R52/53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: high toxicity to birds, acute oral LD50 for Japanese quail is 49 a.i. mg/kg. Effect on fish: moderate toxicity to fish, acute 96 hour LC50 for Rainbow trout is 24.5 a.i.mg/L. Effect on aquatic invertebrates: moderate toxicity to aquatic invertebrates, acute 48 hour EC50 for Daphnia magna is 85.1 a.i.mg/L. Effect on algae: low toxicity to algae, acute 72 hour EC50 for Raphidocelis subcapitata is 60.6 a.i.mg/L. Effect on honeybees: moderate toxicity to honeybees, contact acute 48 hour LD50 is 38.82 a.i.μg/bee, oral acute 48 hour LD50 is 17.32 a.i.μg/bee. Effect on earthworms: moderate toxicity to earthworms, acute 14 day LC50 is 105 a.i.mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Thiacloprid's production may result in its release to the environment through various waste streams; it's use as an insecticide will result in its direct release to the environment. If released to air, a vapor pressure of 6.0×10-12 mm Hg at 20 deg C indicates thiacloprid will exist solely in the particulate phase in the ambient atmosphere. Particulate-phase thiacloprid will be removed from the atmosphere by wet and dry deposition. If released to soil, thiacloprid is expected to have slight mobility based upon an estimated Koc of 4,700. Volatilization from moist soil surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon an estimated Henry's Law constant of 1.1×10-14 atm-cu m/mole. Thiacloprid is not expected to volatilize from dry soil surfaces based upon its vapor pressure. If released into water, thiacloprid is expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon the estimated Koc. Volatilization from water surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon this compound's estimated Henry's Law constant. An estimated BCF of 2 suggests the potential for bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is low. Hydrolysis is not expected to be an important environmental fate process since this compound lacks functional groups that hydrolyze under environmental conditions. Occupational exposure to thiacloprid may occur through inhalation and dermal contact with this compound at workplaces where thiacloprid is produced or used. (SRC)
Usage: Reported by A. Elbert et al., (Proc. BCPC Conf. - Pests Dis., 2000, 1, 21) and developed by Bayer AG and Nihon Bayer Agrochem. First registered in Brazil in 1999. Manufacturers: Bayer CropScience.
Application: Biochemistry Acts as an agonist of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in the central nervous system, thus disturbing synaptic signal transmissions. Mode of action Acute contact and stomach poison, with systemic properties. Uses For use by foliar application against sucking and biting insects, at 48-216 g/ha, in pome fruit, stone fruit, small berries, cotton, vegetables, sugar beet, potatoes, rice and ornamentals. Pests controlled include aphids, whiteflies, beetles (e.g. Leptinotarsa decemlineata, Anthonomus pomorum, Lissorhoptrus oryzophilus) and Lepidoptera such as leaf miners and Cydia pomonella.
| 






