CLOTHIANIDIN 噻虫胺
Introduction: Clothianidin is a higheffective, wide spectrum insecticide. Spectroscopy, internal absorption of pesticides, mainly for rice, vegetables, fruit trees and other crops, prevent and treat aphids, leafhoppers, thrips, planthoppers, Hemiptera, Coleoptera Diptera and certain Lepidoptera pests.
Common name: Clothianidin
Another name: Celero, (E)-clothianidin, Dantotsu, Fullswing, Clutch, Dantop, Pancho, Poncho, Apacz, Belay
Chemical name: (E)-1-(2-chloro-1,3-thiazol-5-ylmethyl)-3-methyl-2-nitroguanidine
Empirical formula: C6H8ClN5O2S
Structural formula:
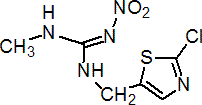
Mol. Weight: 249.7 g/mol
CAS No.: 210880-92-5
Specifications
Leading Clothianidin supplier
Clothianidin 25% WDG
Clothianidin 80% WDG
Clothianidin 60% FS
Clothianidin 95% TC
Clothianidin 97% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Soild: 25kg/Bag, 25kg/Drum, 50kg/Drum etc.
SMALL PACKING
Soild: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Customerized packing label
Clothianidin FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H302: Harmful if swallowed.
H400: Very toxic to aquatic life.
H410: Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P264: Wash ... thoroughly after handling.
P270: Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product.
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P301+P312: IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER/doctor/... IF you feel unwell.
P330: Rinse mouth.
P391: Collect spillage.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to ...
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rat: >500 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rabbit: >2000 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rat: >5.54 a.i. mg/L. 4) Non- irritating to skin (rabbits). 5) Slightly irritating to eyes (rabbits). 6) Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). NOEL (2 y) for male rats is 27.4, female rats is 9.7 mg/kg b.w. daily; (1 y) for male dogs is 7.8, female dogs is 8.5 mg/kg b.w. daily. Not mutagenic. Not oncogenic in rats and mice. Not teratogenic in rats and rabbits.
ADI(JMPR): 0.1 mg/kg b.w. [2010]
Classification:
Xn - Harmful: R22; N - Dangerous for the environment: R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: moderate toxicity to birds, acute LD50 for Bobwhites quail is 430 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: low toxicity to fish, acute 96 hour LC50 for Rainbow trout is >104.2 a.i.mg/L. Effect on aquatic invertebrates: moderate toxicity to aquatic invertebrates, acute 48 hour EC50 for Daphnia magna is >40 a.i.mg/L. Effect on algae: low toxicity to algae, acute 72 hour EC50 for Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata is 55 a.i.mg/L. Effect on honeybees: high toxicity to honeybees, contact acute 48 hour LD50 is 0.044 a.i.μg/bee; Oral acute 48 hour LD50 is 0.004 a.i.μg/bee. Effect on earthworms: moderate toxicity to earthworms, acute 14 day LC50 for Eisenia foetida is 13.21 a.i.mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Clothianidin's production may result in its release to the environment through various waste streams; it's use as an insecticide will result in its direct release to the environment. If released to air, a vapor pressure of 9.8×10-10 mm Hg at 25 deg C indicates clothianidin will exist solely in the particulate phase in the ambient atmosphere. Particulate-phase clothianidin will be removed from the atmosphere by wet and dry deposition. If released to soil, clothianidin is expected to have high mobility based upon an estimated Koc of 60. Reported half-lives for the biodegradation of chlothianidin in soil range from 148 to 1,155 days. Volatilization from moist soil surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon a Henry's Law constant of 2.9×10-16 atm-cu m/mole. Clothianidin is not expected to volatilize from dry soil surfaces based upon its vapor pressure. A half-life of 34 days has been reported for photolysis on soil. If released into water, clothianidin is not expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon the estimated Koc. The aquatic anaerobic biodegradation half-life of clothianidin was measuredr as 27 days. Volatilization from water surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon this compound's Henry's Law constant. An estimated BCF of 0.3 suggests the potential for bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is low. Hydrolysis is not expected to occur due to the lack of hydrolyzable functional groups. This compound is expected to undergo direct photolysis based on an aqueous photolysis half-life of less than 1 day. Occupational exposure to clothianidin may occur through inhalation and dermal contact with this compound at workplaces where clothianidin is produced or used. (SRC)
Usage: Discovered by Takeda Chemical Industries (now Sumitomo Chemical Takeda Agro Company Ltd) and under development jointly with Bayer AG. Reported by Y. Ohkawara et al., Proc. BCPC Conf. - Pests Dis., 2002, 1, 51 and M. Schwarz et al., ibid., 59. Manufacturers: Bayer CropScience; Sumitomo Chemical Takeda.
Application: Selective systemic and contact insecticide with broad spectrum, it has a better effect than the other Neonicotinoid Insecticides. No cross resistance with other pesticides. It is used to control insects with hewing mouth parts, such as Hemipterous, Lepidoptera, Coleoptera and some Diptera on rice, vegetable, fruit tree, tee, ornamental, etc. Control of planthopper on rice: 18~30g a.i./ha. Specific dosage depends on different situation.
| 






