Fosthiazate 噻唑膦
Introduction: Fosthiazate is a soil applied nematicide and insecticide used to control nematodes and sucking/chewing ground insects such as Potato Cyst Nematode (Globodera rostochiensis, Globodera pallida), Wireworms in potatoes, tomatoes, and vegetables field.
Common name: Fosthiazate
Another name: Nemathorin, Fosthiazate [ISO:BSI], IKI 1145, ASC-66824, CHEBI:38692, (RS)-S-sec-butyl-O-ethyl-2-oxo-1,3-thiazolidin-3-ylphosphonothioate
Chemical name: (RS)-[S-(RS)-sec-butyl O-ethyl 2-oxo-1,3-thiazolidin-3-ylphosphonothioate]
Empirical formula:C9H18NO3PS2
Structural formula:
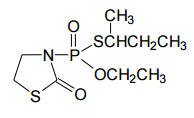
Mol. Weight: 283.4 g/mol
CAS No.: 98886-44-3
Specifications
Leading Fosthiazate supplier
Fosthiazate 5% GR
Fosthiazate 10% GR
Fosthiazate 400 g/L EC
Fosthiazate 85% TC
Fosthiazate 92% TC
Packing:
BULK PACKING
Powder: 25KG/Bag, 25KG/Drum, 50KG/Drum etc.
Liquid: 200L/Drum, 20L/Drum, 10L/Drum ect.
SMALL PACKING
Powder: 1kg/Alu bag, 500g/Alu bag, 200g/Alu bag, 100g/Alu bag, 50g/Alu bag, 15g/Alu bag etc.
Liquid: 5L/Drum, 1L/Bottle, 500ml/Bottle, 250ml/Bottle, 100ml/Bottle, 50ml/Bottle etc.
Customerized Packing label
Fosthiazate FAO standard
Professional registration
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard statement(s)
H301: Toxic if swallowed.
H312: Harmful in contact with skin.
H317: May cause an allergic skin reaction.
H331: Toxic if inhaled.
H410: Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P261: Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapors/spray.
P264: Wash ... thoroughly after handling.
P270: Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product.
P271: Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area.
P272: Contaminated work clothing should not be allowed out of the workplace.
P273: Avoid release to the environment.
P280: Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection.
P301+P310: IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER/doctor/...
P302+P352: IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of water.
P304+P340: IF INHALED: Remove person to fresh air and keep comfortable for breathing.
P311: Call a POISON CENTER or doctor/...
P312: Call a POISON CENTER or doctor/... if you feel unwell.
P321: Specific treatment (see ... on this label).
P322: Specific measures (see ...on this label).
P330: Rinse mouth.
P333+P313: IF SKIN irritation or rash occurs: Get medical advice/attention.
P363: Wash contaminated clothing before reuse.
P391: Collect spillage.
P403+P233: Store in a well-ventilated place. Keep container tightly closed.
P405: Store locked up.
P501: Dispose of contents/container to ...
Supplemental Hazard Statements: none
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Acute toxicity: 1) Acute oral LD50 for rat: 57 a.i.mg/kg. 2) Acute dermal LD50 for rat: 853 a.i.mg/kg. 3) Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rat: 0.56 a.i. mg/L. 4) No irritating effect. 5) Strong irritant with the danger of severe eye injury. 6) Sensitization possible through skin contact. Prolonged or repeated exposure may cause allergic reactions in certain sensitive individuals. The preceding data, or interpretation of data, was determined using Quantitative Structure Activity Relationship (QSAR) modeling. No component of this product present at levels greater than or equal to 0.1% is identified as probable, possible or confirmed human carcinogen by IARC.
ADI: 0.004 mg/kg b.w.
Classification:
EC Risk Classification: T - Toxic: R23/25, R39; Xn - Harmful: R21, R41, R43; N - Dangerous for the environment: R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Effect on birds: high toxicity to birds, acute LD50 for Bobwhite quail is 10 a.i.mg/kg. Effect on fish: low toxicity to fish, acute 96 hour LC50 for Rainbow trout is 114 a.i.mg/L. Effect on aquatic invertebrates: moderate toxicity to aquatic invertebrates, acute 48 hour EC50 for Daphnia magna is 0.282 a.i.mg/L. Effect on algae: moderate toxicity to algae, acute 72 hour EC50 for Anabaena flos-aquae is ˃4.51 a.i.mg/L. Effect on honeybees: high toxicity to honeybees, contact acute 48 hour LD50 is 0.256 a.i.μg/bee; Oral acute 48 hour LD50 is 0.61 a.i.μg/bee. Effect on earthworms: moderate toxicity to earthworms, acute 14 day LC50 is 209 a.i.mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Fosthiazate's production may result in its release to the environment through various waste streams; its use as a nematicide/insecticide will result in its direct release to the environment. If released to air, a vapor pressure of 4.20×10-6 mm Hg at 25 deg C indicates fosthiazate will exist in both the vapor and particulate phases. Vapor-phase fosthiazate will be degraded in the atmosphere by reaction with photochemically-produced hydroxyl radicals; the half-life for this reaction in air is estimated to be 1.5 hours. Particulate-phase fosthiazate will be removed from the atmosphere by wet or dry deposition. Fosthiazate contains chromophores that absorb at wavelengths >290 nm, and therefore may be susceptible to direct photolysis by sunlight. If released to soil, fosthiazate is expected to have high mobility based upon an estimated Koc of 71. Volatilization from moist soil surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon a Henry's Law constant of 1.7×10-10 atm-cu m/mole. Fosthiazate may not volatilize from dry soil surfaces based upon its vapor pressure. The compound was shown to be more persistent in soils with a pH of <6, exhibiting half-lives ranging from 53.3 to 57.7 days versus 14.1 to 20.7 days for soils with pH >7. If released into water, fosthiazate is not expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon the estimated Koc. Volatilization from water surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon this compound's Henry's Law constant. An estimated BCF of 6 suggests the potential for bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is low. Fosthiazate hydrolyzes in the environment under alkaline conditions with a half-life of <7 days reported. Under neutral conditions, hydrolysis is slow as suggested by a half-life of 104 days. Photodegradation in water is not an important environmental fate process. Occupational exposure to fosthiazate may occur through inhalation and dermal contact with this compound at workplaces where fosthiazate is produced or used. Limited data indicate that the general population may be exposed to fosthiazate via ingestion of contaminated food.
Usage: History Nematicide discovered by Ishihara Sangyo Kaisha, Ltd and launched in Japan in 1992. Manufacturers Ishihara Sangyo.
Application: Biochemistry Cholinesterase inhibitor. Mode of action Systemic, non-fumigant, soil-applied. Uses Control of nematodes (Meloidogyne spp., Heterodera spp. and Pratylenchus spp.), aphids, mites, thrips, etc., in vegetables, potatoes and bananas, etc. Applied at 2.0-5.0 kg/ha.
| 






