Triflumuron 杀铃脲, 杀虫隆, 杀虫脲
Introduction: Triflumuron is an insecticide used to protect against a range of insect pests including flea larvae, immature cockroaches, sliverfish, lice, miosquitoes, beetles in Fruit including apples, pears, nectarines, peaches; Non-cropped situations including households, commercial and industrial sites. It is also used as an ecoparasitic treatment in veterinary medicine.
Common name: Triflumuron
Another name: Alsystin, Trifluron, Mascot, Alsystine,
Chemical name: 1-(2-chlorobenzoyl)-3-(4-trifluoromethoxyphenyl)urea
Empirical formula: C15H10ClF3N2O3
Structural formula:
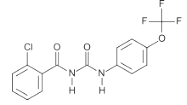
Mol. Weight: 358.70 g/mol
CAS No.: 64628-44-0
Specifications
Leading Triflumuron supplier
Triflumuron 480 g/L SC
Triflumuron 80% WDG
Triflumuron 95% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Powder: 25KG/Bag, 25KG/Drum, 50KG/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum ect.
SMALL PACKING
Powder: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized Packing label
Triflumuron FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H330 (97.18%): Fatal if inhaled.
Precautionary statement(s)
P260: Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapors/spray.
P271: Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area.
P284: [In case of inadequate ventilation] Wear respiratory protection.
P304+P340: IF INHALED: Remove person to fresh air and keep comfortable for breathing.
P310: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician.
P320: Specific treatment is urgent (see ... on this label).
P403+P233: Store in a well-ventilated place. Keep container tightly closed.
P405: Store locked up.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to ...
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rat: ˃5000 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rat: ˃5000 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rat: ˃5.03 a.i. mg/L. 4) Non irritating (rabbit). 5) Non irritating (rabbit). 6) Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). No component of this product present at levels greater than or equal to 0.1% is identified as probable,
possible or confirmed human carcinogen by IARC, ACGIH, NTP, or OSHA.
ADI: 0.014 mg/kg b.w.
Classification:
Toxicity class WHO (a.i.): U (Unlikely to present an acute hazard)
US EPA Classification (formulation): IV (Caution - Not acutely toxic)
EC Risk Classification: N - Dangerous for the environment: R50/53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: moderate toxicity to birds, acute LD50 for Bobwhite quail is 561 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: high toxicity to fish, acute 96 hour LC50 for sunfish is ˃0.021 a.i.mg/L. Effect on aquatic invertebrates: high toxicity to aquatic invertebrates, acute 48 hour EC50 for Daphnia magna is 0.0016 a.i.mg/L. Effect on algae: moderate toxicity to algae, acute 72 hour EC50 for Scenedemus subspicatus is ˃0.025 a.i.mg/L. Effect on honeybees: low toxicity to honeybees, contact acute 48 hour LD50 is ˃200 a.i.μg/bee; Oral acute 48 hour LD50 is ˃226 a.i.μg/bee. Effect on earthworms: moderate toxicity to earthworms, acute 14 day LC50 for Eisenia foetida is >500 a.i.mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Triflumuron labelled in the 2-chlorobenzoyl moiety was metabolised in rats by hydrolytic cleavage, forming metabolites which contained only the 2-chlorophenyl ring and were partly hydroxylated and conjugated. Correspondingly, in experiments with labelling in the 4-trifluoromethoxyphenyl group, metabolites were found which contained only the 4-trifluoromethoxyphenyl ring, partly in hydroxylated form. Plants Following spray application to apples, soya beans and potatoes, triflumuron is only slightly metabolised; metabolites were the same as those formed in animals. For residue analyses, it is sufficient to determine the parent compound in the harvested crops. Soil/Environment Degradation: In laboratory tests, triflumuron was moderately quickly degraded in the soil; degradation in the field was more rapid by a factor of 3-5. Repeated applications over 3 years to soil without vegetation did not result in any accumulation in the soil. In practice-relevant applications in forests, the concentrations of residues found in the soil were very low at all times, and declined below the limit of detection after a few months. Metabolism: In soil, 50% of applied triflumuron labelled in the 2-chlorobenzoyl moiety was degraded to CO2 within 112 days and c. 20% of the radioactivity was bound to the soil. When using triflumuron labelled in the 4-trifluoromethoxyphenyl moiety, the compound was mineralised more slowly, while the percentage of bound residues was markedly increased. Metabolism was mainly induced by microbes, and resulted in metabolites which contained just one of the two rings in each case.
Usage: History Insecticide reported by G. Zoebelein et al. (Int. Congr. Plant Prot., 9th, Annu. Mtg. Am. Phytopathol. Soc., 71st, 1979, Abstract 309) and by I. Hammann & W. Sirrenberg (Pflanzenschutz-Nachr. (Engl. Ed.), 1980, 33, 1). Introduced by Bayer AG. Patents DE 2601780 Manufacturers Bayer CropScience; Sundat.
Application: Mainly stomach and contact action. Inhibit insect chitin synthesis, molt the larvae, not form new skin and then make the body deformity and death. Due to its high efficiency, low toxicity and broad-spectrum, it can be used to control corn, cotton, forest, fruit Coleoptera, Diptera and Lepidoptera pests. 225 g/ha can be used to control cotton bollworm and 37.5 g/ha can be used to control pine moth.
| 






